Notes - Life In The Temperate Grasslands
Category : 7th Class
Life In The Temperate Grasslands
Large rolling terrains of grasses, flowers, shrubs and herbs cover almost one-fourth of the total land area of the earth. There are two different kinds of grasslands: tropical and temperate. The Tropical grasslands are found in the warm climate where the annual rainfall is about 50 to 127 cm. The Savanna in Africa are such grasslands. The Temperate grasslands are found in the drier zones and have shorter grasses. Grasslands go by many names. In this chapter, we will study about the Prairies and the Velds.
TEMPERATE GRASSLANDS
THE PRAIRIES
Location and extent
Prairie is a French word. It means 'a meadow' or "a grassland'. The Prairies of North America are found both in USA and Canada. They stretch from Texas (USA) in the south to Alberta (Canada) and Saskatchewan (Canada) in the north. The Canadian Prairies extend over the provinces of Manitoba, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Ontario. While in the USA, they cover the states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, Wisconsin, Nebraska, Iowa and Texas. In the USA, the Prairies are drained by the tributaries of the Mississippi river and in Canada by the tributaries' of the Saskatchewan River. These areas have flat to gently rolling hilly land. They are treeless areas except for poplars and willows in river valleys or at places where water is found in abundance. The Prairies are regions of long grasses. The grasses vary in height according to rainfall and soil, reaching up to more or less 2 metres.
Climate
The Prairies are located in the interior of the continent of North America and thus experience a continental type of climate. The summer temperature varies from 19°C to 28°C. The rainfall varies too, i.e. from 50 mm to 500 mm in the west to 1000 mm in the east. In winter, temperature goes down well below freezing point; a major part of the Prairies is covered in a thick blanket of snow. In early spring, the warm Chinook winds blow down the leeward side of the Rockies (Rocky Mountains) and help in the melting of snow as well as in the growth of spring wheat and other crops.
z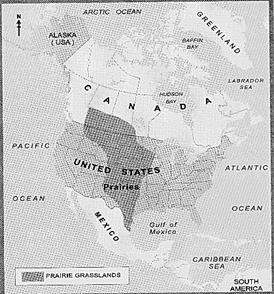
Mop No.10.1 the Prairies in North America
Flora and Fauna
Flora is basically grass. The Prairies are treeless but near the valleys woodlands can be found, such as willows, alders and poplars. Tall grasses unto two metres high dominate the landscape. It is actually a 'sea of grass'. Soil found in the Prairies has a high humus content. It is dark, fertile and is known as chemozem soil. This soil is most suitable for the growth of grasses.
It is believed that before the arrival of the Europeans, the Prairies were home to bisons (American buffaloes). The Europeans started hunting them and the number of bisons dropped to a large extent; they have become almost extinct now. The other animals found in these grasslands are antelopes, grizzly bears, coyotes, gophers, rabbits, wolves and prairie dogs.
Many species of birds such as hawks, larks and buntings (finches) are found in this region in great numbers.
Economic Activities
Cattle rearing is the main activity in the Western Prairies. Large size cattle farms known as ranches are built in these areas. As these areas receive scanty rainfall, short grasses grow in these areas and are suitable for cattle rearing.
Cattle are looked after by some sturdy men called cowboys.

Dairy farming is one of the major industries in the Prairie region. The dairy region extends from the Great Lakes in the west to the Atlantic Coast in the east. Thus, cattle have commercial value for the people of the Prairies.

Advanced dairy farming
The cattle are fed on grain and silage and sent to the slaughter houses for meat. A serious problem of overgrazing has occurred in the area experiencing low rainfall such as Alberta, Montana, Western Dakota and Nebraska.
Fodder crops are fed to the animals during the long cold winter.
Cereal-farming started in the Prairies on a large scale after the 1840s, i.e. when the steel ploughs started to be used for digging fields in the Prairies. Now, these areas are rich, extensive fields of cultivation, wheat, barley and oats are grown in these fields commercially. Other major crops grown in these areas are maize, potato, soyabean and cotton. The alfalfa grasses are grown in these areas to feed cattle.
The use of modern agricultural machines such as tractors, harvesters and combines1 has helped these areas to be the top food producers in the world. A farmer with the help of a combine can do all the work without any help from anyone. A good network of rail and ports helps in the transportation and export of agricultural produce to distant countries.
Geography Reveals
The Prairies are known as the 'Granaries of the World5.

Modern farming in the Frames
Farms are usually divided into sections for crop rotation. This also helps in obtaining good yield. To prevent soil erosion, contour ploughing and strip cropping are widely practised. However, farmers are now diversifying into non- agricultural activities such as leisure work and tourism. The important towns of the Prairies are Indianapolis, Denver and Chicago in the USA and Calgary, Edmonton and Winnipeg in Canada. A variety of mineral deposits such as coal, iron and petroleum and efficient system of transport and communication have helped the Prairies develop as the most industrialised region in the world.
THE VELDS
Location and extent
Veld is a Dutch word that means 'a field'. The temperate grasslands of South Africa are called the Velds or Veldts. These grasslands occupy the eastern part of the plateau. These rolling plateaus vary in height from 600 metres to 1000 metres.
The Velds are bounded by the Drakensberg Mountains in the east and Kalahari Desert in the west. A low, sedimentary range of hills called the Witwaterstrand runs across the Velds. The Limpopo and Orange rivers drain the area. On the basis of their elevations, the Velds can be divided into: (i) Highveld, (ii) Middleveld, and (iii) Lowveld.
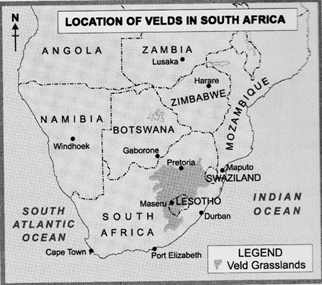
Mop No. 10.2 Location of Velds in South Africa
Geography Reveals
The area between the Vaal River and Johannesburg in the north-east of the Southern Africa is known as the 'Witwaterstrand'. It is one of the richest goldmining areas of the world.
Climate
The Velds lie in the warm, temperate zone. This region is under the influence of two oceans namely, the Indian Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. The presence of the Benguela Current which flows along the west coast of Southern
Africa makes the Veld Region cooler, milder and pleasant. The Average summer temperature is less than 20°C while winter temperature is 5°C to 10°C. July is the coldest month and summer is very short in duration. Rainfall occurs in the summer months, i.e. from November to February. However, drought may occur during the summer if the rainfall is scanty.
Flora and Fauna
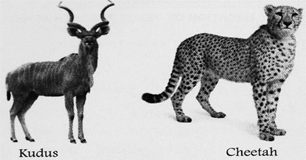
Due to low range of rainfall in the Velds, the vegetation cover is sparse. Red grass grows in the Bushvelds, whereas the Highveld?s have trees like acacia and maroola. The animals found in the Velds are lions, leopards, cheetahs and kudus.
Economic Activities
The Velds are best suited for cattle and sheep rearing. Merino sheep are bred in the Veld region mainly for obtaining the best quality warm wool. After Australia/ South Africa is the second largest exporter of Merino wool. The Angora goats are also bred in the Veld region of Southern Africa. The fleece of an Angora goat is called Mohair. Mohair is a lustrous fibre of white colour which is used to produce winter wear. Angora goats yield not only Mohair but leather too. South Africa is the largest producer of Mohair in the world.
Dairy farming is another important occupation here. Cattle are reared in those areas of the Velds which are wetter and warmer. Dairy products such as butter and cheese are produced for local use as well as for the international market.

The word 'gold' comes from the old English word 'GEOLU' meaning Yellow. In South Africa, almost.' 500,000 people work in gold mines and gold exports? Were over $ 3.8 billion.
Frozen meat is exported mainly to the South European countries, i.e. countries around the Mediterranean Sea.
Although soil in the Veld region is not very fertile/ farmers cultivate crops like maize, wheat, barley, oat and potato wherever possible.
The Velds have rich mineral reserves. Gold is found in the hill range of Witwaterstrand and diamonds are found in the mines of Kimberley (Northern Cape). It was the availability of gold and diamonds on a large scale which attracted the early European settlers to South Africa. Iron and coal too are found in abundance. The rich availability of coal and iron near Johannesburg, the gold capital of the world, has led to the development of big iron and steel industries around Pretoria, the administrative capital of South Africa. Therefore, the Veld region of Southern Africa has developed an excellent network of transport and communication.

Deep Gold Mines of South Africa
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
