CHAPTER-8 ENERGY RESOURCES
Energy is the capacity to do work and is required for life processes. Energy is the fundamental resource for the development and the progress of any region. Energy consumption and development are synonymous. If any state is rich in energy resources, it has direct impact on industrial development, economic development and standard of living.
An energy resource is something that can produce heat, power, move objects, or produce electricity. Energy resources are all forms of fuels used in the modem world, either for heating, generation of electrical energy, or for other forms of energy conversion processes.
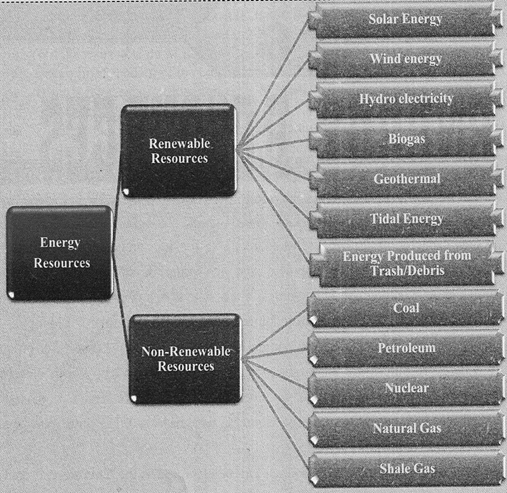
On the basis of generation, energy sources can be classified into two types:
Nonrenewable and Renewable.
On the basis of the uses the energy sources can be classified as the Commercial energy and Noncommercial energy.
Nonrenewable resources
Non-renewable energy is a source of energy that will eventually run out, such as fossil fuels and nuclear material. These resources have been the most used type of energy in the modem era. These are also known as conventional sources of Energy.
Renewable resources
Renewable energy is energy produced from sources that do not deplete or can be replenished within a human's life time such as wind, water, solar, and geothermal, come from sources that regenerate as fast as they are consumed and are continuously available. Such as biofuel produced from food crops and other plants, are replenished every growing season. In the early part of the twenty-first century, renewable sources have become more popular as nonrenewable sources have begun to be depleted. These are also known as Non- conventional sources of energy.
Commercial energy
The energy sources that are used to generate electricity and that are available in the marketplace with a specific price are known as Commercial energy sources. The most commercialized forms of energy sources are electricity, coal, advanced petroleum products and nuclear energy etc.
Non-commercial energy
Non-commercial energy sources, which include fuels such as cattle dung and agricultural and urban waste, are conventionally gathered and not bought at a price used particularly in rural areas. These are also called Traditional fuels and are often ignored in energy accounting.
Energy Resources in Madhya Pradesh
There are various conventional sources of energy in Madhya Pradesh which are coal, oil and mineral oil, natural gas, atomic energy. Non-conventional sources of energy are solar energy, wind energy etc. The two main sources of energy in Madhya Pradesh are coal and Hydel power. The reorganization of state has affected its electricity production drastically.
Conventional Sources of Energy in MP
Some important conventional energy sources are discussed below-

1. Coal
- Coal is a major conventional energy sources. It was formed from me remains of the trees and ferns grew in swamps around 500 millions year ago.
- The coal reserves are found in the states like Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Orissa, west Bengal, M.P. and Andhra Pradesh. Some important coal fields are: Talcher, Raniganj, Jharia, Bokaro, Pench - Kanhan, Singrouli, Chanda etc.
- Madhya Pradesh has 20.55 billion tonnes of coal which accounts around 7-8% coal of total coal reserve in India. Major producing areas are Sohagpur (Shahdol), Umaria, Singrauli. (Singrauli is also known as energy capital of Madhya Pradesh).
2. Petroleum and Natural Gases
- The most commonly seen energy resource of these days is petroleum and its various products. It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, mostly alkanes and cycle alkanes. It occurs naturally below the earth crust.
- The composition of Natural gas is a mixture of mainly methane, (95.0%); small amounts of ethane, propane and butane (3.6%) and traces of CO2 (0.48%) and N2 (1.92%).
3. Hydropower
- Energy obtained from water flow or water falling from a higher potential to lower potential, is known is hydro-power. In this the potential energy is converted into electrical energy. It is a conventional and renewable form of energy which can be transmitted to long distance trough cables and wires.
- Madhya Pradesh generates substantial amount of hydropower from projects like Chambal multipurpose project. Ban Sagar project, major projects on Narmada River etc.
4. Thermal Energy
- Thermal Power is the most important sources of energy for Madhya Pradesh. The main thermal power plants are located in the main coal producing regions so as to reduce the cost of Transportation. The main thermal power plants of Madhya Pradesh are Shri Singaji TPS Dongalia, Chandani Thermal power centre, Jabalpur thermal power plant, Sanjay Gandhi Birsinghpur, Amarkantak thermal power plant and Satpura thermal power plant.
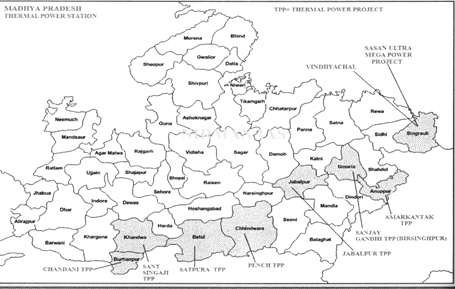
Coal Based Power Plants in MP
- Chandni Thermal Power plant (Captive power plant)
- It was set up in 1953.
- Its initial capacity was 17MW which now increased to 177 MW.
- Pathar Kheda coal fields supplies coal to this plant.
- This plant Supplies power to Nepanagar paper mill of Burhanpur.
- Amarkantak Thermal Power Plant
- Amarkantak Thermal Power Plant is located at Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh, India.
- The First unit of the Plant came to existence in March 1977.
- This Thermal Power Plant is coal based and owned by MPPGCL.
- This Thermal Power station has a power generating capacity of 450.00 MW.
- Satpura Thermal Power Plant
- Thermal Power Plant is situated in Sami village which is close to the Ghora Dongri Railway station, Betui district in Madhya Pradesh.
- This efficient thermal Power station in Madhya Pradesh is a coal based plant under the ownership of MPPGCL.
- The Plants has an installed capacity of 1330 MW.
- This is a joint initiative of MP and Rajasthan.
- Plant is established with the financial help given by USA.
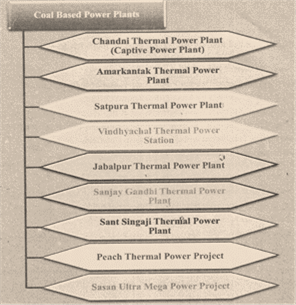
- Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station
- The Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station is located in Singrauli district in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- It was established in year 1987 with the financial help of Soviet Union.
- It is one of the largest coal-fired power stations of NTPC.
- It has an installed capacity of 4,760 MW.
- The coal for the power plant is sourced from Nigahi mines, and the water is sourced from the discharge canal of Singrauli Super Thermal Power Station.
- Jabalpur Thermal Power Plant
- It was set up in Jabalpur by MP Electricity Board in 1960.
- Uses coal of Jabalpur Coal field & Water of Narmada River.
- Its total capacity is 15 MW.
- Sanjay Gandhi Thermal Power plant
- This Power Plant was set up in 1993 in Birsinghpur (District Umaria).
- It uses the coal of Johila coal field.
- Water is supplied from the dam constructed on Johila River
- Its total capacity is now 1340 MW.
- Sant Singaji Thermal Power Plant
- Shree Singaji Super Thermal Power Project is a coal-fired power plant located near Dongaliya village near by Mundi of Khandwa District.
- First phase of the plant was constructed in 2014.
- The water required is taken from Indira Sagar Reservoir on Narmada River.
- Coal linkage is achieved with South Eastern Coalfields Limited
- Power generation capacity-1200 MW.
- Pench Thermal Power Project
- It is located in Chhindwara.
- It was set up in year 2012.
- Coal linkage is achieved from Pench valley coal fields.
- Water required is taken from dam constructed on Pench River.
- It has a capacity of 1320 MW.
- Sasan Ultra Mega Power project
- It is located in Sasan village of Singrauli, Madhya Pradesh.
- Sasan UMPP is among the world's largest integrated power generation and coal mine project with 3,960 MW Power Plant and 20 MT per year coal mining capacity.
- It is presently the 4th largest electricity generation power plant in India.
- The plant is operated by Sasan Power Limited, a subsidiary of Reliance Power Limited
Gas Based Power plants
- Gas based power plant was first constructed in 1992 in the Bhander(Datia) in Madhya Pradesh. However its effective operation was started by the Essar Company in 1994 .This project has the generating capacity of 342 MW. Gas is supplied from Hazira-Vijaypur- Jagdishpur gas pipeline.
- Reliance Industries has established a Gas based power plant in Shahdol district.
- GAIL India is establishing 380MW gas based power plant in Vijaypur in Guna district.
Nuclear Energy
Energy derived from nuclear reactions is known as Nuclear energy. There are two types of nuclear reactions viz. Fission and Fusion. A small amount of radioactive substance (U235) can produce a vast amount of energy through the process of nuclear fission. The nuclear energy can be used in production of electrical energy, as a fuel for marine vessel and space crafts and for the generation of heat in chemical processing plants.
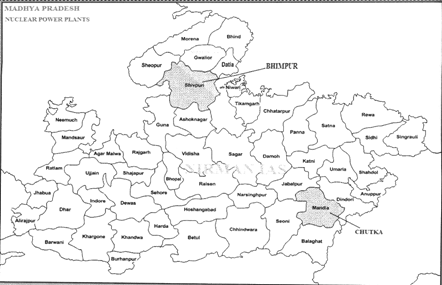
Nuclear power plants in MP
- Chutka Nuclear Power plant
- The Chutka Nuclear Power Plant is a proposed nuclear power plant to be built on a 1,200 acres (490 ha) area, near Chutka Village of Mandla district.
- The site is near Kanha National Park, one of the tiger reserves of India and the largest national park of Madhya Pradesh state in India.
- The project will have an installed capacity of 1400 Megawatt.
- Bhimpur Nuclear Power plans
- Bhimpur Nuclear Power plant is under construction in Bhimpur village in Shivpuri district
- The project will have an installed capacity of 2800 Megawatt.
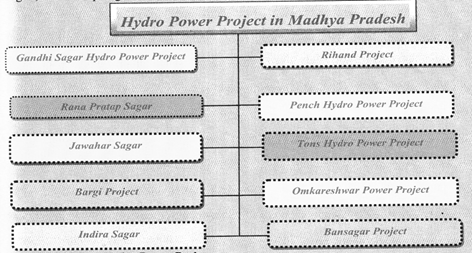
Hydro Power Project in Madhya Pradesh
Hydro-electric Power is one of the cleanest and most viable renewable sources of energy. Madhya Pradesh government has been constantly promoting setting up of non-conventional power plants, including hydro, through various policies, incentives and special agencies, made for this purpose. Madhya Pradesh has ideal conditions for constructing dam projects,
particularly in the western part where many perennial rives originate and flow.
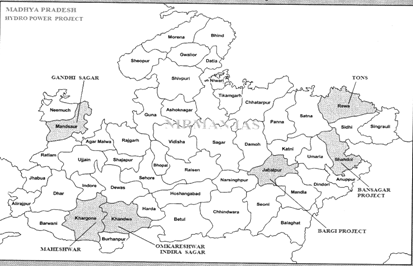
Some of the important hydropower projects are Kota or Jawaharsagar, Bargi project, Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar and Ban Sagar project.
- Gandhi Sagar Hydro Power Project
- Gandhi Sagar Hydropower plant is constructed on Chambal River in Mandsaur District (Tehsil Bhanpura).
- 5 units with capacity of 23,000 KW are set up under the project.
- Total Capacity is 115 MW.
- MP and Rajasthan Shares power in the ratio of 50:50.
- Rana Pratap Sagar
- Constructed in Rawatbhata (Chittorgarh) on Chambal River.
- Its production capacity is 172 MW.
- MP & Rajasthan Shares the power equally.
- Jawahar Sagar
- This dam is 32 km away from Rana Pratap Sagar Dam.
- Three units have been placed for power production.
- Total capacity is 99 MW.
- MP receives 45.9 MW Electricity from it.
- MP & Rajasthan Equally Shares the power.
- All above projects have been set up under the Chambal valley project during second five year plan as joint projects of Madhya Pradesh & Rajasthan.
- Bargi Project
- This project is also known as Avantibai sagar Project.
- Situated in Bijora village, Jabalpur on the Narmada River.
- Total Capacity: 90MW
- Rihand Project
- Located in Pipri Sonbhadra district (U .P.)
- It is a joint project of UP &MP.
- Total Capacity: 300MW
- Pench Hydro Power Project
- Located in Nagpur district.
- Joint Project of MP& Maharastra.
- Total Capacity: 160 MW.
- Out of which 107 MW goes to MP & rest utilized by Maharashtra.
- Situated in Rewa district on river Tons,
- Total capacity: 315 MW.
- Located in Maheshwar in Khargone district on river Narmada.
- Started working in 1994
- Total capacity of 400 MW.
- Omkareshwar power project
- Located in Khandwa district on Narmada River.
- This project has total capacity of 520 MW.
- Started production in 2007.
- Indira Sagar
- Set up on river Narmada in Punasa in Khandwa district.
- This project has a total capacity of 1000 MW.
- Started production in 2007.
- Bansagar Project
- Set up in year 1994-95, on River Son in Shahdol district.
- Joint project of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh & Bihar.
- Total Capacity 425MW
- Power generation started in 2008.
Importance of Hydropower in Economic Development of Madhya Pradesh
- Hydropower is fueled by water, so it's a clean fuel source, meaning it won't pollute the air like power plants that burn fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas.
- Hydroelectric power is a domestic source of energy, allowing each state to produce their own energy without being reliant on international fuel sources.
- The energy generated through hydropower relies on the water cycle, which is driven by the sun, making it a renewable power source, making it a more reliable and affordable source than fossil fuels that are rapidly being depleted.
- Impoundment hydropower creates reservoirs that offer a variety of recreational opportunities, notably fishing, swimming, and boating. Most water power installations are required to provide some public access to the reservoir to allow the public to take advantage of these opportunities.
- Some hydropower facilities can quickly go from zero power to maximum output. Because hydropower plants can generate power to the grid immediately, they provide essential back-up power during major electricity outages or disruptions.
- In addition to a sustainable fuel source, hydropower efforts produce a'number of benefits, such as flood control, irrigation, and water supply.
Non-Conventional Energy in Madhya Pradesh
- Energy is a prime mover of the development of any economy. While conventional fuels like coal and oil have been the primary sources for energy, their long term availability has been an area of concern. Further, their increased usage has led to high concentrations of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the atmosphere, which is a growing concern with regard to global warming and resultant climate changes.
- Efforts are being constantly made in Madhya Pradesh to produce energy from alternative sources of renewable energy along with conventional energy production. New innovations are also being made in this field.
- Madhya Pradesh government constituted a Separate Department of New and renewable Energy in April 2010-Separate policies have been formulated for implementation of small Hydel energy, wind energy, bio-mass energy and solar energy.
Wind Energy
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh has been promoting the setting up of Renewable Energy based power plants including wind through various policy initiatives and incentives for the investors/developers.
- Wind energy is an economically effective and pollution free source of energy.
- Wind mills have been established in the Indore, Ratlam, Dewas, Mandsaur, Rajgarh and Agar-Malwa districts.
- In the year 1995 windmills were established in the Jamgodrani hills of Dewas.
- MP's largest wind energy project has been established at Matakheda in Ratlam district.
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh has issued the Incentive Policy for encouraging generation of power in Madhya Pradesh through Non-conventional Energy Sources (2006). The policy provides incentives for installation of wind power projects in Madhya Pradesh.
- Madhya Pradesh houses the seventh largest installed wind power generation capacity in the country. The state's wind capacity at the end of 2018 stood at 2,520 MW.
Suitability of Wind Energy in Madhya Pradesh
- The ideal speed of wind for wind energy should be 8 meters per second to 23 meters per second. In Madhya Pradesh, the average wind speed is around 10 meters per second, so suitable conditions for wind energy production exist in the state.
- The maximum area of ideal wind speed is located at high and plateau parts, which leads to greater compatibility in setting up wind power plants.
- In areas with ideal wind speeds, there is sufficient amount of unusable land for windmills.
- Locally, wind energy is a better option for remote areas in Madhya Pradesh. Because it is completely pollution-free and renewable.
- Madhya Pradesh is a developing state, so there is a need for cheap and environment friendly energy.
Wind Energy Sites
|
S.No.
|
Site
|
District
|
|
1.
|
Jamgodrani
|
Dewas
|
|
2.
|
Kukru
|
Betul
|
|
3.
|
Mahuriya
|
Shajapur
|
|
4.
|
Mamatkheda
|
Ratlam
|
|
5.
|
Negda
|
Ujjain
|
|
6.
|
Sendhwa
|
Barwani
|
|
|
Bariyalpani
|
Barwani
|
Wind power project policy
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh has been promoting the setting up of Renewable Energy based power plants including wind through various policy initiatives and incentives for the investors/developers.
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh has issued the Incentive Policy for encouraging generation of power in Madhya Pradesh through Non-conventional Energy Sources.
- The policy provides incentives for installation of wind power projects in Madhya Pradesh.
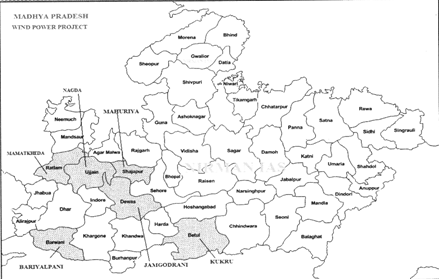
- Wind power project proposal are being accepted at potential sites where wind power Density (WPD) is equal or above 200 W7m2 above 50 Metres ground level.
Solar Energy
- Madhya Pradesh receives a high solar radiation of more than 5.5 kWh per square Metres per day with around 300 days of clear sun.
- In 2012, the state came out with its solar policy to avail the open access facility for selling power to third-party consumers or captive power users.
- Owing to the availability of solar energy and a favourable policy environment, the state saw a rapid addition in its solar capacity.
- Madhya Pradesh houses the seventh-largest installed solar power generation capacity in the country. The state's solar capacity at the end of 2018 stood at 1,526 MW.
- With the Participation of Private sector in solar power generation Government is aspiring to create new milestones in the field of Solar Energy.
Efforts taken by State Government to promote Solar Energy
The state would take appropriate steps to set up solar parks to promote investment in solar power generation in the state either on its own or through a PPP mode. Solar technology parks for generation and manufacturing units in equipment & related ancillaries for Solar systems shall be promoted and established at appropriate locations in
the state of Madhya Pradesh.
Solar Power park development policy is designed to promote setting up of large capacity solar power plants in a integrated approach. Projects of over 100 MW are to be setup under solar power parks.
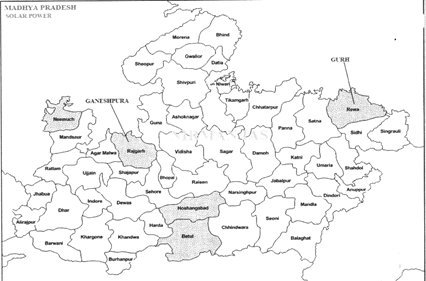
- The first solar Energy park being set up at Ganeshpura (Dist. Rajgarh), capacity: 100 KW
- The solar energy park in Bhopal has capacity of 10 KW.
- Almost 11 solar parks have been set up in Jhabua, Betui, Hoshangabad Rewa, Neemuch etc.
- Solar Photovoltaic Programme
- The energy Development corporation of Madhya Pradesh is also developing off- grid standalone solar photovoltaic power systems in the state.
- Under the Programme, solar power equipments are being installed at Government Buildings like police stations, health centers, Zila and janpad panchayats, educationalj institutions and all other public offices.
Rewa Ultra Mega Solar plant
- State's largest solar power plant (750 MW) to be set up in Gurh (District Rewa).
- Rewa Ultra Mega Solar is an operational solar park spread over an area of 1,590 acres (6.4 km2) in the Gurh tehsil of Rewa district of Madhya Pradesh. The project was commissioned with 750 MW Capacity in December 2019.
- Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Limited (RUMSL), the implementing agency of the project, is a joint venture between the Madhya Pradesh Urja Vikas Nigam Limited (MPUVNL) and the Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI).
- This plant is expected to reduce the country's emission drastically, by an amount equivalent to 15.7 lakh tonne of carbon dioxide annually.
- 76% of power generated from the project is being provided to the state power management company and 24% to Delhi Metro.
- Country's first project, which obtained loan from the World Bank for internal grid management under clean technology fund.
- Solar power projects of 5000 MW are under construction in Madhya Pradesh. RUMS, a company formed for the first Rewa solar project in the state, has started work on these projects that are to be set up in Agar, Shajapur, Neemuch, Chhatarpur, Omkareshwar and Morena.
- Work for setting up of solar parks for generation of 550 MW power at Agar, 450 MW at Shajapur, 500 MW at Neemuch, 1500 MW at Chhatarpur, 600 MW at me Omkareshwar floating Omkareshwar dam site and 1400 MW at Morena is in progress.
- Farmers are being encouraged to make maximum use of solar energy through solar pumps in the state. So far, solar pumps have been installed for 14250 farmers under the Mukhya Mantri Solar Pump Yojana. A target has been set to install 2 lakh solar pumps in the next three years.
So far, 30 MW solar rooftop plants have been installed in the state. Solar rooftops of 50 MW Capacity are proposed to be installed on 700 government buildings of the state this year. The rate obtained from the electricity generated from solar rooftop plants was Rs 1.38 paisa. The government is making efforts to install rooftop plants in every house so that electricity is available at low rates. Solar plants are being installed on government buildings on models, in which the beneficiary does not have to pay any money to the department or institution. The plant developer will make low cost electricity available.
Solar energy is being promoted for the industrial development of the state. Work is being done on 32 MW solar rooftop projects for 400 industrial units in Mandideep near Bhopal. This will pace up development in the industrial sector by providing low cost electricity to the industries. Promotion of solar energy is the need of the hour. Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has set a target of producing one lakh MW of renewable energy in the country. Madhya Pradesh is moving fast in this direction. Certainly Madhya Pradesh will have a significant contribution in solar energy generation and it will emerge as a major centre of the country.
- MP Solar energy Policy
- To encourage participation of Private Sector to set up Solar Power based projects in the State.
- To define the incentives and benefits to be provided to the participants of the Private Sector in clear terms.
- To build a favorable atmosphere for setting up Solar Power projects.
- Lay down framework for policy implementation.
- To encourage broader community involvement and growth of decentralizd Renewable Energy Systems.
- To reduce dependence on conventional sources of energy and reduce carbon emissions.
- To provide impetus to growth of clean technology in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- To reduce distribution losses of distribution licensees by decentralized generation.
- To improve tail-end grid voltages and reduce system congestion.
- To help the State achieve its RPO (Renewable Purchase Obligation).
- To develop sustainable energy solution for future, and help in achieving energy Security of the nation
Bio-Mass Energy
- Biomass has always been an important energy source for the country considering the benefits it offers. It is renewable, widely available, carbon-neutral and has the potential to provide significant employment in the rural areas.
- Biomass is also capable of providing firm energy. About 32% of the total primary energy use in the country is still derived from biomass and more than 70% of the county?s population depends upon it for its energy needs.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has realized the potential and role of biomass energy in the Indian context and hence has initiated a number of programmes for promotion of efficient technologies for its use in various sectors of the economy to ensure derivation of maximum benefits.
- For efficient utilization of biomass, bagasse based cogeneration in sugar mills and biomass power generation have been taken up under biomass power and cogeneration programme.
- Biomass power & cogeneration programme is implemented with the main objective of promoting technologies for optimum use of country's biomass resources for grid power generation. Biomass materials used for power generation include bagasse, rice husk, straw, cotton stalk, coconut shells, soya husk, de-oiled cakes, coffee waste, jute wastes,
- and groundnut shells, saw dust etc.
- The current availability of biomass in India is estimated at about 500 million metric tonnes per year. Studies sponsored by the Ministry has estimated surplus biomass availability at about 120-150 million metric tonnes per annum covering agricultural and forestry residues corresponding to a potential of about 18,000 MW. This apart, about 7000 MW additional power could be generated through bagasse based cogeneration in the country's 550 Sugar mills, if these sugar mills were to adopt technically and economically optimal levels of cogeneration for extracting power from the bagasse produced by them
- Technology
1. Bagasse based Co-generation
- In simple terms, cogeneration is the process of using a single fuel to produce more than one form of energy in sequence. Cogeneration of steam and electricity can significantly increase the overall efficiencies of fuel utilization in processindustries. A minimum condition for cogeneration is the simultaneous requirement of heat and electricity in a favourable ratio, which is well fulfilled in the sugar industry.
2. Biomass based Power Generation
- The technology for generation of electricity from these biomass materials is similar to the conventional coal-based thermal power generation. The biomass is burnt in boilers to generate steam, which drives a turbo alternator for generation of electricity.
3. Biomass Gasification
- Biomass gasification is Thermo-chemical conversion of solid biomass into a combustible gas mixture (producer gas) through a partial combustion route with air supply restricted to less than that theoretically required for full combustion. Typical composition of producer gas is
- Nitrogen (45%-55%), Carbon Monoxide (18%-20%), Hydrogen (15%-20%), Carbon dioxide (9%-12%), Methane (1%-5%). The calorific value of the producer gas is in the range of 1000-1200 kcal/m3.
- Efforts made by the Madhya Pradesh Government to promote Biomass energy
- Till December 2017 45.336MW Biomass energy projects have been established in Madhya Pradesh
- In Kheda of Dhar district 0.59MW rice husk based power project has been established.
- Bio-methanization project based on urban waste has been established in Bhopal and Indore.
- First biomass energy project has been established in Sami, second in Vidisha and third in Mudwara (Kami).
- In Bhadbhada veterinary department, Bhopal a 85m3 biogas plant has been established.
- Till now 21.80 thousand new domestic biogas projects have been established in Madhya Pradesh.
- Gau Samvardhan Scheme- Under this scheme biogas is to be used for cooking and in production of bio-fertilizers. Under this scheme high quality biogas plants with capacities between 25 to 85 m3 have been established.
Bio Gas
- Biogas is produced when bio-degradable organic materials/wastes such as cattle-dung, biomass from farms, gardens, kitchens, industry, poultry droppings, night soil and municipals wastes are subjected to a scientific process, called Anaerobic Digestion (A.D.) in a Biogas Plants.
- Biogas Plant designs depend upon several factors and the feed stock to be processed is of paramount importance.
- Biogas is the mixture of gases (primarily methane (CH4) and Carbon di-oxide (CO2) and traces of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S), Moisture) produced by the decomposition/breakdown of bio-degradable organic matter in the absence of oxygen from raw materials such as agricultural waste, cattle dung, poultry droppings, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste or food/kitchen waste.
- Biogas has a calorific value of about 5000 kcal per m3.
- The digested slurry produced from Biogas Plants as a by-product is a better source of nutrient enriched organic manure for use in Agriculture. It not only helps in improving the crop yield but also maintain soil health.
- Bio Gas potential in India
- There is ample potential of setting up biogas plants considering the livestock population of 512.06 million, which includes about 300 million (299.98 million) total population of bovines (comprising of cattle, buffalo, mithun and yak). The livestock sector contributes about significantly to India's GDP and will continue to increase. The dissemination of biogas technology is a boon for Indian farmers with its direct and collateral benefits.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy promotes installation of biogas plants by implementing two Central Sector Schemes under Off-Grid/distributed and decentralized Renewable Power. The two ongoing schemes are:
- New National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme (NNBOMP), for Biogas Plant size ranging from 1 cu.m. to25 cu.m. per day.
- Biogas Power Generation (Off-grid) and Thermal energy application Programme (BPGTP), for setting up biogas plants in the size range of 30 m3 to 2500 m3 per day, for corresponding power generation capacity range of 3 kW to 250 kW from biogas or raw biogas for thermal energy /cooling applications.
- Biogas contains about 55-65 % of methane, 35- 44 % of carbon dioxide and traces of other gases, such as Hydrogen Sulphide, Nitrogen and Ammonia. Biogas, in its raw form that is without any purification can be used as clean cooking fuel like LPG, lighting, motive power and generation of electricity. It can be used in diesel engines to substitute diesel up to 80% and up to 100% replacement of diesel by using 100% Biogas Engines. Further, Biogas can be purified and upgraded up to 98% purity of methane content to make it suitable to be used as a green and clean fuel for transportation or filling in cylinders at high pressure of 250 bar or so and called as Compressed Bio-Gas (CBG).
- In Madhya Pradesh - State's first Bio methanation plant that can generate biogas to power street lights or for other similar use, was inaugurated in the state capital Bhopal. The waste-to-energy plant will daily use municipal solid waste and produce biogas that will then be utilised to generate electricity for lighting up street lights at Bittan Market.
- The 'Biomass Resource Atlas of India" projects the gross potential for energy generation from Agricultural sources at 1386.2 KWe and 2060.6 KWe from forests ,wastelands respectively in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- The biomass wise potential in the state has been given below:
|
Biomass
|
Power Potential (KWe)
|
|
Husk
|
248.161
|
|
Stalks
|
886.57
|
|
Leaves
|
561.467
|
|
Cobs
|
41.08
|
|
Shell
|
158.11
|
|
Bark
|
477.15
|
|
Residue
|
0.3
|
|
Branches
|
477.15
|
|
Others
|
0.06
|
|
Twigs
|
477.15
|
|
Straw
|
44
|
|
Pod
|
75.3
|
Problems in Energy Management in MP
- Losses in transmission & Distribution
- Losses occurring in transmission between the power Generation plants to grid and then grid to the user is the transmission and distribution loss. In MP this loss is about 40% of the power generated.
- Lack of availability of modern technology
- The available technology in Industries and domestic consumption is of old technology which use more energy. Like traditional bulbs consume more energy compare to LEDs and CFL.
- Lack of public awareness
- Lack of Public awareness about the energy Conservation leads to wasteful use of energy.
- Financial burden of new technology
- New technology comes at a cost which deters the Industrialists and domestic users to adopt it and they try to avoid investment in new and efficient technology.
- Theft of electricity
- Theft of electricity through illegal connections puts economic burden on electricity distribution companies.
- Environmental loss
- In present times energy resources are used extensively and it is causing environmental damage, climate change and Global warming.
Efforts Made by Government in Energy Sector
- National Energy Policy
- It aims to create independence in the energy sector and to provide 24x7 hours power to all.
- To provide energy at a minimum cost to all
- It Focus on energy independence through rationalization of costs, subsidy & boost to renewable sector.
- It aims to produce 175GW energy from the renewable sector till 2022.
- 100 GW from solar energy
- 60 GW from wind energy
- 10 GW from bio energy
- 5 GW from small hydro power
- Emphasis on transition from the coal to clean energy for domestic use.
- Focus on the infrastructure development
- Madhya Pradesh URJA Vikas Nigam
- Madhya Pradesh Urja Vikas Nigam was established by the Government of Madhya Pradesh in 1982 as the nodal agency and is working towards implementation of various programs and policies of the Government of India as well as the state Government for the renewable energy sector. The Scope of activities of MPUVN extends from implementing various schemes for meeting the energy needs of rural areas to the promotion and setting up of industrial and commercial projects for the use of non-conventional power.
- Madhya Pradesh Electricity Development Corporation
- Madhya Pradesh Electricity Development Corporation' was established in 1982 for the development and maximum utilization of Non-conventional energy resources beside the sources of conventional energy from commercial point of view corporation started working in 1983-84.
- Madhya Pradesh Policy for Rooftop Renewable Energy Projects, 2016
- To harness the abundantly available renewable energy potential in the state, the Government of Madhya Pradesh wishes to encourage the development of decentralized renewable energy installations.
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh in its endeavor to promote rooftop Renewable Energy Systems would encourage them to operate in the following ways:
- Objectives
- To encourage broader community involvement and growth of decentralized Renewable Energy Systems.
- To reduce dependence on conventional sources of energy.
- To provide impetus to growth of clean technology in the state of Madhya Pradesh.
- To reduce distribution losses of distribution licensees by decentralized generation.
- To improve tail-end grid voltages and reduce system congestion.
- To reduce carbon emissions.
- To help the State achieve its RPO (Renewable Purchase Obligation)
- To develop sustainable energy solution for fixture, and help in achieving energy security of the nation.
- To encourage job creation in the downstream Renewable Energy market segment.
- To help the community realize the importance of judicious use of electricity and involve them in the process of reducing dependence on conventionally produced electricity
- This policy aims to promote all rooftop renewable energy, including Net Metered Renewable Energy Systems, Renewable Energy Systems for captive use or third party sale and Off-Grid Renewable Energy Systems.
- Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for AH (UJALA) was launched by Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi on 1 May 2015, replacing the "Baehat Lamp Yojana". The project is spear headed by the Energy Efficiency Services Limited. In non-subsidized LED lamp distribution projects, this program is considered the world's largest.
- The Saubhagya Scheme or Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana is an Indian government project to provide electricity to the households.
- The project was announced in September 2017 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who said that the aim was to complete the electrification process by December 2018.
- Certain households identified via the Socio-economic and Caste Census (SECC) of 2011 will be eligible for free electricity connections, while others will be charged Rs. 500.
- Indira Kisan Jyoti Yojana
- Under Indira Kisan Jyoti Yojana, Rs 1400 per HP (Horse Power) payable for pre- existing agricultural pump connections.
- Pump consumers of up to 10 HP reducing the fee per year to Rs 700 per HP Payable in two equal installments at me rate of per year. Besides, 50 percent relaxation in energy charges has also been given to permanent and temporary agricultural pump connections with meters up to 10HP.
- Enacted from 1st April 2019 in Madhya Pradesh.
- Indira Griha Jyoti Yojana
- Enacted in Madhya Pradesh from 25 February 2019.
- The main objective of Indira Griha Jyoti Yojana is to provide electricity to the poor people especially the poor family at cheap prices, so that the extra burden of electricity bill does not fall on them.
- If 100 units of electricity are used under the scheme, the consumer will have to pay only flat 100 rupees electricity bill.
- This scheme was started from 1st April 2013.
- Under this scheme relief is provided to permanent agriculture consumers in their electricity bills. Scheme is being implemented by Madhya Pradesh Power Distribution Company, such consumers can pay electricity bills at flat rate of Rs 1200 per horsepower in two equal installments in a year.
- The Energy Department has launched MP Saral Bijli Bill Scheme under the flagship Mukhyamantri Jan Kalyan (Sambal) Yojana to ensure availability of electricity to the families of registered at a nominal price of Rs 200 per month for domestic use.
- People living in the state on a permanent basis will be allowed to get benefits of the scheme. Only those families of workers whose overall domestic power supply consumption is less than 1000 watts per month are eligible to avail the benefits of this scheme.
- Din Bandhu Yojana
- This scheme was started from 30 June 2013 for Below Poverty Line consumers.
- Under this scheme surcharge on pending bills will be paid by distribution companies and the remaining bills will be paid by state government.
- This scheme was started by the Madhya Kshetra Vidyut Vitaran Company in 10 villages of Raisen,Vidisha and Rajgarh districts.
- Its aim is to empower women through Women Self Help Groups. SHGs are provided with the responsibilities of electricity bill distribution, revenue collection, meter reading etc.
Summary
Energy Resource
An energy resource is something that can produce heat, power life, move objects, or produce electricity.
Types of Energy resources
On the basis generation energy sources can be classified into two types: nonrenewable and renewable.
On the basis of the uses the energy sources can be classified as the Commercial energy and Noncommercial energy.
Nonrenewable resources
Non-renewable energy is a source of energy that will eventually run out, such as fossil fuels and nuclear material, are removed from the earth and can be depleted. These resources have been the most used type of energy in the modem era. These are also known as conventional sources of Energy.
Renewable resources
Renewable energy is energy produced from sources that do not deplete or can be replenished within a human's life time such as wind, water, solar, and geomermal, come from sources mat regenerate as fast as they are consumed and are continuously available.
Some, such as biofuel produced from food crops and other plants, are replenished every growing season, m the early part of the twenty- first century, renewable sources have become more popular as nonrenewable sources have begun to be depleted. These are also known as
Non-conventional sources of energy.
Commercial energy
The energy sources that are used to generate electricity and that are available in the marketplace with a specific price are known as commercial energy sources. The most
commercialized forms of commercial energy sources are electricity, coal, advanced petroleum products and nuclear energy etc.
Non-commercial energy
Noncommercial energy sources, which include fuels such as logs, cattle dung, and agricultural and urban waste, are conventionally gathered and not bought at a price used particularly in rural areas. These are also called traditional fuels and are often Kored in energy accounting.
Energy Resources in MP
There are various conventional sources of energy in Madhya Pradesh which are coal, oil and mineral oil, natural gas, atomic mineral.
Non-conventional sources of energy are solar energy, wind energy, biomass energy etc.
Thermal Energy in MP
Thermal Power is the most important sources of energy for Madhya Pradesh.
- Chandni Thermal Power plant
- Amarkantak Thermal Power Plant (Anuppur)
- Satpura Thermal Power Plant (Patharkheda, Betui)
- Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station (Baidhan, Singrauli)
- Jabalpur Thermal Power Plant
- Shree Singaji Thermal Power Plant (Dongalia, Khandwa)
Hydel Power in MP
- Gandhi Sagar Hydro Power Project- (Mandsaur)
- Rana Pratap Sagar- (Chittorgarh, Rajasthan)
- Jawahar Sagar- Bargi Project (Avantibai Sagar Project Jabalpur)
- Rihand Project (Sonbhadra, U.P.)
- Pench Hydro Power Project
- Tons Hydro Power Project (Rewa)
Wind Energy in MP
- Total Power capacity-2519 MW.
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh has been promoting the setting up of Renewable Energy based power plants including wind through various policy initiatives and incentives for the investors/developers.
- Wind energy is an economical and pollution free source of energy.
- Wind mills have been established in the Indore, Ratlam, Dewas, Mandsaur, Rajgarh and Agar-Malwa districts.
- 7th largest producer in India.
Solar Energy in MP
- Madhya Pradesh receives a high solar radiation of more than 5.5 kWh per square metres per day with around 300 days of clear sun.
- Madhya Pradesh houses the seventh- largest installed solar power generation capacity in the country. The state's solar capacity at the end of 2018 stood at 1,526 MW.
MP Solar Energy Policy
- To encourage participation of Private Sector to set up Solar Power based projects in the State.
- To define the incentives and benefits to be provided to the participants of the Private Sector in clear terms.
- To build a favorable atmosphere for setting up Solar Power projects.
- Lay down framework for policy implementation.
Madhya Pradesh URJA Vikas Nigam
- Madhya Pradesh Urja Vikas Nigam was established by the Government of Madhya Pradesh in 19% as the nodal agency and is working towards implementation of various programs and policies of the Government of India as well as the state Government for the renewable energy sector.
Problems in energy management in MP
- Losses in transmission &. Distribution
- Lack of availability of modem technology
- Lack of public awareness
- Financial burden of new technology
- Theft of electricity
Efforts made by Government in energy sector
- National energy policy
- Madhya Pradesh URJA Vikas Nigam
- Madhya Pradesh Policy for Rooftop Renewable Energy Projects, 2016
- UJALA
- Saubhagya Scheme
- Indira Kisan Jyoti Yojana
- Flat Rate Scheme
Important facts
- The generation of electricity started in the state in the year 1905.
- Madhya Pradesh electricity board is the first electricity board established after independence in the country.
- Madhya Pradesh Electricity Board was founded in the year 1950 and it was activated in the year 1952.
- Madhya Pradesh generates 15158MW electricity from conventional sources and 3502 MW from non-conventional sources.
- At the time of formation of MP, the electricity generation capacity of MP was 82MW which now has increased to 18660MW (Economic Survey 2018-19)
- As per the Economic survey 2018-19 agriculture consumers are getting 10 hours of electricity supply while the non-agriculture consumers are getting 24 hour electricity supply.
- Chandni in Nepanagar is the 1st thermal power plant of state set up in 195 3.
- First Hydro power plant of the MP is GandhiSagar power plant (1960-61) constructed on Chambal River.
- Indira Griha Jyoti Yojana
- SaralBijli bill scheme
Probable Questions
1. Very Short Questions
- Name the conventional source of energy in MP.
- Name the non-conventional source of energy in MP.
- Name the major coal based power plants in MP.
- Name the major Hydel power projects in MP.
- Name the source of coal and water for Sant Singa Ji Thermal power project.
- Name the gas based power projects in MP.
- Write a note on the availability of the energy resources in MP.
- Discuss the challenges of energy management before MP.
- Write the location of proposed nuclear power plants in MP.
- Give three names of thermal power stations of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC-2018)
2. Short Questions
- Give details of major thermal power projects of M.P
- Discuss the hydro power projects of M.P
- Discuss the non-conventional sources of energy in M.P
- Discuss the Solar power policy of M.P.
- Discuss the Nuclear Power projects in M.P.
- Give a brief account about the Rewa Ultra mega solar power project?
3. Long Question
- There are suitable condition for development of non-conventional energy in M.P Discuss
- What is solar energy? Discuss the development of solar energy in M.P
- Discuss the solar power policy of MP, and the efforts made by the government in this direction.
- "M.P has suitable conditions for the development of the Bio-mass energy". Discuss.
- Discuss the efforts made by the MP government for the development and conservation of the energy.
- Describe mineral and energy resources of Madhya Pradesh. (MPPSC-2016)










