A) \[\frac{({{\alpha }^{2}}+{{\beta }^{2}})t}{\alpha \,\beta }\]
B) \[\frac{({{\alpha }^{2}}-{{\beta }^{2}})t}{\alpha \,\beta }\]
C) \[\frac{(\alpha +\beta )t}{\alpha \,\beta }\]
D) \[\frac{\alpha \beta t}{\alpha \,+\beta }\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
Key Idea: When car starts from rest, initial velocity is zero but when car is decelerating, final velocity is zero.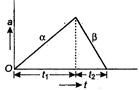 From equation of motion, we have \[v=u+\alpha t\] Let \[{{t}_{1}}\] be time of acceleration, and \[{{t}_{2}}\] be time of deceleration. Initial velocity \[u=0\], \[\therefore \] \[v=0+\alpha {{t}_{1}}\] \[{{t}_{1}}=\frac{v}{\alpha }\] ... (i) Similarly, when car is decelerating, the fina velocity is zero, \[\therefore \] \[0=v-\beta \,{{t}_{2}}\] ?. (ii) \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{t}_{2}}=\frac{v}{\beta }\] Total time \[t={{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}\] \[=\frac{v}{\alpha }+\frac{v}{\beta }=v\left( \frac{1}{\alpha }+\frac{1}{\beta } \right)\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[t=v\left( \frac{\alpha +\beta }{\alpha \,\beta } \right)\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[v=\frac{\alpha \beta \,t}{\alpha +\beta }\]
From equation of motion, we have \[v=u+\alpha t\] Let \[{{t}_{1}}\] be time of acceleration, and \[{{t}_{2}}\] be time of deceleration. Initial velocity \[u=0\], \[\therefore \] \[v=0+\alpha {{t}_{1}}\] \[{{t}_{1}}=\frac{v}{\alpha }\] ... (i) Similarly, when car is decelerating, the fina velocity is zero, \[\therefore \] \[0=v-\beta \,{{t}_{2}}\] ?. (ii) \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{t}_{2}}=\frac{v}{\beta }\] Total time \[t={{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}\] \[=\frac{v}{\alpha }+\frac{v}{\beta }=v\left( \frac{1}{\alpha }+\frac{1}{\beta } \right)\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[t=v\left( \frac{\alpha +\beta }{\alpha \,\beta } \right)\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[v=\frac{\alpha \beta \,t}{\alpha +\beta }\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
