Number System
Category : 4th Class
Number System
Learning Objectives
Numbers
Numbers are words and symbols representing a count by which we express date, time, position, quantity, etc.
For example:
(1) I will go to school at 8 O’clock - Time
(2) I stayed in the party for 2 hours - Time
(3) My birthday is on January 15 - Date
(4) Exam will be starting from 1st March - Date
(5) 15th person in the row is Jack - Position
(6) 7th book from the left end is the book of Mathematics - Position
(7) There are 5 books on the table - Quantity
(8) There are 5 kg of flour - Quantity
Numeration Systems
Numeration systems are methods of representing quantities. As a simple example, suppose we have a basket of apples. We might want to keep track of the number of apples in the basket, or we might want to sell the apples to someone else, or we might simply want to give the basket a numerical code that could be used to tell when and where the apples come from. In order to perform any of these simple mathematical operations, we would have to begin with some kind of numeration system. In this section, we will study about the following two types of numeration systems:
Indian System of Numeration
Indian system of numeration is also known as Hindu-Arabic numeral system. This method of numeration is based on the following place value chart:
Place Value Chart
|
Period |
Kharab |
Arab |
Crores |
Lakhs |
Thousands |
Ones |
|||||||
|
Places |
Ten Kharab (T-KH) 1000000000000 |
Kharab (KH) 100000000000 |
Ten Arab (T-A) 10000000000 |
Arab (A) 1000000000 |
Ten Crores (T-C) 100000000 |
Crores (C) 10000000 |
Ten Lakhs (T-L) 1000000 |
Lakhs (L) 100000 |
Ten thousands (T-TH) 10000 |
Thousands (TH) 1000 |
Hundreds (H) 100 |
Tens (T) 10 |
Ones (O) 1 |
International System of Numeration
International system of numeration is widely used in the most part of the world. The following table shows the place value chart for international system of numeration:
|
Period |
Billions |
Millions |
Thousands |
Ones |
||||||||
|
Places |
Hundred billions |
Ten billions |
Billions |
Hundred millions |
Ten billions |
Billions |
Hundred millions |
Ten billions |
Billions |
Hundred millions |
Ten billions |
Billions |
In this system of numeration, every period has three groups. The digits under the same period are read together along with the period.
Face Value of a Digit
The face value of a digit in the numeral is the value of digit itself. For example, the face value of 9 in the number 1932 is 9 itself.
Place Value of a Digit
When we multiply the face value of a digit with the value of its period, it gives the place value of digit. In the above example, the place value of 9 is (\[9\times 100\]) or 900.
Expanded Form
Expanded form means expansion of a number according to the place value of the digits For example, expanded form of 15874587458 is:
\[1\times 10000000000+5\times 1000000000+8\times 100000000+7\times 10000000+4\times 1000000+5\times 100000+8\times 10000+\]
\[7\times 1000+4\times 100+5\times 10+8\times 1\]
Successor of a Number
It is defined as a number which is one more than the given number.
Predecessor of a Number
It is defined as a number which is one less than the given number.
Ascending Order
Numbers in a group are said to be in ascending order when they are arranged from the smallest to the largest number.
Descending Order
Numbers in a group are said to be in descending order when they are arranged from the largest to the smallest number.
Symbols of Roman Numerals
Here is a chart that has all the Roman numerals, what they stand for. The system is based on seven different symbols in total. These symbols can be used to write any Roman numerals.
|
Roman Numeral |
Hindu-Arabic Numeral |
|
I |
1 |
|
V |
5 |
|
X |
10 |
|
L |
50 |
|
C |
100 |
|
D |
500 |
|
M |
1000 |
Roman Numerals up to 30
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
V |
VI |
VII |
VIII |
IX |
X |
|
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
|
XI |
XII |
XIII |
XIV |
XV |
XVI |
XVII |
XVIII |
XIX |
XX |
|
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
|
XXI |
XXII |
XXIII |
XXIV |
XXV |
XXVI |
XXVII |
XXVIII |
XXIX |
XXX |
Example:
1. The product of predecessor and successor of 11 is:
(a) 99 (b) 210
(c) 120 (d) 108
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here, given number = 11
So, the predecessor of 11 = 10 and the successor of 11 = 12
Therefore, the required product =\[10\times 12\]= 120
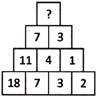
2. Find the missing number (?) in the number pattern given below.
(a) 1 (b) 3
(c) 4 (d) 5
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Here, numbers are arranged in a pyramid pattern of subtraction in which the difference of two consecutive numbers of fourth row or bottom row is equal to the number given above in its third row.
Hence, \[18-7=11;\text{ }7-3=4;\text{ }3-2=1\]
Similarly, \[11-4=7\]; \[4-1=3\]
Therefore, the required missing number = \[7-3=4\]
3. Find the value of the Roman numeral XXIX.
(a) 31 (b) 29
(c) 27 (d) 32
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: According to Roman numeral rules,
XXIX = \[10+10+(10-1)=(20+9)=29\]
4. Which one of the following statements is not correctly matched?
(a) C + D + M = 1600 (b) Five times of C = Ten times of L
(c) V + L + D = 1555 (d) L + L + L = CL
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct,
Explanation: In the option (a): C + D + M = \[100+500+1000=1600\]
In option (B): Five times C = \[5\times 100=500\] and Ten times of L = \[10\times 50=500\]
In option (C): V + L + D = \[5+50+500=555\]
In option (D): L + L + L = \[50+50+50=150\] and CL= \[100+50=150\]
5. Roman numerals for the greatest 3 digit number is:
(a) CMXCIX (b) IM
(c) CMIC (d) CMIXIX
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: The greatest 3 digit number = 999
Now, 999 = \[900+90+9\] = \[(1000-100)+(100-10)+(10-1)\]
= (CM) + (XC) + (IX) = CMXCIX
6. The value of sum (\[\text{XC}-\text{XL}\]) in Roman numerals is:
(a) C (b) L
(c) XXX (d) XC
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Here, \[\text{XC}-\text{XL}=(100-10)-(50-10)=90-40=50\] = L
7. The sum of two numbers is 52149. If one of them is 14732, then find the other number.
(a) 37417 (b) 39557
(c) 35527 (d) 38687
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: Here, the sum of numbers = 52149 and one number = 14732
Therefore, the other number = \[52149-14732\] = 37417
8. I earn Rs.25500 per month. My total monthly expenditure is Rs.13850. How much do I save every month?
(a) Rs.11000 (b) Rs.12150
(c) Rs.11650 (d) Rs.10840
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: My earning per month = Rs.25500
My expenditure per month = Rs.13850
Therefore, My saving per month = \[\begin{align}
& \text{ }Rs.\text{ 25500} \\
& \underline{-\text{ }Rs.\text{ 13850}} \\
& \underline{\text{ }Rs.\text{ 11650}} \\
\end{align}\]
So, I save Rs.11650 every month.
9. There were 2912 chocolates packed equally in 26 boxes. How many chocolates were packed in each box?
(a) 106 (b) 112
(c) 194 (d) 126
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Number of chocolates in 26 boxes = 2912
Number of chocolates in 1 box = \[2912\div 26\]
\[\begin{align}
& 26\overset{112}{\overline{\left){2912}\right.}} \\
& \text{ }\underline{-26\text{ }} \\
& \text{ }31 \\
& \text{ }\underline{\text{ }-26\text{ }} \\
& \text{ }52 \\
& \text{ }\underline{\text{ }-52\text{ }} \\
& \text{ }\underline{\text{ }0\text{ }} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, the number of chocolates in each box is 112.
10. How much money is collected from 2714 students of a school for a charity show. If each student contributes Rs.205?
(a) Rs.566930 (b) Rs.582680
(c) Rs.556370 (d) Rs.513560
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct.
Explanation: Number of students = 2714
Contribution of each student = Rs.205
Now, for total money:
\[\begin{align}
& \text{ }2714 \\
& \text{ }\underline{\times \text{ }205} \\
& \text{ }13570 \\
& \text{ }0000 \\
& \underline{5428\text{ }} \\
& \underline{556370} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, total contribution = \[Rs.\text{ }(2714\times 205)=Rs.\text{ }556370\]
Commonly Asked Question
1. Which one of the following statements is correct for the Roman numerals given below?
(a) XXVIII < 20 (b) XXXVI = 34
(c) XXXIX > 40 (d) XXXIV = 34
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Here, in option (a), XXVIII = 28 > 20
In option (b), XXXVI = 36
In option (c), XXXIX = 39 < 40
In option (d), XXXIV =34
Therefore, the statement given in option (d) is correct.
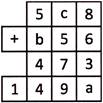
2. Find the values of a, b and c in the addition pattern given below.
(a) a = 8; b = 5; c = 3 (b) a = 7; b = 5; c = 4
(c) a = 9; b = 4; c = 5 (d) a = 7; b = 4; c = 6
(e) None of these
Answer (d) is correct.
Explanation: Adding ones, we get, \[8+6+3=17\]. Therefore, a = 7
Adding tens, we get, c + 5 +7 + (carry 1) = 19
or, (c) + 13 = 19; or, (6) + 13 = 19, therefore, c = 6
Adding hundreds, we get, 5 + b + 4 + (carry 1) = 14; or, b + 10 = 14;
or, (b) + 10 = (4) + 10. Therefore, b = 4. Hence, a = 7, b = 4 and c = 6
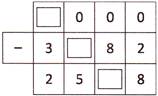
3. Some digits are missing in the subtraction pattern given below. The sum of three missing digits is:
(a) 10 (b) 11
(c) 12 (d) 9
(e) None of these
Answer (b) is correct.
Explanation: Here, subtraction is as follows:
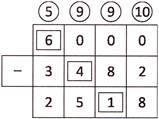
We have, missing digits in the given subtraction are: 6, 4, 1
Hence, the required sum of digits = \[6+4+1=11\text{ }\]
4. The population of three blocks in a colony are 19832, 25169 and 3766, respectively. Total population of the colony is:
(a) 87753 (b) 89233
(c) 82663 (d) 84243
(e) None of these
Answer (c) is correct,
Explanation: Population of three blocks are as follow:
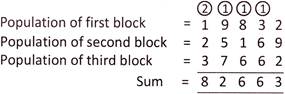
Hence, total population of the colony = 82663
5. Product of two numbers is 12544. If one of the numbers is 196, then the other number is:
(a) 64 (b) 128
(c) 72 (d) 96
(e) None of these
Answer (a) is correct.
Explanation: Product of two numbers = 12544
One number = 196
Therefore, the other number = \[12544\div 196\]
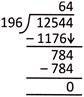
Hence, the required number is 64, where \[196\times 64=12544\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
