A) move away from the wire
B) move towards the wire
C) remain stationary
D) rotate about an axis parallel to the win
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
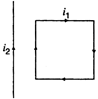
The force of attraction/repulsion for current carrying conductors is \[\pi \] where d is distance between conductors. \[{{Q}^{2}}(4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{a}^{2}})\] \[-{{Q}^{2}}(4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{a}^{2}})\] Hence, lesser the distance, more is the force. Also we know that two wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other while that flowing in opposite direction repel each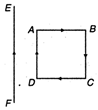 other. In the given circuit force of attraction is more between EF and AD that of repulsion between EF and BC, hence current loop is move towards the wire.
other. In the given circuit force of attraction is more between EF and AD that of repulsion between EF and BC, hence current loop is move towards the wire.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
