NCERT Extracts - Structure and Physiography
Category : UPSC
Location
- India is a vast country. Lying entirely in the Northern hemisphere the main land extends between latitudes 8°4'N and 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E and 97°25'E.
- The Tropic of Cancer (23°30'N) divides the country into almost two equal parts. To the southeast and southwest of the mainland, lie the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep islands in Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea respectively.
- The southernmost point of the Indian Union - 'Indira Point' got submerged under the sea water in 2004 during the Tsunami.
Size
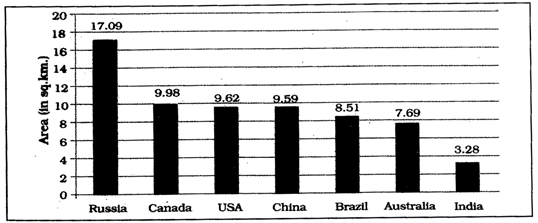
- The land mass of India has an area of 3.28 million square km. India's total area accounts for about 2.4 per cent of the total geographical area of the world.
- India is the seventh largest country of the world. India has a land boundary of about 15,200 km and the total length of the coast line of the mainland including Andaman and Nicobar and Lakshadweep is 7,516.6 km.
- From Gujarat to Arunachal Pradesh there is a time lag of two hours. Hence, time along the Standard Meridian of India (82°30'E) passing through Mirzapur (in Uttar Pradesh) is taken as the standard time for the whole country.
- Since the opening of the Suez Canal in 1869, India's distance from Europe has been reduced by 7,000 km.
The Peninsular Block
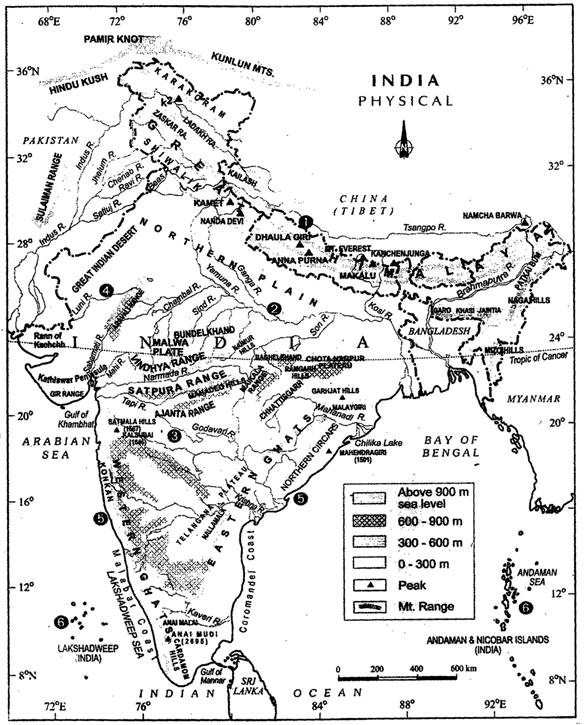
India Physical
- Current estimation shows that the earth is approximately 460 million years old.
- Based on the variations in its geological structure and formations, India can be divided into three geological divisions. These geological regions broadly follow the physical features.
- The Peninsula is formed essentially by a great complex of very ancient gneisses and granites, which constitutes a major part of it.
- Since the Cambrian period, the Peninsula has been standing like a rigid block with the exception of some of its western coast which is submerged beneath the sea and some other parts changed due to tectonic activity without affecting the original basement.
- As a part of the Indo-Australian Plate, it has been subjected to various vertical movements and block faulting.
- The rift valleys of the Narmada, the Tapi and the Mahanadi and the Satpura block mountains are some examples of it.
- The
- Peninsula mostly consists of relict and residual mountains like the Aravali hills, the Nallamala hills, the Javadi hills, the Veliconda hills, the Palkonda range and the Mahendragiri hills, etc.
- The river valleys here are shallow with low gradients.
The Himalayan and other Peninsular Mountains
- The Himalayas along with other Peninsular mountains are young, weak and flexible in their geological structure unlike the rigid and stable Peninsular Block.
- Consequently, they are still subjected to the interplay of exogenic and endogenic forces, resulting in the development of faults, folds and thrust plains.
- These mountains are tectonic in origin, dissected by fast-flowing rivers which are in their youthful stage.
- Various landforms like gorges, V-shaped valleys, rapids, waterfalls, etc. are indicative of this stage.
Indo-Ganga-Brahmaputra Plain
- The third geological division of India comprises the plains formed by the river Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
- Originally, it was a geo-synclinal depression which attained its maximum development during the third phase of the Himalayan mountain formation approximately about 64 million years ago.
- Since then, it has been gradually filled by the sediments brought by the Himalayan and Peninsular rivers. Average depth of alluvial deposits in these plains ranges from 1,000- 2,000 m.
Physiography
- Based on these macro variations, India can be divided into the following physiographic divisions: The Northern and North-eastern Mountains, The Northern Plain, The Peninsular Plateau, The Indian Desert, The Coastal Plains and The Islands.
The North and Northeastern Mountains
- The North and Northeastern Mountains consist of the Himalayas and the Northeastern hills. The Himalayas consist of a series of parallel mountain ranges.
- Some of the important ranges are the Greater Himalayan range, which includes the Great Himalayas and the Trans-Himalayan range, the Middle Himalayas and the Shiwalik.
- The general orientation of these ranges is from northwest to the southeast direction in the northwestern part of India.
- Himalayas in the Darjiling and Sikkim regions lie in an eastwest direction, while in Arunachal Pradesh they are from southwest to the northwest direction.
- In Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram, they are in the northsouth direction.
- The approximate length of the Great Himalayan range, also known as the central axial range, is 2,500 km from east to west, and their width varies between 160- 400 km from north to south.
- Himalayas are not only the physical barrier, they are also a climatic, drainage and cultural divide.
- There are large-scale regional variations within the Himalayas. On the basis of relief, alignment of ranges and other geomorphological features, the Himalayas can be divided into the following sub-divisions:
Kashmir or Northwestern Himalayas
- It comprise a series of ranges such as the Karakoram, Ladakh, Zaskar and Pir Panjal.
- The northeastern part of the Kashmir Himalayas is a cold desert, which lies between the Greater Himalayas and the Karakoram ranges.
- Between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal range, lies the world famous valley of Kashmir and the famous Dal Lake.
- Important glaciers of South Asia such as the Baltoro and Siachen are also found in this region.
- The Kashmir Himalayas are also famous for Karewa formations, which are useful for the cultivation of Zafran, a local variety of saffron.
- Some of the important passes of the region are Zoji La on the Great Himalayas, Banihal on the Pir Panjal, Photu La on the Zaskar and Khardung La on the Ladakh range.
- Some of the important fresh lakes such as Dal and Wular and salt water lakes such as Pangong Tso and Tso Moriri are also in this region.
- This region is drained by the river Indus, and its tributaries such as the Jhelum and the Chenab.
- The Kashmir and northwestern Himalayas are well-known for their scenic beauty and picturesque landscape.
- The landscape of Himalayas is a major source of attraction for adventure tourists.
- Some famous places of pilgrimage such as Vaishno Devi, Amamath Cave, Charar-e-Sharif, etc. are also located here.
- Srinagar, capital city of the state of Jammu and Kashmir is located on the banks of Jhelum river. Dal Lake in Srinagar presents an interesting physical feature.
- Jhelum in the valley of Kashmir is still in its youth stage and yet forms meanders - a typical feature associated with the mature stage in the evolution of fluvial land form.
- In Kashmir Valley, the meanders in Jhelum river are caused by the local base level provided by the erstwhile larger lake of which the present Dal Lake is a small part.
- The southernmost part of this region consists of longitudinal valleys known as 'duns'. Jammu dun and Pathankot dun are important examples.
The Himachal and Uttarakhand Himalayas
- This part lies approximately between the Ravi in the west and the Kali (a tributary of Ghaghara) in the east.
- It is drained by two major river systems of India, i.e. the Indus and the Ganga.
- Tributaries of the Indus include the river Ravi, the Beas and the Satluj, and the tributaries of Ganga flowing through this region include the Yamuna and the Ghaghara.
- The northernmost part of the Himachal Himalayas is an extension of the Ladakh cold desert, which lies in the Spiti subdivision of district Lahul and Spiti.
- All the three ranges of Himalayas are prominent in this section also. These are the Great Himalayan range, the Lesser Himalayas (which is locally known as Dhaoladhar in Himachal Pradesh and Nagtibha in Uttarakhand) and the Shiwalik range from the North to the South.
- In this section of Lesser Himalayas, the altitude between 1,000-2,000 m specially attracted to the British colonial administration, and subsequently, some of the important hill stations such as Dharamshala, Mussoorie, Shimla, Kaosani and the cantonment towns and health resorts such as Shimla, Mussoorie, Kasauli, Almora, Lansdowne and Ranikhet, etc. were developed in this region.
- The two distinguishing features of this region from the point of view of physiography are the 'Shiwalik' and 'Dun formations'.
- Some important duns located in this region are the Chandigarh-Kalka dun, Nalagarh dun, Dehra Dun, Harike dun and the Kota dun, etc.
- Dehra Dun is the largest of all the duns with an approximate length of 35-45 km and a width of 22-25 km.
- In the Great Himalayan range, the valleys are mostly inhabited by the Bhotia's.
- These are nomadic groups who migrate to 'Bugyals' (the summer glasslands in the higher reaches) during summer months and return to the valleys during winters.
- The famous 'Valley of flowers' is also situated in this region. The places of pilgrimage such as the Gangotri, Yamunotri, Kedamath, Badrinath and Hemkund Sahib are also situated in this part.
- The region is also known to have five famous Prayags (river confluences).
The Shiwalik
- The word shiwalik has its origin in the geological formation found in and around a place called Sivawala near Dehra Dun which was once a headquarter of the Imperial Survey and which subsequently established its permanent headquarters at Dehra Dun.
The Darjiling and Sikkim Himalayas
- They are flanked by Nepal Himalayas in the west and Bhutan Himalayas in the east. It is relatively small but is a most significant part of the Himalayas.
- Known for its fast-flowing rivers such as Tista, it is a region of high mountain peaks like Kanchenjunga (Kanchengiri), and deep valleys.
- The higher reaches of this region are inhabited by Lepcha tribes while the southern part, particularly the Darjiling Himalayas, has a mixed population of Nepalis, Bengalis and tribals from Central India.
- The British, taking advantage of the physical conditions such as moderate slope, thick soil cover with high organic content, well distributed rainfall throughout the year and mild winters, introduced tea plantations in this region.
- As compared to the other sections of the Himalayas, these along with the Arunachal Himalayas are conspicuous by the absence of the Shiwalik formations.
- In place of the Shiwaliks here, the 'duar formations' are important, which have also been used for the development of tea gardens.
- Sikkim and Darjiling Himalayas are also known for their scenic beauty and rich flora and fauna, particularly various types of orchids.
The Arunachal Himalayas
- These extend from the east of the Bhutan Himalayas up to the Diphu pass in the east.
- The general direction of the mountain range is from southwest to northeast. Some of the important mountain peaks of the region are Kangtu and Namcha Barwa.
- These ranges are dissected by fast-flowing rivers from the north to the south, forming deep gorges. Bhramaputra flows through a deep gorge after crossing Namcha Barwa.
- Some of the important rivers are the Kameng, the Subansiri, the Dihang, the Dibang and the Lohit.
- These are perennial with the high rate of fall, thus, having the highest hydro- electric power potential in the country.
- An important aspect of the Arunachal Himalayas is the numerous ethnic tribal community inhabiting in these areas. Some of the prominent ones from west to east are the Monpa, Abor, Mishmi, Nyishi and the Nagas.
- Most of these communities practise Jhumming. It is also known as shifting or slash and bum cultivation.
- This region is rich in biodiversity which has been preserved by the indigenous communities.
- Due to rugged topography, the inter-valley transportation linkages are nominal. Hence, most of the interactions are carried through the duar region along the Arunachal-Assam border.
The Eastern Hills and Mountains
- These are part of the Himalayan mountain system having their general alignment from the north to the south direction. They are known by different local names.
- In the north, they are known as Patkai Bum, Naga hills, the Manipur hills and in the south as Mizo or Lushai hills.
- These are low hills, inhabited by numerous tribal groups practising Jhum cultivation.
- Most of these ranges are separated from each other by numerous small rivers. The Barak is an important river in Manipur and Mizoram.
- The physiography of Manipur is unique by the presence of a large lake known as 'Loktak' lake at the centre, surrounded by mountains from all sides.
- Mizoram which is also known as the 'Molassis basin' which is made up of soft unconsolidated deposits.
- Most of the rivers in Nagaland form the tributary of the Brahmaputra.
- While two rivers of Mizoram and Manipur are the tributaries of the Barak river, which in turn is the tributary of Meghna; the rivers in the eastern part of Manipur are the tributaries of Chindwin, which in turn is a tributary of the Irrawady of Myanmar.
The Northern Plains
- The northern plains are formed by the alluvial deposits brought by the rivers – the Indus, the Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
- These plains extend approximately 3,200 km from the east to the west. The average width of these plains varies between 150-300 km. The maximum depth of alluvium deposits varies between 1,000-2,000 m.
- From the north to the south, these can be divided into three major zones : the Bhabar, the Tarai and the alluvial plains.
- The alluvial plains can be further divided into the Khadar and the Bhangar.
- Bhabar is a narrow belt ranging between 8-10 km parallel to the Shiwalik foothills at the break-up of the slope.
- As a result of this, the streams and rivers coming from the mountains deposit heavy materials of rocks and boulders, and at times, disappear in this zone.
- South of the Bhabar is the Tarai belt, with an approximate width of 10-20 km where most of the streams and rivers re-emerge without having any properly demarcated channel, thereby, creating marshy and swampy conditions known as the Tarai.
- This has a luxurious growth of natural vegetation and houses a varied wild life.
- The south of Tarai is a belt consisting of old and new alluvial deposits known as the Bhangar and Khadar respectively.
- These plains have characteristic features of mature stage of fluvial erosional and depositional landforms such as sand bars, meanders, oxbow lakes and braided channels.
- The Brahmaputra plains are known for their riverine islands and sand bars.
- Most of these areas are subjected to periodic floods and shifting river courses forming braided streams.
- The mouths of these mighty rivers also form some of the largest deltas of the world, for example, the famous Sunderbans delta.
- Otherwise, this is a featureless plain with a general elevation of 50-150 m above the mean sea level.
- The states of Haryana and Delhi form a water divide between the Indus and the Ganga river systems.
- As opposed to this, the Brahmaputra river flows from the northeast to the southwest direction before it takes an almost 90° southward turn at Dhubri before it enters into Bangladesh.
- These river valley plains have a fertile alluvial soil cover which supports a variety of crops like wheat, rice, sugarcane and jute, and hence, supports a large population.
The Peninsular Plateau
- Rising from the height of 150 m above the river plains up to an elevation of 600- 900 m is the irregular triangle known as the Peninsular plateau.
- Delhi ridge in the northwest, (extension of Aravalis), the Rajmahal hills in the. east, Gir range in the west and the Cardamom hills in the south constitute the outer extent of the Peninsular plateau.
- However, an extension of this is also seen in the northeast, in the form of Shillong and Karbi-Anglong plateau.
- The Peninsular India is made up of a series ofpatland plateaus such as the Hazaribagh plateau, the Palamu plateau, the Ranchi plateau, the Malwa plateau, the Coimbatore plateau and the Kamataka plateau, etc.
- This is one of the oldest and the most stable landmass of India. The general elevation of the plateau is from the west to the east, which is also proved by the pattern of the flow of rivers.
- On the basis of the prominent relief features, the Peninsular plateau can be divided into three broad groups:
The Deccan Plateau
- This is bordered by the Western Ghats in the west, Eastern Ghats in the east and the Satpura, Maikal range and Mahadeo hills in the north.
- Western Ghats are locally known by different names such as Sahyadri in Maharashtra, Nilgiri hills in Kamataka and Tamil Nadu and Anaimalai hills and Cardamom hills in Kerala.
- Western Ghats are comparatively higher in elevation and more continuous than the Eastern Ghats.
- Their average elevation is about 1,500 m with the height increasing from north to south.
- 'Anaimudi' (2,695 m), the highest peak of Peninsular plateau is located on the Anaimalai hills of the Western Ghats followed by Dodabetta (2,637 m) on the Nilgiri hills.
- Most of the Peninsular rivers have their origin in the Western Ghats.
- Eastern Ghats comprising the discontinuous and low hills are highly eroded by the rivers such as the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, the Kaveri, etc.
- Some of the important ranges include the Javadi hills, the Palconda range, the Nallamala hills, the Mahendragiri hills, etc. The Eastern and the Western Ghats meet each other at the Nilgiri hills.
The Central Highlands
- They are bounded to the west by the Aravali range. The Satpura range is formed by a series of scarped plateaus on the south, generally at an elevation varying between 600-900 m above the mean sea level.
- This forms the northernmost boundary of the Deccan plateau. It is a classic example of the relict mountains which are highly denuded and form discontinuous ranges.
- The extension of the Peninsular plateau can be seen as far as Jaisalmer in the West, where it has been covered by the longitudinal sand ridges and crescent- shaped sand dunes called barchans.
- This region has undergone metamorphic processes in its geological history, which can be corroborated by the presence of metamorphic rocks such as marble, slate, gneiss, etc.
- The general elevation of the Central Highlands ranges between 700-1,000 m above the mean sea level and it slopes towards the north and northeastern directions.
- Most of the tributaries of the river Yamuna have their origin in the Vindhyan and Kaimur ranges.
- Banas is the only significant tributary of the river Chambal that originates from the Aravalli in the west.
- An eastern extension of the Central Highland is formed by the Rajmahal hills, to the south of which lies a large reserve of mineral resources in the Chotanagpur plateau.
The Northeastern Plateau
- In fact it is an extension of the main Peninsular plateau. It is believed that due to the force exerted by the northeastward movement of the Indian plate at the time of the Himalayan origin, a huge fault was created between the Rajmahal hills and the Meghalaya plateau.
- Later, this depression got filled up by the deposition activity of the numerous rivers.
- Today, the Meghalaya and Karbi Anglong plateau stand detached from the main Peninsular Block.
- The Meghalaya plateau is further sub-divided into three : The Garo Hills; The Khasi Hills and The Jaintia Hills, named after the tribal groups inhabiting this region.
- An extension of this is also seen in the Karbi Anglong hills of Assam.
- Similar to the Chotanagpur plateau, the Meghalaya plateau is also rich in mineral resources like coal, iron ore, sillimanite, limestone and uranium.
- This area receives maximum rainfall from the south west monsoon. As a result, the Meghalaya plateau has a highly eroded surface.
- Cherrapunji displays a bare rocky surface devoid of any permanent vegetation cover.
The Indian Desert
- To the northwest of the Aravali hills lies the Great Indian desert. It is a land of undulating topography dotted with longitudinal dunes and barchans.
- This region receives low rainfall below 150 mm per year; hence, it has arid climate with low vegetation cover.
- It is because of these characteristic features that this is also known as Marusthali.
- It is believed that during the Mesozoic era, this region was under the sea. This can be corroborated by the evidence available at wood fossils park at Aakal and marine deposits around Brahmsar, near Jaisalmer.
- Some of the well pronounced desert land features present here are mushroom rocks, shifting dunes and oasis (mostly in its southern part).
- Most of the rivers in this region are ephemeral. The Luni river flowing in the southern part of the desert is of some significance.
- Low precipitation and high evaporation makes it a water deficit region.
- There are some streams which disappear after flowing for some distance and present a typical case of inland drainage by joining a lake or playa.
- The lakes and the playas have brackish water which is the main source of obtaining salt.
The Coastal Plains
- On the basis of the location and active geomorphological processes, it can be broadly divided into two:
- the western coastal plains;
- the eastern coastal plains.
- The western coastal plains are an example of submerged coastal plain.
- It is believed that the city of Dwaraka which was once a part of the Indian mainland situated along the west coast is submerged under water.
- Because of this submergence it is a narrow belt and provides natural conditions for the development of ports and harbours.
- Kandia, Ma'zagaon, JLN port Navha Sheva, Marmagao, Mangalore, Cochin, etc. are some of the important natural ports located along the west coast.
- The western coastal plains are narrow in the middle and get broader towards north and south.
- The rivers flowing through this coastal plain do not form any delta. The Malabar coast has got certain distinguishing features in the form of 'Kayals' (backwaters), which are used for fishing, inland navigation and also due to its special attraction for; tourists.
- Every year the famous Nehru Trophy Vallamkali (boat race) is held in Punnamada Kayal in Kerala.
- As compared to the western coastal plain, the eastern coastal plain is broader and is an example of an emergent coast.
- There are well developed deltas here, formed by the rivers flowing eastward in to the Bay of Bengal.
- These include the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri. Because of its emergent nature, it has less number of ports and harbours.
- The continental shelf extends up to 500 km into the sea, which makes it difficult for the development of good ports and harbours.
The Islands
- There are two major island groups in India - one in the Bay of Bengal and the other in the Arabian Sea. The Bay of Bengal island groups consist of about 572 islands/ islets.
- The two principal groups of islets include the Ritchie's archipelago and the Labrynth island.
- The entire group of island is divided into two broad categories - the Andaman in the north and the Nicobar in the south.
- They are separated by a water body which is called the Ten degree channel.
- It is believed that these islands are an elevated portion of submarine mountains.
- However, some smaller islands are volcanic in origin. Barren island, the only active volcano in India is also situated in the Nicobar islands.
- Some important mountain peaks in Andaman and Nicobar islands are Saddle peak (North Andaman - 738 m), Mount Diavolo (Middle Andaman - 515 m), Mount Koyob (South Andaman - 460 m) and Mount Thuiller (Great Nicobar - 642 m).
- The coastal line has some coral deposits, and beautiful beaches. These islands receive convectional rainfall and have an equatorial type of vegetation.
- The islands of the Arabian sea include Lakshadweep and Minicoy.
- The entire island group is built of coral deposits. There are approximately 36 islands of which 11 are inhabited. Minicoy is the largest island with an area of 453 sq.km.
- The entire group of islands is broadly divided by the Eleventh degree channel, north of which is the Amini Island and to the south of the Canannore Island.
- The Islands of this archipelago have storm beaches consisting of unconsolidated pebbles, shingles, cobbles and boulders on the eastern seaboard.
Some Important Facts
- India is a vast country with varied landforms.
- In fact, our country has practically all major physical features of the earth i.e. mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus and islands.
- We find different types of rocks; some are very hard like marble which has been used for making the Taj Mahal, and some are very soft like soap stone which is used in making talcum powder.
- The colour of soil varies from one place to the other because soil is formed out of different types of rocks.
- India is a large landmass formed during different geological periods which has influenced her relief. Besides geological formations, a number of processes such as weathering, erosion and deposition have created and modified the relief to its present form.
- Earth scientists have attempted to explain the formation of physical features with the help of some theories based on certain evidences. One such plausible theory is the "Theory of Plate Tectonics".
- According to this theory, the crust (upper part) of the earth has been formed out of seven major and some minor plates.
- The movement of the plates results in the building up of stresses within the plates and the continental rocks above, leading to folding, faulting and volcanic activity. Broadly, these plate movements are classified into three types.
- While some plates come towards each other and form convergent boundary. Some plates move away from each other and form divergent boundary.
- In the event of two plates coming together they may either collide and crumble, or one may slide under the other. At times, they may also move horizontally past each other and form transform boundary.
- The movement of these plates have changed the position and size of the continents over millions of years. Such movements have also influenced the evolution of the present landform features of India.
- Most volcanoes and earthquakes in the world are located at plate margins, but some do occur within the plates.
- The oldest landmass, (the Peninsula part), was a part of the Gondwana land. The Gondwana land included India, Australia, South Africa, South America and Antarctica as one single land mass.
- The convectional currents split the crust into a number of pieces, thus leading to the drifting of the Indo-Australian plate after being separated from the Gondwana land, towards north.
- The northward drift resulted in the collision of the plate with the much larger Eurasian Plate.
- Due to this collision, the sedimentary rocks which were accumulated in the geosyncline known as the Tethys were folded to form the mountain system of western Asia and Himalaya.
- Gondwana land: It is the southern part of the ancient super continent Pangea with Angara Land in the northern part.
- The Himalayan uplift out of the Tethys sea and subsidence of the northern flank of the peninsular plateau resulted, in the formation of a large basin.
- In due course of time this depression, gradually got filled with deposition of sediments by the rivers flowing from the mountains in the north and the peninsular plateau in the south.
- A flat land of extensive alluvial deposits led to the formation of the northern plains of India.
- The land of India displays great physical variation. Geologically, the Peninsular Plateau constitutes one of the ancient landmasses on the earth's surface.
- It was supposed to be one of the most stable land blocks.
- The Himalayas and the Northern Plains are the most recent landforms.
- From the view point of geology, Himalayan mountains form an unstable zone. The whole mountain system of Himalaya represents a very youthful topography with high peaks, deep valleys and fast flowing rivers.
- The northern plains are formed of alluvial deposits. The peninsular plateau is composed of igneous and metamorphic rocks with gently rising hills and wide valleys.
- The latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India are roughly about 30 degrees, whereas the actual distance measured from north to south extremity is 3,214 km, and that from east to west is only 2,933 km.
- This difference is based on the fact that the distance between two longitudes decreases towards the poles whereas the distance between two latitudes remains the same everywhere.
- From the values of latitude, it is understood that the southern part of the country lies within the tropics and the northern part lies in the sub-tropical zone or the warm temperate zone.
- This location is responsible for large variations in land forms, climate, soil types and natural vegetation in the country.
- There is a general understanding among the countries of the world to select the standard meridian in multiples of 7°30' of longitude.
- That is why 82°30'E has been selected as the 'standard meridian' of India.
- Indian Standard Time is ahead of Greenwich Mean Time by 5 hours and 30 minutes.
- There are some countries where there are more than one standard meridian due to their vast east-to-west extent. For example, the USA has seven time zones.
- Peninsular part of India extends towards the Indian Ocean.
- This has provided the country with a coastline of 6,100 km in the mainland and 7,517 km in the entire geographical coast of the mainland plus the island groups Andaman and Nicobar located in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea.
- Statute mile = 63,360 inches
- Nautical mile = 72,960 inches
- 1 Statute mile = about 1.6 km (1.584 km)
- 1 Nautical mile = about 1.8 km (1.852 km)
Seven Largest Countries of the world


