Answer:
(i) Schottky defect.
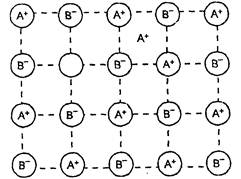
This type of defect is created when equal
number of positive and negative ions are missing from their respective
positions leaving behind holes. Since the number of missing positive ions is
equal to the number of missing negative ions the crystal as a whole is
electrically neutral. This defect is more common in ionic compounds with high
coordination number and where the ions (positive and negative) are of similar
size. For example NaCI, KCI, CsCI and KBr.
Since the number of ions decreases,
therefore as a result of large number of Schottky defects in solid, the density
of solid decreases.
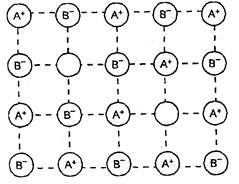 (ii) Frenkel defect
This type of defect is created when an ion
leaves its lattice site and occupies an interstitial site. In this case the
crystal remains electrically neutral because the number of anions and cations
remain the same. Since there is no absence of ions from the lattice, the
density remains the same. Frenkel defects generally occur in ionic compounds
(i) which have low co-ordination number,
and
(ii) in which anions are much larger in
size than the cations.
These defects can be found in silver
halides (such as AgCI, AgBr or Agl) because of small size of the Ag+ ion,
it can go into the interstitial sites.
(ii) Frenkel defect
This type of defect is created when an ion
leaves its lattice site and occupies an interstitial site. In this case the
crystal remains electrically neutral because the number of anions and cations
remain the same. Since there is no absence of ions from the lattice, the
density remains the same. Frenkel defects generally occur in ionic compounds
(i) which have low co-ordination number,
and
(ii) in which anions are much larger in
size than the cations.
These defects can be found in silver
halides (such as AgCI, AgBr or Agl) because of small size of the Ag+ ion,
it can go into the interstitial sites.
 (iii) Interstitials. Interstitial
sites are the holes or voids in the crystals. Atoms (or ions) which occupy the
vacant interstitial positions in a crystal are called Interstitials.
(iv) F-centres (Farbe's centre or
colour centres) F-centres are the free electrons trapped in the anionic
vacancies which are responsible for colour and electrical conductance in non-stoichiometric
compounds.
e.g., When sodium chloride is heated in an
atmosphere of sodium vapours, the excess of metal atoms get deposited on the
surface of alkali metal crystal. Halide ions then diffuse to the surface where
they combine with metal ions. The electrons so produced by the ionisation of the
metal diffuse back into the crystal and occupy anion vacancy. These electrons
absorb some energy of the white light, giving yellow colour to NaCl. These
amionic sites occupied by unpaired electron are referred to as F-ccntres
(German : Farbezenter means colour centre).
(iii) Interstitials. Interstitial
sites are the holes or voids in the crystals. Atoms (or ions) which occupy the
vacant interstitial positions in a crystal are called Interstitials.
(iv) F-centres (Farbe's centre or
colour centres) F-centres are the free electrons trapped in the anionic
vacancies which are responsible for colour and electrical conductance in non-stoichiometric
compounds.
e.g., When sodium chloride is heated in an
atmosphere of sodium vapours, the excess of metal atoms get deposited on the
surface of alkali metal crystal. Halide ions then diffuse to the surface where
they combine with metal ions. The electrons so produced by the ionisation of the
metal diffuse back into the crystal and occupy anion vacancy. These electrons
absorb some energy of the white light, giving yellow colour to NaCl. These
amionic sites occupied by unpaired electron are referred to as F-ccntres
(German : Farbezenter means colour centre).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
