-
question_answer1)
If \[f(x)=0\]is a quadratic equation such that \[f(-\pi )=f(\pi )=0\]and \[f\left( \frac{\pi }{2} \right)=-\frac{3{{\pi }^{2}}}{4}\], then \[\underset{x\to -\pi }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{f(x)}{\sin (sinx)}\]is equal to
A)
0 done
clear
B)
\[\pi \] done
clear
C)
\[2\pi \] done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
\[\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{1}{x}{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \frac{1-{{x}^{2}}}{1+{{x}^{2}}} \right)\]is equal to
A)
1 done
clear
B)
0 done
clear
C)
2 done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
The value of \[\underset{x\to 2}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\sqrt{1+\sqrt{2+x}}-\sqrt{3}}{x-2}\] is
A)
\[\frac{1}{8\sqrt{3}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{4\sqrt{3}}\] done
clear
C)
0 done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
If \[\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left\{ \frac{{{x}^{3}}+1}{{{x}^{2}}+1}-(ax+b) \right\}=2\], then
A)
\[a=1,\text{ }b=1\] done
clear
B)
\[a=1,\text{ }b=2\] done
clear
C)
\[a=1,\text{ }v=-2\] done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer5)
\[\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\sum\limits_{x=1}^{20}{{{\cos }^{2n}}(x-10)}\]is equal to
A)
0 done
clear
B)
1 done
clear
C)
19 done
clear
D)
20 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
The value of \[\underset{m\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{\left( \cos \frac{x}{m} \right)}^{m}}\]is
A)
1 done
clear
B)
\[e\] done
clear
C)
\[{{e}^{-1}}\] done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer7)
The value of \[\underset{x\to 2}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{2}^{x}}+{{2}^{3-x}}-6}{\sqrt{{{2}^{-x}}}-{{2}^{1-x}}}\]is
A)
16 done
clear
B)
8 done
clear
C)
4 done
clear
D)
2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
\[\underset{n\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{\left( \frac{{{n}^{2}}-n+1}{{{n}^{2}}-n-1} \right)}^{n(n-1)}}\]is equal to
A)
\[e\] done
clear
B)
\[{{e}^{2}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{e}^{-1}}\] done
clear
D)
1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer9)
\[\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\sin ({{x}^{2}})}{in(cos(2{{x}^{2}}-x))}\]is equal to
A)
2 done
clear
B)
-2 done
clear
C)
1 done
clear
D)
-1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
\[\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,{{\left( \frac{{{x}^{2}}+5x+3}{{{x}^{2}}+x+3} \right)}^{1/x}}\]is equal to
A)
\[{{e}^{4}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{e}^{2}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{e}^{3}}\] done
clear
D)
1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
If \[y={{x}^{({{x}^{x}})}}\], then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]is
A)
\[y\left[ {{x}^{x}}(logex)logx+{{x}^{x}} \right]\] done
clear
B)
\[y\left[ {{x}^{x}}(logex)logx+x \right]\] done
clear
C)
\[y\left[ {{x}^{x}}(logex)logx+{{x}^{x-1}} \right]\] done
clear
D)
\[y\left[ {{x}^{x}}(lo{{g}_{e}}x)logx+{{x}^{x-1}} \right]\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer12)
If \[y={{\left( x+\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}} \right)}^{n}}\], then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]is
A)
\[\frac{ny}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[-\frac{ny}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{nx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[-\frac{nx}{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
If \[y=1+x+\frac{{{x}^{2}}}{2!}+\frac{{{x}^{3}}}{3!}+...+\frac{{{x}^{n}}}{n!}\], then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]is equal to
A)
y done
clear
B)
\[y+\frac{{{x}^{n}}}{n!}\] done
clear
C)
\[y-\frac{{{x}^{n}}}{n!}\] done
clear
D)
\[y-1-\frac{{{x}^{n}}}{n!}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
If \[y=\sqrt{\log x+\sqrt{\log x+\sqrt{\log x+...\infty },}}\]then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]is
A)
\[\frac{x}{2y-1}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{x}{2y+1}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{x(2y-1)}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{1}{x(1-2y)}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
If \[y=a{{e}^{mx}}+b{{e}^{-mx}}\], then \[\frac{{{d}^{2}}y}{d{{x}^{2}}}-{{m}^{2}}y\]is equal to
A)
\[{{m}^{2}}(a{{e}^{mx}}-b{{e}^{-mx}})\] done
clear
B)
1 done
clear
C)
0 done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
If \[y={{\tan }^{-1}}\sqrt{\frac{x+1}{x-1}}\]. Then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]is
A)
\[\frac{-1}{2\left| x \right|\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{-1}{2x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{2x\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}\] done
clear
D)
none of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
If
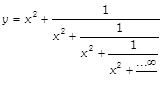
then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] is
A)
\[\frac{2xy}{2y-{{x}^{2}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{xy}{y+{{x}^{2}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{xy}{y-{{x}^{2}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2xy}{2+{{\frac{x}{y}}^{2}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer18)
If \[\sqrt{1-{{x}^{2}}}+\sqrt{1-{{y}^{2}}}=a(x-y)\], then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\]=
A)
\[\sqrt{\frac{1-{{x}^{2}}}{1-{{y}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\sqrt{\frac{1-{{y}^{2}}}{1-{{x}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\sqrt{\frac{{{x}^{2}}-1}{1-{{y}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\sqrt{\frac{{{y}^{2}}-1}{1-{{x}^{2}}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer19)
Let y be an implicit function of x defined by \[{{x}^{2x}}-2{{x}^{x}}\cot y-1=0\]. Then y'(1) equals
A)
-1 done
clear
B)
1 done
clear
C)
\[log\text{ }2\] done
clear
D)
\[-log\text{ }2\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer20)
If \[{{x}^{m}}{{y}^{n}}={{(x+y)}^{m+n}}\], then \[dy/dx\]is equal to
A)
\[\frac{y}{x}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{x+y}{xy}\] done
clear
C)
\[xy\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{x}{y}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
If\[f(x)=\frac{2}{x-3},g(x)=\frac{x-3}{x+4},\]and\[h(x)=-\frac{2(2x+1)}{{{x}^{2}}+x-12}\], then \[\underset{x\to 3}{\mathop{\lim }}\,[f(x)+g(x)+h(x)]\]is __________.
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
\[\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{(1-cos2x)(3+cosx)}{x\tan 4x}\] is equal to _________.
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
if\[f(0)=0,f'(0)=2\], then the derivative of
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
Suppose the function \[f(x)-f(2x)\]has the derivative 5 at x=1 and derivative 7 at x = 2. The derivative of the function \[f(x)-f(4x)\]at x=1has the value equal to __________.
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
If \[f(x+y)=f(x)f(y)\forall x,y\]and\[f(5)=2,f'(0)=3\], then f'(5) is equal to _______.
View Solution play_arrow
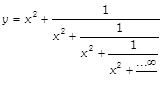 then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] is
then \[\frac{dy}{dx}\] is 