NCERT Extracts - Cultural Contacts
Category : UPSC
Indian's with the Asian Countries
- India maintained contacts with its Asian neighbours since Harappan times. Many Harappan seals between 2400 B.C.-1700 B.C. have been found there.
- From the beginning of the Christian era onwards, India maintained commercial contacts with China, South-East Asia, West Asia and the Roman Empire. Indian land routes were connected with the Chinese Silk Route.
- India sent its missionaries, conquerors and traders to the neighbouring countries where they founded settlements.
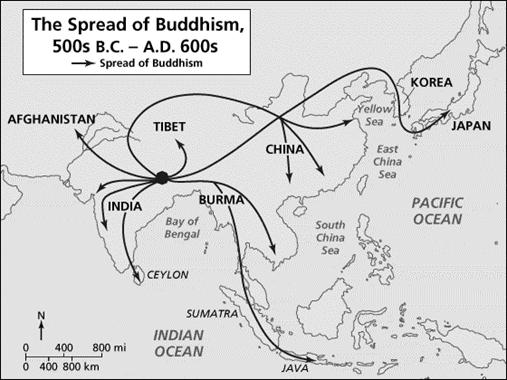
- The propagation of Buddhism promoted India's contacts with Sri Lanka, Myanmar, China and Central Asia.
- In the early centuries of the Christian era Buddhism spread from India to Burma (modem Myanmar). The Burmese developed the Theravada form of Buddhism.
- The Burmese and Sri Lanka Buddhists produced a rich corpus of Buddhist literature, not to be found in India. All the Pali texts were compiled and commented upon in Sri Lanka.
- Beginning with the reign of Kanishka a large number of Indian missionaries went to China, Central Asia and Afghanistan for preaching their religion.
- From China Buddhism spread to Korea and Japan, and it was in search of Buddhist texts and doctrines that several Chinese pilgrims such as Fa-hsien and Hsuan Tsang came to India.
- The Indians leamt the art of growing silk from China, and the Chinese leamt from India the art of Buddhist painting.
- The two other great centres of Buddhism in ancient times were Afghanistan and Central Asia. In Afghanistan many statues of the Buddha and monasteries have been discovered.
- Begram and Bamiyan situated in the north of this country are famous for such relics.
- Begram is famous for ivory work, which is similar to Indian workmanship in Kushan times. Bamiyan had the distinction of possessing the tallest Buddha statue sculptured out of rock in the early centuries of the christian era.
- It has thousands of natural and artificial caves in which the monks lived.
- Indian culture also spread to South-East Asia, but not through the medium of Buddhism.
- Except in the case of Burma it was mostly diffused through the brahmanical cults.
- The name Suvarnabhumi was given to Pegu and Maulmein in Burma, and merchants from Broach, Banaras and Bhagalpur traded with Burma.
- Considerable Buddhist remains of Gupta times have been found in Burma.
- From the first century A.D. India established close trading relations with Java in Indonesia, Which was called suvarnadvipa or the island of the gold by the ancient Indians
- In the early centuries of the Christian era the pallavas founded their colonies in Sumatra.
- Eventually these flowered into the kingdom of Sri Vijaya, which continued to be an important from the fifth to the tenth century A.D.
- The Indian settlements in java and Sumatra became channels for the radiation of India culture. The process of founding settlements continued afterwards.
- In indo- china, which is at present divided into Vietnam, Combodia and Laos, the Indians set up two powerful kingdom in Kamboja and champa.
- The powerful kingdom of kamboja identical with modern Cambodia was founded in the sixth century A.D. its rules were devotees of Shiva.
- They developed kamboja as a centre of Sanskrit learning.
- The king of Champa was also a Shaiva, and the official language of champa was Sanskrit. This country was considered to be a great centre of education in the Vedas and Dharmashastras.
- The greatest Buddhist temple is found in Borobudur in Indonesia.
- Considered to be the large Buddhist temple in the whole word, it was constructed in the eight century A.D, and 436 images of Buddha were engraved on it.
- The temple of Ankorvat in Cambodia is larger than that of Borobudur.
- This temple belongs to medieval times. The stories of the Ramayana and Mahabharata are narrated in relief on the walls of the temple.
- The story of the Ramayana is so popular in Indonesia that many folk plays are performed on its basis. The Indonesian language called Bahasa Indonesia contains numerous Sanskrit words.
- It would be wrong to think that religion alone contributed to the spread of Indian culture. Missionaries were backed by traders and conquerors.
- Trade evidently played a vital part in establishing India's relations with Central Asia and South-East Asia.
- The very names Suvamabhumi and Suvamadvipa given to territories in South-East Asia, suggest Indian's search for gold.
- Trade led not only to exchange of goods but also to that of elements of culture.
- It would be inaccurate to hold that Indians alone contributed to the culture of their neighbours. It was a two-way traffic.
- The Indians acquired the craft of minting gold coins from the Greeks and Romans.
- They leamt the art of growing silk from China, that of growing betel leaves from Indonesia, and several other products from the neighbouring countries.
- Similarly, the method of growing cotton spread from India to China and Central Asia.
- Indian contribution seems to be more important in art, religion, script and language.

