Answer:
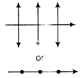
Polarisation by reflection from a transparent medium. Characteristic Unpolarised light Plane polarised light Vibration of electric field vector Electric field vectors are symmetrically distributed in all directions perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave Electric field vectors are confined in a plane parallel to a fixed line perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave. Symbol 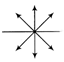
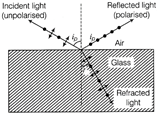 The reflected, completely plane polarised light makes an angle of \[90{}^\circ \] with the direction of corresponding refracted light. Brewster's law According to Brewster, the polarising angle \[{{i}_{p}},\] the reflected plane polarised light and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, then \[{{i}_{p}}+r=90{}^\circ \] where, r = angle of refraction. \[r=90{}^\circ -{{i}_{p}}\] \[\because \]Snell's law, \[\mu =\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\sin \,r}=\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\sin (90{}^\circ -{{i}_{p}})}\] \[\mu =\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\cos {{i}_{p}}}\Rightarrow \mu =\tan {{i}_{p}}\] This relation is known as Brewster's law.
The reflected, completely plane polarised light makes an angle of \[90{}^\circ \] with the direction of corresponding refracted light. Brewster's law According to Brewster, the polarising angle \[{{i}_{p}},\] the reflected plane polarised light and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, then \[{{i}_{p}}+r=90{}^\circ \] where, r = angle of refraction. \[r=90{}^\circ -{{i}_{p}}\] \[\because \]Snell's law, \[\mu =\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\sin \,r}=\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\sin (90{}^\circ -{{i}_{p}})}\] \[\mu =\frac{\sin {{i}_{p}}}{\cos {{i}_{p}}}\Rightarrow \mu =\tan {{i}_{p}}\] This relation is known as Brewster's law.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
