| Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous 'decrease' both in demand and supply but there is no change in market price. Explain with the help of a schedule how it is possible. |
| Or |
| Market for a good is in equilibrium. Explain the chain of reaction in the market if the price is (i) higher than equilibrium price and (ii) lower than equilibrium price. |
Answer:
When the Quantity Supplied and Quantity demanded are equal then the market price is in equilibrium. According to the demand supply schedule given below, the equilibrium price is Rs. 7 where the quantity of demand and supply both are 16 units in other situation there is simultaneous decrement in both supply and demand but there is no change in market price. Therefore according to the new condition di and Si is drawn. There is no change in market price, new demand and supply are equal at 12 units. Therefore the equilibrium quantity is 16 in the original condition. In the new situation equilibrium quantity is different but the price is the same i.e., Rs. 7. This has been possible because there is equal decrease both in demand and supply in the new situation. It is because of that the equilibrium quantity has fallen from 16 to 12 units.
Price
Demand
Supply
(Rs.)
D
\[{{D}_{1}}\]
S
\[{{S}_{1}}\]
5
24
20
9
4
6
29
16
12
6
7
16
12
16
12
8
12
8
20
16
9
8
4
24
20
10
4
0
28
24
Or
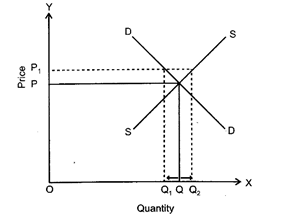
(i) When market price is higher than the equilibrium price. There is excess supply of goods and producers are not in a situation to sell all they want to sell at the given price. This leads to competition among producers which leads to lowering of price which in turn raises the demand and the supply reduces.
As shown in the diagram, equilibrium price is OP where equilibrium quantity is OQ. Say, if market price is fixed at \[O{{P}_{1}}\] then there will be disequilibrium between demand and supply. Demand will be \[O{{Q}_{1}}\] and supply\[O{{Q}_{2}}\], thus there will be excess of supply equal to\[{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}\]. For bringing equality between demand and supply, market price should be reduced from \[O{{P}_{1}}\] to OP, so that there is no excess supply.
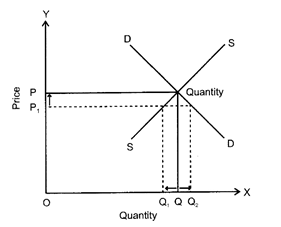
(ii) When market price is lower than the equilibrium price.
There is excess demand and consumers are not able to buy all they want to buy at the given price. This leads to competition between consumers which leads to a rise in price. Rise in price reduces demand while raises supply. As shown in the diagram equilibrium price is OP and quantity demanded OQ. If \[O{{P}_{1}}\] is fixed as market price (lower than the equilibrium price there will be excess demand equal to\[{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}\]. Therefore for bringing about an equality between demand and supply market price needs to be increased from \[O{{P}_{1}}\] to OP, so that there is no excess demand.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
