Respiration
Category : 10th Class
All the living organisms requires energy for their life processes. They derive this energy from the food they eat. The respiration is the process of breaking down of complex food molecules into simpler form with the release of energy. It is of two types, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. The respiration which takes place in presence of oxygen is called aerobic respiration and the respiration which takes place in absence of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration.
![]() Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic Respiration
The respiration, which takes place in absence of oxygen or with limited supply of oxygen is called anaerobic respiration. In this process, the sugar molecule is broken down into simpler form either in absence of oxygen or with the limited supply of oxygen. It takes place in the cell which lacks mitochondria. In absence of oxygen, glucose is converted into lactic acid or ethanol in different condition. Whereas with limited supply of oxygen yeast convert pyruvate into ethanol and carbon dioxide. Thus, different path is followed after glycolysis. In presence of oxygen pyruvate is oxidized into carbon dioxide and water, with the release of energy.
![]() Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic Respiration
The respiration, which takes place in presence of oxygen is called aerobic respiration. It takes place in mitochondria. The product of this reaction is ATP. Inside mitochondria, when an inorganic phosphate group gets attached to compound called ADP, a molecule of ATP is formed. There it forms 38 molecules of ATP which is the unit for energy in the cell.
The exchange of gases in human being is called breathing. Breathing takes place through respiratory system. The human respiratory system consists of nostril, larynx, windpipe, trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli.
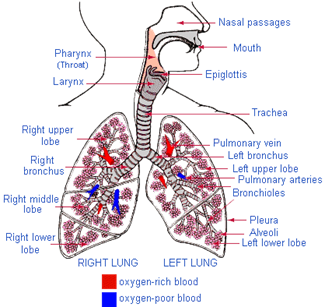
Air enters into our body through nostril. This air is filtered by fine hairs that is present in the inner lining of nostril. From there air passes through the wind pipe into lungs via trachea.
The trachea consists of rings of cartilage muscles, which prevents it from collapsing when we inhale the air. The trachea is further divided into two parts before entering into two lungs called bronchi. The bronchi when enters into the lungs, it gets further subdivided into smaller capillaries called bronchioles, which finally terminates in balloon like structure called alveoli.
The alveoli helps in the exchange of gases between lungs and blood vessels.
The spherical surface of alveoli increases the surface for the exchange of gases.
The blood brings carbon dioxide from the rest of the body and release it into lungs and takes up oxygen from lungs and carries it back to the body.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
