| A thin metallic disc of radius R is rotating with constant angular velocity co about a vertical axis that is perpendicular to plane of disc and passes through its centre. |
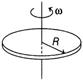 |
| Rotation causes free electrons in the disc to redistribute. If there is no external electric or magnetic field is present, then potential difference between centre and rim of disc is |
A) \[0\]
B) \[\frac{m{{\omega }^{2}}{{R}^{2}}}{e}\]
C) \[\frac{m{{\omega }^{2}}{{R}^{2}}}{2e}\]
D) \[\frac{2m{{\omega }^{2}}{{R}^{2}}}{e}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
| In rotating disc, let a potential difference dV occurs across radial distance dr. |
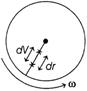 |
| In equilibrium, electric field balances centrifugal force on an electron. |
| \[\therefore \]\[e\frac{dV}{dr}=m{{\omega }^{2}}r\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[dV=\frac{m}{e}{{\omega }^{2}}rdr\] |
| \[\therefore \]Integrating between limits, we have, \[V=\int_{0}^{V(R)}{dV=\int_{0}^{R}{\frac{m}{e}{{\omega }^{2}}rdr}}\] |
| \[V(R)=\frac{-m{{\omega }^{2}}{{R}^{2}}}{e\cdot 2}\] |
| Note That outer rim will be negatively charged In practice the potential difference is very small. |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
