Various Terms Related to Magnetism
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
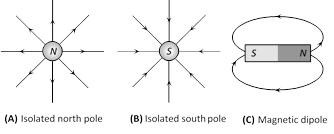
(1) Magnetic field and magnetic lines of force : Space around a magnetic pole or magnet or current carrying wire within which it's effect can be experienced is defined as magnetic field. Magnetic field can be represented with the help of a set of lines or curves called magnetic lines of force.
(2) Magnetic flux \[(\phi )\] and flux density (B)
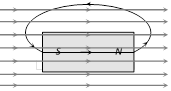
(i) The number of magnetic lines of force passing normally through a surface is defined as magnetic flux \[(\phi )\]. It's S.I. unit is weber (wb) and CGS unit is Maxwell. Remeber \[1\,wb={{10}^{8}}\] Maxwell.
(ii) When a piece of a magnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field the substance becomes magnetised. The number of magnetic lines of induction inside a magnetised substance crossing unit area normal to their direction is called magnetic induction or magnetic flux density \[(\overrightarrow{B}).\] It is a vector quantity.
It's SI unit is Tesla which is equal to \[\frac{wb}{{{m}^{2}}}=\frac{N}{amp\times m}=\frac{J}{amp\times {{m}^{2}}}=\frac{volt\times \sec }{{{m}^{2}}}\]
and CGS unit is Gauss. Remember 1 Tesla \[={{10}^{4}}\] Gauss.
(3) Magnetic permeability : It is the degree or extent to which magnetic lines of force can enter a substance and is denoted by \[\mu \]. Or characteristic of a medium which allows magnetic flux to pass through it is called it's permeability. e.g. permeability of soft iron is 1000 times greater than that of air.
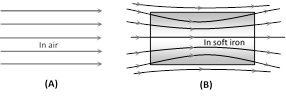
Also \[\mu ={{\mu }_{0}}\,{{\mu }_{r}};\,\] where \[{{\mu }_{0}}=\] absolute permeability of air or free space = \[4\pi \times {{10}^{-7}}tesla\times m/amp.\]
and \[{{\mu }_{r}}=\] Relative permeability of the medium = \[\frac{B}{{{B}_{0}}}=\frac{\text{flux}\,\text{density in material}}{\text{flux density in vacuum}}.\]
(4) Intensity of magnetising field \[\mathbf{(}\overrightarrow{H}\mathbf{)}\] (magnetising field) : It is the degree or extent to which a magnetic field can magnetise a substance. Also \[H=\frac{B}{\mu }\].
It's SI unit is \[A/m.=\frac{N}{{{m}^{2}}\times Tesla}=\frac{N}{wb}=\frac{J}{{{m}^{3}}\times Tesla}=\frac{J}{m\times wb}\]
It's CGS unit is Oersted. Also 1 Oersted = 80 A/m
(5) Intensity of magnetisation (I) : It is the degree to which a substance is magnetised when placed in a magnetic field.
It can also be defined as the pole strength per unit cross sectional area of the substance or the induced dipole moment per unit volume.
Hence \[l=\frac{m}{A}=\frac{M}{V}.\] It is a vector quantity, it's S.I. unit is Amp/m.
(6) Magnetic susceptibility \[({{\chi }_{m}})\] : It is the property of the substance which shows how easily a substance can be magnetised. It can also be defined as the ratio of intensity of magnetisation (I) in a substance to the magnetic intensity (H) applied to the substance, i.e. \[{{\chi }_{m}}=\frac{I}{H}\]. It is a scalar quantity with no units and dimensions.
(7) Relation between permeability and susceptibility : Total magnetic flux density B in a material is the sum of magnetic flux density in vacuum \[{{B}_{0}}\] produced by magnetising force and magnetic flux density due to magnetisation of material \[{{B}_{m}}\]. i.e. \[B={{B}_{0}}+{{B}_{m}}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[B={{\mu }_{0}}H+{{\mu }_{0}}I={{\mu }_{0}}(H+I)={{\mu }_{0}}H(1+\]\[{{\chi }_{m}})\]. Also \[{{\mu }_{r}}=(1+{{\chi }_{m}})\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
