A)
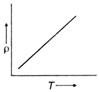
B)
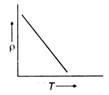
C)
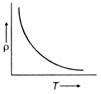
D)
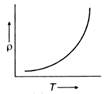
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
The variation of specific resistance with temperature is as follows \[\rho ={{\rho }_{ref}}+[1+\alpha (T-{{T}_{ref}})]\] where \[\rho \]= specific resistance at temperature T \[{{\rho }_{ref}}\] = specific resistance of reference temperature \[\alpha \] = temperature of coefficient of resistance. Rearranging the terms we have \[\rho ={{\rho }_{0}}+{{\rho }_{0}}\,\,\alpha \,(T-{{T}_{0}})\] On comparing the equation with equation of straight line \[y=mx+c\] we have, the slope negative.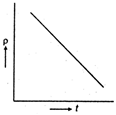 Note: The temperature coefficient of resistance of semiconductors is negative that is their electrical resistance decreases (or conductivity increases) with rise in temperature. At absolute zero a semiconductor behaves as an ideal insulator.
Note: The temperature coefficient of resistance of semiconductors is negative that is their electrical resistance decreases (or conductivity increases) with rise in temperature. At absolute zero a semiconductor behaves as an ideal insulator.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
