Grammar
Category : 4th Class
Grammar
1. NOUN
A noun is the name of a person, place or thing, etc.
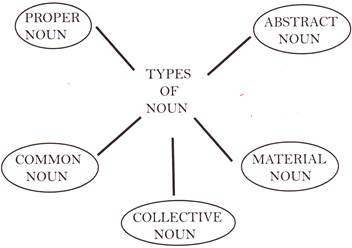
1. Proper Noun
A proper noun is the name of some particular person, place or thing.
For example:
Ashoka was a wise king. Here, Ashoka is the proper noun.
2. Common Noun
A common noun is a name given in common to every person or thing of the same class or kind.
For example:
The boy plays in the playground. Here, boy is the common noun.
3. Collective Noun
A collective noun is name of a number of person or things taken together.
For example:
There was a great crowd. Here, crowd is the collective noun.
4. Material Noun
A material noun is the word used for the substance of which things are made.
For example: Brass is yellow. Here, brass is the material noun.
5. Abstract Noun
An abstract noun is usually the name of a quality, action, or state considered apart from the object to which it belongs.
For example:
I remember my childhood. Here, childhood is an abstract noun.
2. PRONOUN
A pronoun is a word which is used in place of a noun.
Kinds of Pronoun:
1. Personal Pronoun
Personal pronoun stands for person or thing.
For example:
I am young. Here, I is a personal pronoun.
2. Interrogative Pronoun
They are used for asking questions.
For example:
Whose is this book? Here, whose is interrogative pronoun.
3. Reflexive Pronoun
Reflexive Pronouns are used when an action done by the subject turns back (reflects) upon the subject itself.
For example:
I hurt myself. Here, myself is reflexive pronoun.
4. Demonstrative Pronoun
It shows the noun in the sentence.
For example:
This book is mine. Here, this is demonstrative pronoun.
5. Indefinite Pronoun
It refers to persons or things in a general way.
For example:
One hardly knows what to do. Here, one is indefinite pronoun.
6. Distributive Pronoun
They refer to persons or things one at a time.
For example:
These horses cost five thousand rupees each. Here, each is distributive pronoun.
7. Relative Pronoun
It refers or relates to some noun introduced earlier.
For example:
I met Hari who had just returned. Here, who is relative pronoun.
8. Reciprocal Pronoun
The pronoun which is made up of two pronouns and shows a relation.
For example:
The girls helped one another. Here, one another is the reciprocal pronoun.
3. VERB
A verb is a word or a group of words that expresses action, feeling or existence.
Kinds of Verb:
1. Intransitive Verb
2. Transitive Verb
3. Linking Verb (Verb of incomplete predication)
4. Auxiliary or Helping Verb
1. Intransitive Verb
Without using an object this verb completes the meaning of sentence.
For example: The baby sleeps.
Robin sings.
2. Transitive Verb
This verb needs object to complete the meaning of sentence.
For example: Graham plays cricket.
Henry loves his aunt.
3. Linking Verb
The verb requires a word to make the sense complete.
For example: Sugar tastes sweet.
She looks happy
4. Auxiliary Verb
It is a helping verb.
For example: Ibrahim is writing a book.
You have spoken the truth.
4. ARTICLES
The words 'a', 'an' and 'the' are called articles. They come before nouns.
The articles a, an and the are further divided into two parts. They are the following:
(i) Indefinite Article
(ii) Definite Article
(i) Indefinite Articles
'A and an' are called indefinite articles, because they do not refer to any particular person, place, animal or thing.
For example:
A doctor; here a doctor signifies to any doctor and not a specific one.
Use of Indefinite Articles A and An
'A' is used before a singular countable noun beginning with consonant.
For example:
In the above given sentences, 'a' has been used before the nouns- teacher, girl, pen and car. These are single countable nouns beginning with consonant letters.
'A' is also used before a singular noun beginning with vowel letter but sounds like a consonant.
For example:
In the above given sentences, 'a' has been used
Before 'university', 'one-rupee note',
"European" and "useful."
These words, though begin with vowel letters, their sounds are like consonants. 'An' is used before a singular noun beginning with a vowel letter.
For example:
In the above given sentences, 'an' has been used before 'Indian', 'umbrella', 'apple' and 'owl'. All of these words begin with vowel letters.
'An' is also used before a singular noun beginning with consonant letters but sounds like vowel.
For example:
In the above given sentences, 'an' has been used before 'S.P.', 'hour', 'M.L.A.' and 'M.P.' These words though begin with consonants but sound like vowel.
Definite Articles
'The' is called definite article, because it refers to
a particular person, place, animal or thing.
For example:
Use of Definite Article 'The'
It is used when we talk about a particular person or thing, or one already referred to:
F'or example:
It is used when a singular noun is meant to represent a whole class:
For example:
Or we may say, 'Cows are useful animals.'
Note: Do not say, 'a kind of a fig tree'. This is a. common error.
The two nouns 'mm and 'woman' can be used. in a general sense without either articles,
For example:
It is used before some proper names. For example:
It is used before the names of certain books. For example:
But we say- Homer's Iliad, Valmikis Ramayana.
Before names of things unique of their kind. For example:
Note: Sometimes 'the' is placed before a Common noun to give it the meaning of an Abstract noun.
For example: At last the warrior (the warlike or martial spirit) in him was thoroughly aroused.
It is used before a Proper noun when it is qualified by an adjective or a defining adjectival clause. For example:
It is used with Superlatives. For example:
It is used with ordinals. For example:
It is used before musical instruments. For example:
It is used before an adjective when the noun is understood. For example:
It is used before a noun (with emphasis) to give the force of a Superlative. For example:
It is used as an Adverb with Comparatives. For example:
(= by how much more, by so much the merrier)
It is used in its original numerical sense of one. For example:
It is used in the vague sense of a certain. For example:
It is used in the sense of any to single out an individual as the representative of a class.
For example:
To make a common noun of a proper noun. For example:
5. PREPOSITIONS
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show its relation to some other word in the sentence.
Look at the following sentences:
Here, 'on' shows the relation between two nouns (book and table) and 'at' shows the relation between two pronouns (she and me). Therefore, these are prepositions.
Kinds of Prepositions
Prepositions are of three types:
1. Simple Prepositions
Some simple prepositions are:
in, on, at, to, from, with, by, etc.
For example:
2. Compound Prepositions
Some compound prepositions are:
about, across, among, betzveen, beside, before, etc.
For example:
3. Phrase Prepositions
Some phrase prepositions are:
according to, in spite of, on account of, in front of, in order to, for the sake of, by means of, with
reference to, in addition to, due to, etc.
For example:
6. CONJUNCTIONS
A conjunction is a word that joins words, phrases, clauses and sentences together.
Look at the use of conjunctions in the following sentences:
The words till, that, or, if, and, because, although, but are conjunctions in these sentences.
7. USE OF POSSESSIVES
Possessive Case of Noun
If there is a relation with the person then we use the possessive case. We often use ?s? instead of using an ?of? phrase.
For Example: Germany's economy or the economy of Germany
When using the possessive case with a time, ?s? is added.
For Example:
A three week's holiday
Look at the following sentence:
This is the doll of Rita.
After using Possessive the sentence will become: This is Rita's doll.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
