Notes - History-When, Where and How
Category : 6th Class
History - When, Where and How
Summary
1. History is a study of the past. It helps us to understand change and how it came about and how the society we live in came to be.
2. Many geographical location in India were inhabited by the early settlers. Humans began settlements near rivers. This gave them access to water. Historians have identified many such sites.
3. The history of a place is shaped by the location and geography of that particular place. The physical features of the Indian subcontinent have greatly influenced its history.
4. Sources of history give us information about the past. Once we get the information, the past can be reconstructed.
5. Archaeologists are people who excavate to find evidence of the past. Archaeologist evidence includes cave paintings, coins, inscriptions, monuments and burials.
6. Literary sources consist of biographies, manuscripts, travelogues, religious and secular literature.
7. The birth of Christ is used as a reference point to measure time in years.
![]()
History is a study of the past. It comes from the Greek word historia meaning information acquired by inquiry. It is the true story of mankind and man's adventures on the earth. No one knows exactly when it began but it is still going on at the present time.
WHAT IS HISTORY
This is a very frequently asked question. Our past and present are inseparable. One cannot divorce the past from the present because the past shapes the future. It helps us to understand change and how it came about and how the society we live in came to be.
Things around us just did not happen. They happened over time. We cannot understand the things and the ways of life today unless we know how they developed. When you are reading this book, you are using paper. Where has this paper come from? Who was the first to make paper? The Egyptians were the first to start the art of papermaking sometime around 3500 BCE. It was made from papyrus reeds. The word "paper" is derived from 'papyrus' itself. A person who studies history is called historian.
History Reveals
The birth of Jesus Christ was earlier mistakenly taken to be 1AD/CE in a medieval attempt to count the years. Today, most scholars generally assume the date of birth of Christ between 6 and 4 BCE/BC
HISTORY, PROTOHISTORY AND PREHISTORY
Historians have classified the past into History, Protohistory and Prehistory.
History of man started when man learnt how to write. They began to keep records of the times. This period is known as history.
Protohistory is the time period for which we have written records but they are few and still cannot be read.
The time before man began writing is called prehistoric era. Prehistory is the period that begins with the appearance of human beings about million years ago and ends with the invention of writing. It is important to point out when prehistory ended and history began since it varies from region to region.
WHERE HUMANS LIVED IN INDIA
Many geographical locations in India were inhabited by the early settlers. Humans began settlements near rivers. This gave them access to water. Historians have identified many such sites.
The banks of the River Narmada were inhabited by humans thousands of years ago. They were hunter-gatherers. They hunted wild animals for food. Also, they gathered fruits, leaves and seeds or dug up roots of plants for their food.
The Kirthar and Sulaiman Hills are the areas where humans first began growing crops about 8000 years ago. They grew wheat and barley and also began domesticating animals.
The Vindhyas in Central India close to the Narmada River and the Garo hills in the north-east show evidence of the development of agriculture. It is here that rice was first cultivated. Humans also lived near the River Indus and its tributaries. In fact, it is here that the first cities came up about 4700 years ago. There is evidence that cities were established near the river Ganga and its tributaries about 2500 years ago. Even large kingdoms came up near the rivers. Magadha was one such large kingdom which grew near the River Son.
THE GEOGRAPHICAL FRAMEWORK
The history of a place is shaped by the location and geography of that particular place. The physical features of the Indian subcontinent have greatly influenced its history.
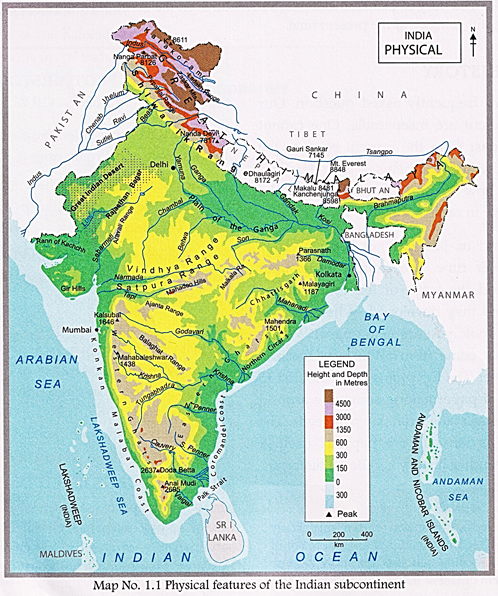
India has mountains, plains, plateaus and sea coasts The Himalayas have acted as a barrier in the north for foreign invaders. The numerous rivers of India led to the rise of human settlements around them. The Harappan Civilisation flourished around the river Indus. The Indo-Gangetic plains lying between the Indus and the Ganges saw the rise of many powerful kingdoms and empires. The coastal plains have been centres of trade and commerce since ancient times. There was an enormous exchange of ideas, cultures and traditions besides merchandise. This resulted in the development of a unique yet diverse culture.
Earliest Names of India
India has been known by many names in the past. About 2500 years ago, the Greeks who came in from the North-West, crossed the River Indus which they called Hindos or Indos. The land beyond the River began to be called India. The name Bharata has been used in the Rig Veda. It was named after King Bharat who was a famous ruler.
SOURCES OF HISTORY
Sources of history give us information about the past. Once we get the information, the past can be reconstructed.
Archaeological Sources
Archaeologists are people who excavate to find evidence of the past. They look for objects like stone tools, pottery, seals, jewellery, toys etc. from excavation sites. These objects provide a lot of information about that period of history.
These are especially important in gathering information about prehistory because no written records are available.
Q. Can you differentiate between a Historian and an Archaeologist?
Archaeological evidence includes cave paintings, coins, inscriptions, monuments and burials. Cave Paintings: Many cave paintings done by early men have been found in many different parts of the world. Bhimbetka caves in India are famous for the cave paintings. They tell us about the animals that early man hunted, the weapons he used etc. Some of the paintings at Bhimbetka are approximately 300 years old.
Q. Can you find out another site in the world where cave paintings have been found?

Coins: The earliest coins were only pieces of metal with a mark to indicate that they were coins and not just bits of metal. Later on, the coins had the name or portrait of the king. So, they give very useful information. Also, the places from which they were discovered give an idea of the size and extent of the kingdom. From the metal used for the coin, historians can guess whether the kingdom was rich or poor. Coins also give information about the religion, clothes and even the pastimes of the people.
The below coins show that Samudragupta was talented and enjoyed music.

Inscriptions: Inscriptions are writings on stone or metal. Many inscriptions have been found all over the world. Emperor Ashoka had inscriptions put all over his kingdom. They tell us about his empire, lifestyle, administration and Buddhism which was his religion. Kings often kept records of victories in battle.
Monuments: The study of monuments is the key to understanding a particular culture. Ancient building culture. Ancient buildings like the Parthenon Stupa, the Parthenon and the Roman Colosseum are the windows to the early civilisations.

Burials: The burial sites also give a wealth of information. For instance, in Burzahom in Kashmir, the burials that have been found are very interesting. The dead were buried in pits lined with lime. Sometimes, pets were buried with their masters. The association of tools and weapons with the skeletal remains also suggests the belief in life after death.
History Reveals
Ancient Egyptians mummified the dead and put the mummies in pyramids along with many grave goods. They removed the brain but saved the heart during mummification.
Literary Sources
There are many ways of finding out about our past. One way is to read books that were written long ago.
Manuscripts: They were written by hand on palm leaves or specially prepared bark of a tree called birch. These deal with all types of subjects. There were epics, poems and plays written in Sanskrit, Prakrit and Tamil. Though many have been destroyed by insects, many still remain preserved carefully in monasteries and temples.

Biographies: These contribute in reconstructing history. Harshacharita by Banabhatta gives a detailed account of the life and reign of Emperor Harsha.
Religious Texts: Religious texts like Vedas and Upanishads tell us about the Vedic age of India. Other religious texts include the Puranas and Bhaguad Gita. The Mahabharata was written by sage Ved Vyasa and the Ramayana by Sage Valmiki. Historians draw information on the economic, social and religious life of the people from these epics.
Secular Literature: Other texts highlight other aspects of life.
? Kalidasa has written Shakuntala and Meghaduta
? Shudraka has written Mricchakatika
? Jayadeva has written Geet Govinda
? Chankya has written Arthashastra
Traveller's accounts: Many foreign travelers have also given good accounts of ancient India. These are called travelogues. These help us understand the past and relate it to the present.
? Megasthenes, a Greek ambassador, in the Mauryan court wrote 'Indica'.
? Fa Hien and Hiuen Tsang were Chinese travellers who visited India and gave detailed accounts of India in their writings.
What do dates mean?
To study history, we must understand the measurement of time. The past is measured in years. The birth of Christ is taken as a reference point. The years before Christ was born are written as BC or before the birth of Christ.
For example, 3000 BC means 3000 years before Christ was born. Nowadays, BC is also written as BCE which means Before the Common era. AD stands for Anno Domini meaning 'in the year of the Lord". Any event that occurred after the birth of Christ is written as AD e.g. India gained independence in 1947 AD, meaning 1947 years after the birth of Christ. It can also be written as CE or Common Era.
Around the World
In ancient Egypt, the people used a kind of picture writing. This writing is called hieroglyphics meaning "holy carving?. At first, the writings represented things such as a bird, sun or water. Later, each small drawing represented a letter.
The Egyptians wrote on a kind of paper called papyrus made from reeds which grew near The Nile River. Many pieces of papyrus were stuck together to form a scroll. The hot and dry weather of Egypt has preserved many old Egyptian scrolls. Earlier no one could understand the writing. However, it has been deciphered and now we know a lot about the ancient Egyptian civilisation from the scrolls.

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
