PRONOUN
Category : 3rd Class
Rea Life Example
Knowledge of subject and predicate will help you to understand grammar?s other parts of speech better.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Generally, pronouns stand for (pro + noun) or refer to a noun, an individual or individuals or thing whose identity is made clear earlier in the sentence.
Pronouns are the words which replace noun. For example
Paras and Amir ride the bus together to school. They also study together.
In the above sentence, "they" is a pronoun as it is used in place of individuals (Paras and Amir). Other examples can be she, it, he, someone, who etc. Here are some more examples.
Instead of: is a good athlete. She is a good athlete. (The pronoun she replaces Leena.)
Instead of: The beans and tomatoes are fresh-picked. They are fresh-picked. (The pronoun they replaces the beans and tomatoes.)
PRONOUN

TYPES OF PRPONOUN
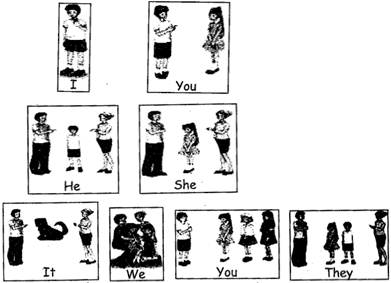
(a) Personal pronoun:
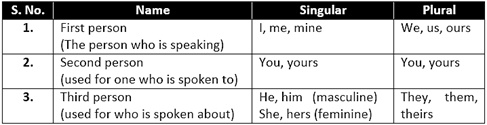
Remember
Use a pronoun instead of noun.
The pronoun you use must follow its noun in number and gender. Example:
Ram is going to market. He has to get mangoes.
(b) Reflexive pronouns: When we add 'self' or ?selves? personal pronoun they become Reflexive pronouns. 'Self' is added to 'my, your, her and him' and 'selves' to our, your and them'.
Example: You must do your homework yourself. They went together themselves.
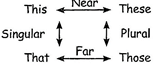
(c) Demonstrative pronouns: These point to the object they belong to. Example:
This is a book.
That is a calendar.
These are books.
Those are calendars.
Poem
I am hungry.
You are hungry.
He is hungry.
She is hungry.
We are hungry.
They are hungry.
Everybody is hungry.
I am thirsty.
You are thirsty.
He is thirsty.
She is thirsty.
We are thirsty.
They are thirsty.
Everybody is thirsty.
I am happy
You are happy.
He is happy.
She is happy.
We are happy.
They are happy.
Everybody is happy.
(d) Interrogative pronouns: To ask questions, the words who, what which, whose, whom' are used/All of them are Interrogative Pronouns. It is used to begin a question, "who, whom, whose' are used for persons, which' is used for persons as well as things. 'What' is used only for things.
Examples:
Who are you?
What is your name?
Which is your book?
Whom does this glass belong to?
The other way to classify pronouns is:
Example: He spends ages looking out the window. After lunch, she and I went to the planetarium.
Example: Tara gave me a trombone.
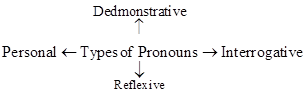

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
