Fertilization
Category : NEET
Fertilization
(i) Definition: Fusion of a haploid male gamete (spermatozoon) and a haploid female gamete (ovum) to form a diploid cell, the zygote, is called fertilization or syngamy.
(ii) Site of fertilization: Fertilization in human female is internal as in other mammals. It takes place usually in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
(iii) Steps of fertilization
(a) Approach of sperm to ovum: Male discharge semen (3.5 ml) high up in the female’s vagina, close to the cervix during coitus. This is called ejaculation or insemination. This ejaculation contains as many as 400 million sperms but only about 100 sperms reach the fallopian tube because many sperms are either killed by the acidity of female genital tract or engulfed by the phagocytes of the vaginal epithelium. The sperm swim in the seminal fluid at the rate of 1-4 mm per minute by the aspiratory action of the uterus and peristaltic movement of the fallopian tube.
Capacitation is the phenomenon of physiological maturation of sperms by breaking of acrosome membrane inside the female genital tract. It takes about 5-6 hours. Ovum is released on the 14th day of menestrual cycle trapped by the fimbriae of the ampulla of fallopian tube and move towards the uterus by peristalsis and ciliary action. At the time of ovulation, egg is at secondary oocyte stage. Fertilizability of human sperm in the female genital tract is of 12 to 24 hours while its survival value is up to 3 days and of ovum is only 24 hours though it can live for about 72 hours.
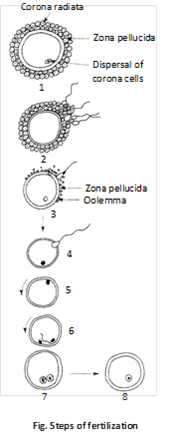
(b) Penetration of sperm: The ovum secretes a chemical substance called fertilizin, which has a number of spermophillic sites on its surface where the sperm of species specific type can be bound by their antifertilizin site. This fertilizin-antifertilizin interaction, causing agglutination (sticking together) of egg and sperm.
The sperm generally comes in contact with ovum in the animal pole (side of ovum with excentric nucleus) while the opposite side of ovum is called vegetal pole. Ovulation in the human female occurs at secondary oocyte stage in which meiosis-I has been completed and first polar body has been released but second maturation is yet to complete. Penetration of sperm is a chemical mechanism. In this acrosome of sperm undergoes acrosomal reaction and releases certain sperm lysins which dissolve the egg envelopes locally and make the path for the penetration of sperm. Sperm lysins are acidic proteins. These sperm lysins contain a lysing enzyme hyaluronidase which dissolves the hyaluronic acid polymers in the intercellular spaces which holds the granulosa cells of corona radiata together; corona penetrating enzyme (that dissolves the corona radiata) and acrosin (which dissolves the zona pellucida). Then it dissolves the zona pellucida. Only sperm nucleus and middle piece enter the ovum. The tail is lost.
(c) Cortical reaction: Immediately after the entry of a sperm into the egg, the later shows a cortical reaction to check the entry of more sperms. In this reaction, the cortical granules present beneath the egg’s plasma membrane release chemical substance between the ooplasm and the plasma membrane (vitelline membrane). These substances raise the vitelline membrane above the egg surface. The elevated vitelline membrane is called fertilization membrane. The increased space between the ooplasm and the fertilization membrane and the chemical present in it effectively check the entry of other sperm. If polyspermy occurs, that is more than one sperm enter the secondary oocyte, the resulting cell has too much genetic material to develop normally.
Sperm penetration into ovum also induces following metabolic activities:
(1) The egg surface produces fertilization cone.
(2) The vitelline membrane is lifted and is converted into fertilization membrane.
(3) The cortical granule explode.
(4) The cytoplasm exhibits movements.
(5) The permeability of plasma membrane increases.
(6) The coenzyme NAD is phosphorylated.
(7) The rate of protein synthesis increases.
(8) Mitosis is initiated.
(9) The breakdown of polysaccharide occurs.
(10) The enzyme dehydrogenase increases.
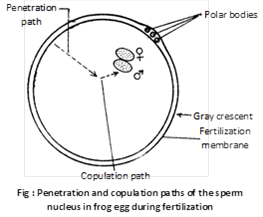
(d) Fusion of gametic nuclei: Entrance of spermatozoon serves to acts as stimulus which causes the second maturation division. As the head and middle piece of the sperm advance into the egg, those parts rotate through an angle of \[{{180}^{{}^\circ }}\] so that the mitochondria and proximal centriole of the associated middle piece assume the leading position. Beside this rotation, the chromatin itself starts swelling by absorbing fluid from the surrounding cytoplasm and becomes vesicular. It is now called male pronucleus. This direction of movement of male pronucleus is called penetration path. The centriole brought in by the spermatozoon subdivides into two and as achromatic spindle is established in the center of the active cytoplasm. With the production of the second polar body, the egg nucleus or female pronucleus is ready for union with the male pronucleus provided by the sperm head.
The male pronucleus which has been advancing the penetration path, now moves directly toward the female pronucleus. This in many cases involves a slight change in the course of sperm. In such cases, the later portion of its course is called the copulation path. The centrioles of middle piece of sperm form a spindle. The nuclear membrane of the gametic nuclei degenerates and two sets of chromosomes initially lie on two poles of the spindle but later these sets of chromosomes mix up and the process is called amphimixis. The fertilized egg is now called zygote and the zygote nucleus is called synkaryon.
(iv) Types of fertilization
(a) External fertilization: In this, the gamete fuse outside the female body and is found in most of bony fishes (e.g. Labeo), amphibians (e.g. frog), all echinoderms (e.g. starfish) and lower chordates (e.g. Herdmania).
(b) Internal fertilization: In this, the fusion of gametes in some part of female genital tract and generally near the ostium. It is found in all terrestrial animals which may be oviparous (all birds, prototherians), ovo-viviparous (rattle-snake) or viviparous (all marsupials and eutherians).
(c) Self-fertilization (Endogamy): In this, two fusing gametes are derived from the same parent (uniparental) e.g. Taenia, Fasciola (sheep, liver fluke).
(d) Cross fertilization (Exogamy): In this, two fusing gametes are derived from different parents (biparental). It is found in all unisexual animals and some bisexual animals e.g. Pheretima (earthworm-due to protandry), Scypha (Sycon-due to protogyny) Fasciola and Taenia (have both self and cross fertilization).
(e) Monospermic fertilization: When only one sperm enters and fuses with ovum. It is found in most of animals.
(f) Polyspermic fertilization: When many sperms penetrate the ovum and may be pathological polyspermy (due to over-ripening of egg) or physiological polyspermy (natural entry of sperms). But only one sperm fuses with ovum.
(v) Significane fertilization
(a) It provides stimulus for the egg to complete its maturation.
(b) It activates the ovum to develop into a new individual by repeated mitotic division.
(c) Fertilization restores the diploid number of chromosomes (46 in man) in the zygote by adding male’s haploid set of chromosomes.
(d) It makes the egg more active metabolically.
(e) It combines the character of two parents and introduces variations. So help in evolution.
(f) Sex chromosomes of sperm is either X or Y and helps in sex determination.
(g) Fertilization membrane formed after sperm entry, checks the entry of additional sperms.
(h) Copulation path sets the axis of division.
Important Tips
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
