| (i) Why are coherent sources necessary to produce a sustained interference pattern? |
| (ii) Describe briefly the formation of diffraction pattern on screen due to a narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic light. Obtain the condition for angular width of secondary minima. |
Answer:
(i) Coherent sources produces light of constant phase difference and hence, permanent fringes pattern produced due to interference of light. (ii) A parallel beam of light with a plane wavefront is made to fall on a single slit UN. As width of the slit LN = a is of the order of wavelength of light, therefore diffraction occurs on passing through the slit. The wavelets from the single wavefront reach the centre C on the screen in same phase and hence, interfere constructively to give central maximum (bright fringe). The diffraction pattern obtained on the screen consists of a central bright band, having alternate dark and weak bright bands of decreasing intensity on both sides. 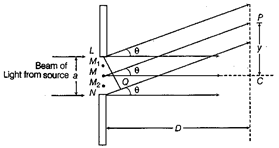 Geometry of a single slit diffraction Consider a point P on the screen at which wavelets travelling in a direction, make an angle \[\theta \] with MC. The wavelets from points L and N will have a path difference equal to NQ. From the right angled \[\Delta LNQ,\] we have \[NQ=LN\sin \theta \] or \[NQ=a\sin \theta \] To establish the condition for secondary minima, the slit is divided into 2, 4, 6,... equal parts such that corresponding wavelets from successive regions interfere with path difference of \[\lambda /2.\] Or for nth secondary minima, the slit can be divided into 2n equal parts. Hence, for nth secondary minima, Path difference \[=\frac{a}{2}\sin \theta =\frac{\lambda }{2}\] or \[\sin {{\theta }_{n}}=\frac{n\lambda }{a}\] (where, n = 1,2,3,?)
Geometry of a single slit diffraction Consider a point P on the screen at which wavelets travelling in a direction, make an angle \[\theta \] with MC. The wavelets from points L and N will have a path difference equal to NQ. From the right angled \[\Delta LNQ,\] we have \[NQ=LN\sin \theta \] or \[NQ=a\sin \theta \] To establish the condition for secondary minima, the slit is divided into 2, 4, 6,... equal parts such that corresponding wavelets from successive regions interfere with path difference of \[\lambda /2.\] Or for nth secondary minima, the slit can be divided into 2n equal parts. Hence, for nth secondary minima, Path difference \[=\frac{a}{2}\sin \theta =\frac{\lambda }{2}\] or \[\sin {{\theta }_{n}}=\frac{n\lambda }{a}\] (where, n = 1,2,3,?)
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
