| (a) A student is unable to see clearly the words written on the black board placed at a distance of approximately 3 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. State the possible causes of this defect and explain the method of correcting it. |
| (b) Why do stars twinkle? Explain. |
| OR |
| (a) Write the function of each of the following parts of human eye: |
| (i) Cornea (ii) Iris (iii) Crystalline lens (iv) Ciliary muscles |
| (b) Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an astronaut on the Moon? Give reason to justify your answer. |
Answer:
(a) The boy is suffering from myopia
This defect is caused:
(i) due to increase in length of eyeball, and
(ii) decrease in focal length of eye lens, when the eye is fully relaxed.
Correction: The image of a distant object (i.e., at infinity) is formed in front of the retina of eye suffering from myopia as shown in figure (a). Rays from infinity
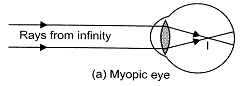
As the image of the object lying at infinity is not formed on the retina of the eye, so such object cannot be seen clearly by the myopic eye. The far point of such an eye is near to the eye as shown in fig. (b).
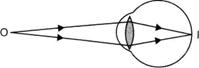
(b) Far point of a myopic eye
This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable focal length. So, a man suffering from this defect wears spectacles having concave lens of suitable focal length. The concave lens diverges the rays of light entering the eye from infinity. Hence this lens makes the rays of light appear come from the far point (O') of the defective eve as shown in figure (c).
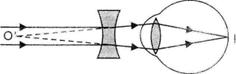
(c) Correction of myopia
(b) The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index.
Since the atmosphere bends starlight towards the normal, the apparent position of the star is slightly different from its actual position. This apparent position of the star is not stationary, but keeps on changing slightly, as the physical conditions of the earth's atmosphere are not stationary. Since the stars are very distant, they approximate point-sized sources of light. As the path of light rays coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers i.e., the star sometimes appear brighter, and at some other time, fainter, which is the twinkling effect.
OR
(a) (i) Cornea : It is a thin membrane, covering the surface of eyeball, through which light enters. It acts as a primary lens, which pro-vides the refraction for light rays entering the eye.
(ii) Iris: It is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil and is located just behind the cornea in the eye.
(iii) Crystalline lens: It is converging in nature, made by the jelly-like proteinaceous material. The focal length of the crystal-line lens is changed by the ciliary muscles. Its function is to focus the incoming light rays from the object on the retina using its refractive property.
(iv) Ciliary muscles: It modifies the curvature and thereby the focal length of the eye lens by contracting or relaxing itself to focus the image of an object on the retina according to the distance of the object. It also holds the eye lens in position.
(b) At the sunrise, the sun looks almost reddish because only red colour \[({{\lambda }_{b}}<{{\lambda }_{r}})\] which is least scattered, is received by our eye and appears to come from the sun. Hence, the appearance of the sun at the sunrise, near the horizon looks almost reddish.
This phenomenon will not be observed by an astronaut on Moon, since there is no atmosphere so no scattering of light takes place, thus the Sun appears dark.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
