Answer:
Krebs' cycle
occurs in the matrix of mitochondria. It is depicted in the following series of
reactions
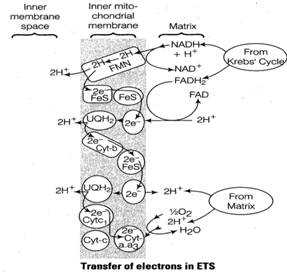
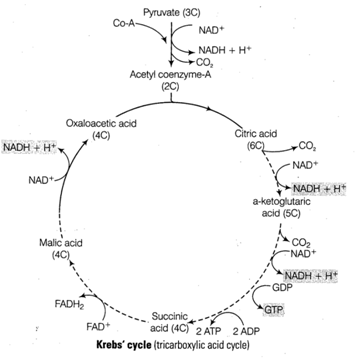 Electron
transport chain is carried out in the inner mitochondria membrane
The inner
mitochondrial membrane is specific about possessing proton
Electron
transport chain is carried out in the inner mitochondria membrane
The inner
mitochondrial membrane is specific about possessing proton ![]() and electron
and electron ![]() acceptors in a
particular sequence called electron transport chain. It has four enzyme complexes.
The
electrons either follow the pathway of complexes 1,111 and IV or II, III and IV
depending upon the substrates from Krebs' cycle.
The transfer
of electrons and hydrogen atoms takes place in the following way Complex I
Consists of flavor proteins of NADH dehydrogenase
acceptors in a
particular sequence called electron transport chain. It has four enzyme complexes.
The
electrons either follow the pathway of complexes 1,111 and IV or II, III and IV
depending upon the substrates from Krebs' cycle.
The transfer
of electrons and hydrogen atoms takes place in the following way Complex I
Consists of flavor proteins of NADH dehydrogenase ![]() of which FMN is the
prosthetic group. Combined with the flavor protein is non-heme iron of NADH
dehydrogenase.
This complex
spans inner mitochondrial membrane and is able to translocate protons across it
from matrix side to outer side.
Complex II
Consists of flavor protein of succinate dehydrogenase, of which FAD is the
prosthetic group. Combined with the flavor protein is non-heme iron of
succinate dehydrogenase.
Between
complexes II and III is the mobile carrier coenzyme-Q (Co-Q) or ubiquinone
(UQ).
Complex III
Consists of cytochrome-b and cytochrome-
of which FMN is the
prosthetic group. Combined with the flavor protein is non-heme iron of NADH
dehydrogenase.
This complex
spans inner mitochondrial membrane and is able to translocate protons across it
from matrix side to outer side.
Complex II
Consists of flavor protein of succinate dehydrogenase, of which FAD is the
prosthetic group. Combined with the flavor protein is non-heme iron of
succinate dehydrogenase.
Between
complexes II and III is the mobile carrier coenzyme-Q (Co-Q) or ubiquinone
(UQ).
Complex III
Consists of cytochrome-b and cytochrome- ![]() . Associated with
cytochrome- b is non-heme iron of complex ill. Between complexes III and IV is
the mobile carrier cytochrome-c.
Complex IV
Consists of cytochrome-a and cytochrome-
. Associated with
cytochrome- b is non-heme iron of complex ill. Between complexes III and IV is
the mobile carrier cytochrome-c.
Complex IV
Consists of cytochrome-a and cytochrome-![]() , and bound copper
that are required for this complex reaction to occur. This cytochrome also
called cytochrome oxidase, is the only electron carrier in which the heme iron
has a free ligand that can react directly with molecular oxygen.
, and bound copper
that are required for this complex reaction to occur. This cytochrome also
called cytochrome oxidase, is the only electron carrier in which the heme iron
has a free ligand that can react directly with molecular oxygen.
 Thus,
hydride ions are transferred from the substance to be oxidised to
Thus,
hydride ions are transferred from the substance to be oxidised to ![]() . From
. From ![]() the hydrogen atoms
are transferred to FMN of flavor protein 1 (Fp'N). After FMN the hydrogen atom
undergoes ionisation, i.e., it splits into an electron and a proton.
In further
stages there is no longer a transfer of hydrogens but of electrons. The
electron passes to co-enzyme- Q, and from co-enzyme Q to cytochromes-
the hydrogen atoms
are transferred to FMN of flavor protein 1 (Fp'N). After FMN the hydrogen atom
undergoes ionisation, i.e., it splits into an electron and a proton.
In further
stages there is no longer a transfer of hydrogens but of electrons. The
electron passes to co-enzyme- Q, and from co-enzyme Q to cytochromes- ![]() a and
a and ![]() . The proton is
released free.
As the
hydrogen atom or electron passes down by fq-f^
particle the chain, there is simultaneous oxidation of one coenzyme and
reduction at another steps. Oxygen is able to diffuse inside the mitochondria.
It is
converted to anionic form
. The proton is
released free.
As the
hydrogen atom or electron passes down by fq-f^
particle the chain, there is simultaneous oxidation of one coenzyme and
reduction at another steps. Oxygen is able to diffuse inside the mitochondria.
It is
converted to anionic form ![]() combines
with 2H"*" and forms metabolic water reduced co-enzyme
combines
with 2H"*" and forms metabolic water reduced co-enzyme ![]() helps in pushing
out three pairs of
helps in pushing
out three pairs of ![]() to outer
chamber while
to outer
chamber while ![]() sends two
pairs of
sends two
pairs of ![]() to outer chamber.
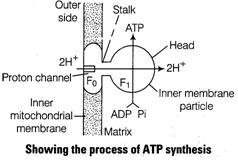
Oxidative
phosphorylation is the synthesis of energy rich ATP molecules, with the help of
energy liberated during oxidation of reduced co-enzyme
to outer chamber.
Oxidative
phosphorylation is the synthesis of energy rich ATP molecules, with the help of
energy liberated during oxidation of reduced co-enzyme ![]() produced in
respiration. The enzyme required for this synthesis is called ATP synthase
present in inner mitochondria membrane.
The
following figures shows this process
produced in
respiration. The enzyme required for this synthesis is called ATP synthase
present in inner mitochondria membrane.
The
following figures shows this process
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
