Reproductive Parts of a Flower
Category : 8th Class
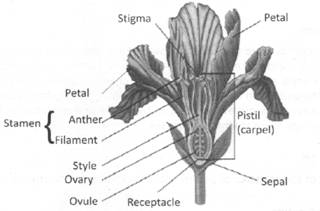
The plants, that reproduce sexually have the reproductive structures called the flowers. The flower is a condensed shoot, with the nodes present very close to each other. The different parts of the plant are attached to the nodes. All the structures present at one node are collectively called the whorl. The first or the outermost two whorls are called the non-reproductive whorls. They are, the calyx and corolla. The inner two whorls, which are the reproductive whorls are androecium and gynoecium.
![]() Calyx
Calyx
It is the outermost and often green in colour. The individual units of calyx is called the sepals. It protects the inner whorls at bud stage.
![]() Corolla
Corolla
It is the next inner part of the whorl, and is coloured differently. The individual units of the corolla are called petals. They act as an attraction for bees, birds, etc, which are the agents of pollination.
The reproductive part of the flowers
![]() Androecium
Androecium
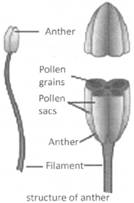
It is the male reproductive part of the flowers. The male organ is called stamens. Each stamen has a thread like filament at its free end, which is attached to the four lobed anther. The anther has four pollen sacs in each lobe. These pollen sacs contain microscopic cell called pollen grains. Each microspore divides once mitotically to produce two male gametes or the sperm cell. Each mother cell produces 8 sperm cells.
![]() Gynoecium
Gynoecium
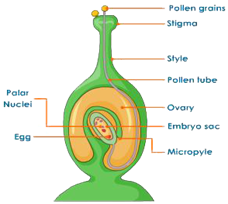
It is the female reproductive part of the flower. Each individual unit is called the carpel or pistil. A flower may have one or many carpels. Each carpels is made up of ovary, style and stigma. Ovules are the chamber where many ovules are attached to the axis. Each ovule consist of haploid egg and other associated cells. The stigma receives pollen grains and the style is the hollow tubules, that provides passage from the male gametes to the female ovary.
![]() Pollination
Pollination
It is the process of the transfer of pollen grains from stamen to stigma. It is of two types:
(i) Self pollination
(ii) Cross pollination
The self pollination, also known as autogamy, is the pollination in which pollens are transferred to the stigma of the same flower. Whereas, in cross pollination the pollens are transferred to the stigma of the different flowers. It is also known as allogamy. The various agents of cross pollinations are wind, water, bees, bats and many other animals.

Pollination
![]() Fertilization
Fertilization
On reaching the stigma, the pollen grains produce a tube. This is called germination of the pollen grain.
The upper most part of the tube contains the male nuclei, which grows and enters into the ovules. It burst at the tip releasing the male gametes. The mate gametes fuses with the egg, results in the formation of zygote that is diploid. This fusion is called fertilizations. The zygote then develops into the embryo.
Fertilization in a flowering plant

![]() In some plants, male and female reproductive part are present in the same flower; but in some plant they are present in different flowers. The male reproductive part of the flower is called:
In some plants, male and female reproductive part are present in the same flower; but in some plant they are present in different flowers. The male reproductive part of the flower is called:
(a) Androecium's
(b) Gynoecium's
(c) Carpel
(d) Cylax
(e) None of these
Answer: (a)
Explanation
The gynoecium is female reproductive part of the flower, where as carple and cylax are part of reproductive system of the flower.
![]() In plants fertilization takes place by transfer of pollen grains. This transfer of pollens is called pollination. It may be self pollination or cross pollination. The self pollination is also called:
In plants fertilization takes place by transfer of pollen grains. This transfer of pollens is called pollination. It may be self pollination or cross pollination. The self pollination is also called:
(a) Allogamy
(b) Autogamy
(c) Monogamy
(d) Polygamy
(e) None of these
Answer: (a)
Explanation
The other name of self pollination is allogamy.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
