Characteristic Curves of a Diode
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
A graph represents the variation of \[{{i}_{p}}\] with \[{{V}_{p}}\] at a given filament current \[({{i}_{f}})\] is known as characteristic curve. 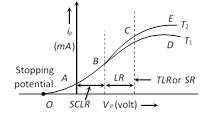
The curve is not linear hence diode valve is a non-ohmic device.
(1) Space charge limited region (SCLR) : In this region current is space charge limited current.
Also \[{{i}_{p}}\,\propto \,V_{p}^{3/2}\]\[\Rightarrow \]\[{{i}_{p}}=kV_{p}^{3/2}\]; where k is a constant depending on metal as well as on the shape and area of the cathode. This is called child?s law.
(2) Linear region (LR) : In this region \[{{i}_{p}}\,\propto \,{{V}_{p}}\]
(3) Saturated region (SR) or temperature limited region (TLR) : In this part, the current is independent of potential difference applied between the cathode and anode. \[{{i}_{p}}\ne f({{V}_{p}})\], \[{{i}_{p}}=f\] (Temperature) The saturation current follows Richardson Dushman equation i.e. \[i=AS{{T}^{2}}{{e}^{-{{\varphi }_{0}}/kT}}\]; Here A = Emission constant =\[\frac{4\pi \ me{{k}^{2}}}{{{h}^{3}}}amp/{{m}^{2}}-{{k}^{2}}\] S = Area of emitter in \[{{m}^{2}}\]; T = Absolute temperature in K \[{{\varphi }_{0}}\]= Work function of metal in Joule; k =Boltzmann constant The small increase in \[{{i}_{p}}\] after saturation stage due to field emission is known as Shottkey effect.
(4) Diode resistance
(i) Static plate resistance or dc plate resistance : \[{{R}_{p}}=\frac{{{V}_{p}}}{{{i}_{p}}}\].
(ii) Dynamic or ac plate resistance : If at constant filament current, a small change \[\Delta {{V}_{P}}\] in the plate potential produces a small change \[\Delta {{i}_{p}}\] in the plate current, then the ratio \[\Delta {{V}_{p}}/\Delta {{i}_{p}}\] is called the dynamic resistance, or the 'plate resistance' of the diode \[{{r}_{p}}=\frac{\Delta {{V}_{p}}}{\Delta {{i}_{p}}}\].
(iii) In SCLR : \[{{r}_{p}}<{{R}_{p}}\],
(iv) In TLR :\[{{R}_{p}}<{{r}_{p}}\] and \[{{r}_{p}}=\infty \].
(5) Uses of diode valve
(i) As a rectifier
(ii) As a detector
(iii) As a transmitter
(iv) As a modulator
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
