A) \[1650Hz\]
B) \[1560Hz\]
C) \[650Hz\]
D) \[560Hz\]
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
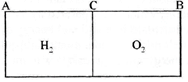
[a]| As ends \[A\] and \[B\] are set in vibrations, so displacement antinodes are formed at these ends. The fundamental |
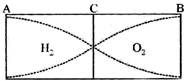 |
| Frequency of each pipe is corresponding to one node and one antinode. If \[{{f}_{1}}\operatorname{and}\,{{f}_{2}}\] be the fundamental frequencies of gases in \[AC\] and \[BC\] respectively, then \[{{f}_{1}}=\frac{{{v}_{1}}}{4L}=\frac{1100}{4\times 0.5}=550\operatorname{Hz}\] and \[{{f}_{2}}=\frac{{{v}_{2}}}{4L}=\frac{300}{4\times 0.5}=150\operatorname{Hz}\] |
| As the two frequencies are different, so the two columns are not vibrating in the fundamental mode. The close column of gas vibrates only in odd harmonics with frequencies \[1:3:5:7:.......\] |
| Thus we can write\[\frac{{{f}_{1}}}{{{f}_{2}}}=\frac{550}{150}=\frac{11}{3},\frac{22}{6},\frac{33}{9}\] or \[3{{f}_{1}}=11{{f}_{2}}\] |
| The common minimum frequency \[=3{{f}_{1}}=3\times 550=1650\operatorname{Hz}\] |
| Also \[=11{{f}_{2}}=11\times 150=1650\operatorname{Hz}\] |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
