Cells and Tissues
Category : 9th Class
Cells and Tissues
Cell
Tie cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
All living organisms are made up of the smallest unit that is cell. The organisms can be of two types unicellular and multicellular. The unicellular organisms such as amoeba, Paramecium has a single cell in their body and this single cell performs all basic life activities. The multicellular organisms such as human beings have millions of cells in their body. Most of these cells are specialised to carry out a few functions efficiently. A group of cells is responsible for performing a specific function. For example, muscle cells contract and relax to cause movement of a body part.
Structure of a Cell
Different cells have different types of structures which depends on their specific functions. The size, shape, number and volume vary largely in multicellular and unicellular organisms. The size of the cell of bacteria is smallest and ostrich egg is largest. The volume of a cell is constant for a particular cell type and is independent of the size of the organism. For example, kidney or liver cells of a bull, horse and mouse are same in size. The number of cells depends on the types of organisms. It is indefinite in multicellular definite in unicellular.
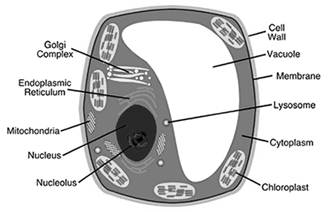
Plant Cell
Different parts of a cell and their functions:
Plasma membrane - outermost covering of the cell which allows only selective substances to pass through it.
Cytoplasm - helps in exchange of materials between different cell organelles.
Endoplastic reticulum - helps in synthesis and transport of proteins and fats.
Mitochondria - oxidises food to release energy in the-from of ATP.
Golgi apparatus - helps in storage of secretory products.
Ribosomes - helps in protein synthesis.
Lysosome - helps in intra-cellular digestion.
Nucleus - helps in cell division and regulates all functions within the cell.
Nucleolus - helps in protein synthesis by forming and storing RNA.
Vacuoles - helps in storage of water and other substances.
Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis
|
Diffusion |
Osmosis |
|
1. It is a process of movement of molecules or ions of a substance from a region of higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration. |
1. It is the diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a semi permeable membrane. |
|
2. It can occur in any medium (solid, siquid and gas) |
2. It occurs in liquid medium only. |
|
3. It does not require any semi-permeable membrane. |
3. It requires a semi-permeable memberane. |
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
|
Animal cell |
Plant cell |
|
1. It is small in size. |
1. It is large in size. |
|
2. Cell wall is absent. |
2. Cell wall is present. |
|
3. Plastids are absent. |
3. Plastids are present. |
|
4. It has centrosome and centrioles. |
4. It lacks centrosome and centrioles. |
Tissues
Various cells together form tissues that perform a particular function in the body. In other words, we can say that a group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to achieve a particular function constitute a tissue.
Plant Tissues
Meristematic tissue
This tissue is found in all the growing parts of a plant
Permanent tissue
This tissue is derived from the meristematic tissue. The cell of this tissue has lost the power of division and has attained its definite form. This tissue is classified into two types:
Difference Between Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma
|
Collenchyma |
Sclerenchyma |
|
1. It consists of living cells. |
1. It consists of dead cells. |
|
2. The cells of collenchyma contain cytoplasm. |
2. The cells of sclerenchyma. |
|
3. The thickening of cell wall is non uniform. |
3. The thickening of cell wall is uniform. |
|
4. Lumen of the cell is wide. |
4. Lumen of the cell is narrow. |
|
5. It provides tensile strength and elasticity to the plant body |
5. It is chiefly mechanical tissue. |
Difference Between Tracheids and Vessels
|
Tracheids |
Vessels |
|
1. These are elongated narrow tube like cells with hard thick walls. |
1. These are cylindrical tubular structure. |
|
2. The end walls remain intact. |
2. End walls get dissolved and become perforated. |
|
3. The walls of tracheids are very thick with a narrow lumen. |
3. The walls of vessels are less thick and they have wider lumen. |
Difference Between Xylem and Phloem
|
Xylem |
Phloem |
|
1. It mainly consists of dead cells except parenchyma. |
1. It consists of living tissue except phloem fibres. |
|
2. It conducts water and minerals from roots to aerial parts of the plant. |
2. It translocates food such as sucrose from leaves to storage organs and growing parts of the plant. |
Difference Between Meristematic Tissue and Permanent Tissue
|
Meristematic Tissue |
Permanent Tissue |
|
1. The cells divide repeatedly. |
1. The cells do not divide. |
|
2. The cells are undifferentiated. |
2. The cells are fully differentiated. |
|
3. The cells are living |
3. The cells may be dead or alive. |
|
4. Intercellular spaces are generally absent. |
4. Visible intercellular spaces are present. |
|
5. Vacuoles are absent. |
5. large vacuoles are present in mature cells |
Animal Tissues
This is the simplest tissue also known as protective tissue of the animal body. This tissue covers most organs and cavities within the body.
Connective Tissue
This tissue connects various body organs such as bones, muscles to bones, etc. This tissue gives support to the various parts of the body by forming packing around organs so that they do not get displaced by body movement.
Muscular Tissue
It consists of elongated cells that are called muscle fibers. It is mainly responsible for movement in our body. Muscles contain special proteins called contractile protein, which contract and relax to cause movement. These muscles help in both voluntary and involuntary movements.
Nervous Tissue
This tissue is mainly responsible for transmitting messages within our body. All the vital organs of the body are part of it such as brain, spinal cord, nerves, etc. This tissue contains neurons, which have the ability to receive stimuli from within or outside the body and conduct impulses to different parts of the body.
Difference Between Tendons and Ligaments
|
Tendons |
Ligaments |
|
1. They are less elastic than ligaments. |
1. They are slightly more elastic than tendons. |
|
2. They join muscles to bones. |
2. They join bones to bones |
|
3. They are white fibrous tissue. |
3. They are yellow elastic tissue. |
|
4. They have great strength and flexibility. |
4. They have considerable strength. |
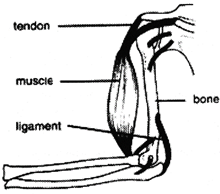
Tendons and ligaments
Difference Between Bones and Cartilages
|
Bones |
Cartilages |
|
1. They are very hard and inflexible. |
1. They are flexible. |
|
2. The matrix in bone is made up of protein and mineral salts. |
2. The matrix in cartilage is made up of proteins and sugars. |
|
3. Cells are known as osteocyte. |
3. Cells are known as chondrocytes. |
|
4. Bones are rich in blood supply. |
4. Cartilages lack blood supply. |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
