Answer:
(i)
Electrophoresis.
The particles of the colloidal solutions possess electrical charge, positive or
negative while the dispersion medium has no charge.
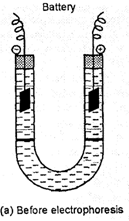
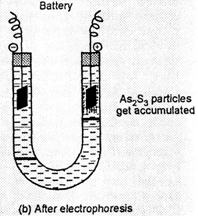 The presence of the
charge on the sol particles and its nature can be determined with the help of a
phenomenon known as electrophoresis in which colloidal particles move towards
oppositely charged electrodes under the influence electrical field. The
phenomenon of movement colloidal particles under the influence of applied
electric field is called electrophoresis.
For example, the
solutions of gold, arsenioussulphide (As2S3) are
negatively charged and the particles move towards the positive electrode while
those of Fe(OH)3,AI(OH)3 have positive charge and the
particles move towards negative electrode.
(ii) Coagulation. The phenomenon of
the precipitation of a colloidal solution by the addition of the excess of an
electrolyte is called coagulation or flocculation.
Mechanism of
coagulation. The
particles of the dispersed phase i.e., colloids bear some charge. When an
electrolyte is added to the sol, the colloidal particles take up ions carrying
opposite charge from the electrolyte. As a result, their charge gets
neutralised and this causes the uncharged particles to come closer and to get
coagulated or precipitated. For example, if BaCl2 solution is added
to As2S3 sol, the Ba2+ ions are attracted by
the negatively charged sol particles and their charge gets neutralised. This
leads to coagulation.
(iii) Dialysis. It is based on the
principle that impurities can pass through the parchment membrane while
colloidal particle cannot. The apparatus used is known as dialyser. The
impurities pass out through the membrane giving pure colloidal solution.
This process is slow
and time consuming. Thus, to fasten the process, an electric field is applied
and the process is known as Electrodialysis.
(iv) When a beam of
light is passed through a colloidal solution, the path becomes illuminated by a
bluish light when seen with a microscope at right angle to the path of light.
This effect is called Tyndall effect and the illuminated path is called Tyndall
cone.
The presence of the
charge on the sol particles and its nature can be determined with the help of a
phenomenon known as electrophoresis in which colloidal particles move towards
oppositely charged electrodes under the influence electrical field. The
phenomenon of movement colloidal particles under the influence of applied
electric field is called electrophoresis.
For example, the
solutions of gold, arsenioussulphide (As2S3) are
negatively charged and the particles move towards the positive electrode while
those of Fe(OH)3,AI(OH)3 have positive charge and the
particles move towards negative electrode.
(ii) Coagulation. The phenomenon of
the precipitation of a colloidal solution by the addition of the excess of an
electrolyte is called coagulation or flocculation.
Mechanism of
coagulation. The
particles of the dispersed phase i.e., colloids bear some charge. When an
electrolyte is added to the sol, the colloidal particles take up ions carrying
opposite charge from the electrolyte. As a result, their charge gets
neutralised and this causes the uncharged particles to come closer and to get
coagulated or precipitated. For example, if BaCl2 solution is added
to As2S3 sol, the Ba2+ ions are attracted by
the negatively charged sol particles and their charge gets neutralised. This
leads to coagulation.
(iii) Dialysis. It is based on the
principle that impurities can pass through the parchment membrane while
colloidal particle cannot. The apparatus used is known as dialyser. The
impurities pass out through the membrane giving pure colloidal solution.
This process is slow
and time consuming. Thus, to fasten the process, an electric field is applied
and the process is known as Electrodialysis.
(iv) When a beam of
light is passed through a colloidal solution, the path becomes illuminated by a
bluish light when seen with a microscope at right angle to the path of light.
This effect is called Tyndall effect and the illuminated path is called Tyndall
cone.
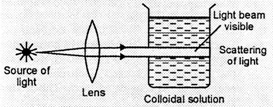 Cause. The colloidal
particle first absorb light energy and become self luminous. Then a part of
light energy is scattered from their surface. Tyndall effect is due to the
scattering of light by the colloidal particles and the colloidal particles are
seen to be moving as points of light moving against dark background.
Cause. The colloidal
particle first absorb light energy and become self luminous. Then a part of
light energy is scattered from their surface. Tyndall effect is due to the
scattering of light by the colloidal particles and the colloidal particles are
seen to be moving as points of light moving against dark background.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
