A) high resistance in series
B) low resistance in parallel
C) high resistance in parallel
D) low resistance in series.
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
Let G be the resistance of the galvanometer and \[{{i}_{g}}\]the current, which on passing through the galvanometer, produces full-scale deflection. Suppose V is the maximum potential difference to be measured which exists between points a and b. On connecting the galvanometer across a and b a current \[{{i}_{g}}\] flows through it. Then from Ohm's law we have.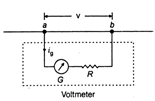 \[{{i}_{g}}=\frac{V}{G+R}\] \[G+R=\frac{V}{{{i}_{g}}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[R=\frac{V}{{{i}_{g}}}-G\] Thus, on connecting a resistance R of above value in series with the galvanometer the galvanometer will become a voltmeter of range 0 to V volts. The value of resistance should be high enough so that it does not draw any current from the circuit. NOTE: Resistance of an ideal voltmeter is high.
\[{{i}_{g}}=\frac{V}{G+R}\] \[G+R=\frac{V}{{{i}_{g}}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[R=\frac{V}{{{i}_{g}}}-G\] Thus, on connecting a resistance R of above value in series with the galvanometer the galvanometer will become a voltmeter of range 0 to V volts. The value of resistance should be high enough so that it does not draw any current from the circuit. NOTE: Resistance of an ideal voltmeter is high.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
