
 Banyan tree Mango tree
Shrubs
Shrubs are small plants. They have many hard branches which grow close to the ground. For example, rose and hibiscus plant.
Banyan tree Mango tree
Shrubs
Shrubs are small plants. They have many hard branches which grow close to the ground. For example, rose and hibiscus plant.

 Rose Plant Hibiscus Plant
Herbs
Herbs are very small plants. They have soft stems. For example, mint, basil.
Rose Plant Hibiscus Plant
Herbs
Herbs are very small plants. They have soft stems. For example, mint, basil.

 Mint Plant Basil Plant
Climbers
Climbers are the plants with weak stems. They need some support to stand straight. For example, grapevine and pea plant.
Mint Plant Basil Plant
Climbers
Climbers are the plants with weak stems. They need some support to stand straight. For example, grapevine and pea plant.

 Grapevine Plant Pea Plant
Creepers
Creepers are the plants which have week stem and grow along the ground.
Grapevine Plant Pea Plant
Creepers
Creepers are the plants which have week stem and grow along the ground.

 Pumpkin Watermelon
Classification of Plants on the Basis of Their Location
Water Plants
There are some plants that grow in water only.
Pumpkin Watermelon
Classification of Plants on the Basis of Their Location
Water Plants
There are some plants that grow in water only.

 Lotus Plant Water lily plant
Desert plants
There are some plants that grow in deserts.
Lotus Plant Water lily plant
Desert plants
There are some plants that grow in deserts.

 Cactus Plant Opuntia Plant
Plants as Our Friends
Plants give us food
Most of our food is given by plants. We eat different parts of plants.
Seeds: Rice, wheat, corn, etc.
Roots: Carrot, turnip, radish and sweet potato.
Stems: Sugarcane grows above the ground but potato and ginger grow under the ground.
Leaves: Coriander, mint, lettuce, spinach and cabbage.
Fruits: Mango, pear, banana, apple, etc.
Flowers: Cauliflower, rose. Jasmine, broccoli, etc.
Plants give us wood
Plants give us fibre
Fibre from the cotton plant is used to make cloth. Fibre from the jute plant is used to make cloth, sacks, ropes and mats.
Plants give us medicine
We make medicines like penicillin and quinine from plants. Tulsi leaves are used to treat common cold and cough.
Sweet-smelling flowers like jasmine and rose are used to make perfumes.
Plants give us other things
Paper is made from bamboo.
Gum is made from the more...
Cactus Plant Opuntia Plant
Plants as Our Friends
Plants give us food
Most of our food is given by plants. We eat different parts of plants.
Seeds: Rice, wheat, corn, etc.
Roots: Carrot, turnip, radish and sweet potato.
Stems: Sugarcane grows above the ground but potato and ginger grow under the ground.
Leaves: Coriander, mint, lettuce, spinach and cabbage.
Fruits: Mango, pear, banana, apple, etc.
Flowers: Cauliflower, rose. Jasmine, broccoli, etc.
Plants give us wood
Plants give us fibre
Fibre from the cotton plant is used to make cloth. Fibre from the jute plant is used to make cloth, sacks, ropes and mats.
Plants give us medicine
We make medicines like penicillin and quinine from plants. Tulsi leaves are used to treat common cold and cough.
Sweet-smelling flowers like jasmine and rose are used to make perfumes.
Plants give us other things
Paper is made from bamboo.
Gum is made from the more... 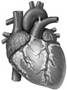 Heart
Brain: It helps us to think and work.
Heart
Brain: It helps us to think and work.
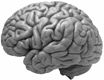 Brain
Lungs: We have two lungs. They help us to breathe.
Brain
Lungs: We have two lungs. They help us to breathe.
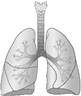 Lungs
Stomach: It looks like a bag. The food we eat goes to stomach.
Lungs
Stomach: It looks like a bag. The food we eat goes to stomach.
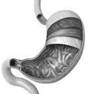 Stomach
Our Sense Organs
Sense organs are those organs through which we get the feeling of our surroundings. We have five sense organs which are as follows:
Eyes: Eyes help us to see.
Nose: Nose helps us to smell.
Ears: Ears help us to hear.
Tongue: Tongue helps us to taste.
Skin: Skin helps us to sense hot and cold. It is the largest organ of our body.
The Skeleton
(i) The framework of bones which gives shape and support to our body is called the skeleton.
(ii) There are 206 bones in a human body.
(iii) Our bones are covered with muscles.
(iv) The place where two or more bones are joined together is called a joint.
Stomach
Our Sense Organs
Sense organs are those organs through which we get the feeling of our surroundings. We have five sense organs which are as follows:
Eyes: Eyes help us to see.
Nose: Nose helps us to smell.
Ears: Ears help us to hear.
Tongue: Tongue helps us to taste.
Skin: Skin helps us to sense hot and cold. It is the largest organ of our body.
The Skeleton
(i) The framework of bones which gives shape and support to our body is called the skeleton.
(ii) There are 206 bones in a human body.
(iii) Our bones are covered with muscles.
(iv) The place where two or more bones are joined together is called a joint. 
 Water animal Water plant
Water
Water is found in rivers, lakes, oceans, seas, etc. These are called water bodies. More than two third of the earth is covered with water. Most of the water on the earth is salt water. We need fresh water to drink, which is only a very little portion of all the available water on earth.
A major portion of fresh water available in the form of glacier ice, at the north and south poles. It is far away from us. Therefore, we cannot use it.
Uses of water
Water animal Water plant
Water
Water is found in rivers, lakes, oceans, seas, etc. These are called water bodies. More than two third of the earth is covered with water. Most of the water on the earth is salt water. We need fresh water to drink, which is only a very little portion of all the available water on earth.
A major portion of fresh water available in the form of glacier ice, at the north and south poles. It is far away from us. Therefore, we cannot use it.
Uses of water
 Wind is blowing
Air is very necessary for all of us to live. We take in air when we breathe. But the air we breathe must be clean and fresh. Unclean air makes us sick. We get fresh air from trees and plants.
Weather
Our earth is surrounded by air. Sometimes this air becomes cold, sometimes hot. Sometimes we have rain, sometimes it is neither too hot nor too cold. This condition of a place, at any given time, is called weather.
Wind is blowing
Air is very necessary for all of us to live. We take in air when we breathe. But the air we breathe must be clean and fresh. Unclean air makes us sick. We get fresh air from trees and plants.
Weather
Our earth is surrounded by air. Sometimes this air becomes cold, sometimes hot. Sometimes we have rain, sometimes it is neither too hot nor too cold. This condition of a place, at any given time, is called weather.

 Flowers Snow
Flowers Snow

 Rain Sunny day
Weather is not same all through the year. It keeps changing from time to time.
Rain Sunny day
Weather is not same all through the year. It keeps changing from time to time.
| Food item obtained from plants | Food item obtained from animals |
| Vegetables | Milk |
| Fruits | Meat |
| Cereals | Egg |
| Pulses | Honey |
| Oils | |
| Spices |
| Thousands | Hundreds | Tens | Ones |
| 4 | 2 | 7 | 6 |
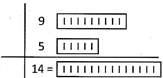 Therefore,
\[9+5=14\]
Rules for Addition
The following are the rules for the addition of more than one digit numbers.
Rule: 1
Start addition with the 1st digit from right, then with 2nd digit from the right and the process goes on.
In another words, add ones 1st: then tens: then hundreds and so on.
Look at the following addition:
\[14+15=?\]
Therefore,
\[9+5=14\]
Rules for Addition
The following are the rules for the addition of more than one digit numbers.
Rule: 1
Start addition with the 1st digit from right, then with 2nd digit from the right and the process goes on.
In another words, add ones 1st: then tens: then hundreds and so on.
Look at the following addition:
\[14+15=?\]
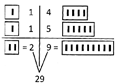 Rule: 2
If addition of one’s gives result in 2 digits, then add the left digit of the result with tens and the process goes on.
Look at the following addition:
\[25+26=?\]
Rule: 2
If addition of one’s gives result in 2 digits, then add the left digit of the result with tens and the process goes on.
Look at the following addition:
\[25+26=?\]
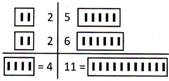 Here, the left 1 of 11 is added to 4 as below
Here, the left 1 of 11 is added to 4 as below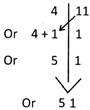 :
:
| Name of articles | Quantity (Pieces) |
| Soap | 33 |
| Tooth brush | 11 |
| Chocolates | 13 |
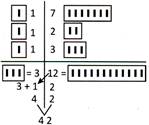 Addition of Images
Addition of images means grouping of more than one images into a single group.
Addition of Images
Addition of images means grouping of more than one images into a single group.
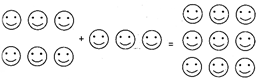 In the
\[{{2}^{nd}}\]
example we add group of [6] more...
In the
\[{{2}^{nd}}\]
example we add group of [6] more... 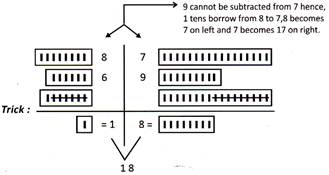 Subtraction of Three Numbers
Remember the steps for the subtraction:
Step 1: Add the numbers having '-'(minus) sign and write the result with-sign.
Step II: Add the numbers having '+' (plus) sign and write the result with + sign. This method is applied when addition and subtraction are given. Simultaneously.
Step III: Finally subtract the numbers.
Subtraction of Three Numbers
Remember the steps for the subtraction:
Step 1: Add the numbers having '-'(minus) sign and write the result with-sign.
Step II: Add the numbers having '+' (plus) sign and write the result with + sign. This method is applied when addition and subtraction are given. Simultaneously.
Step III: Finally subtract the numbers.
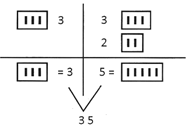 Step II: is not applicable here.
Step III: {45} – {35}
Step II: is not applicable here.
Step III: {45} – {35}
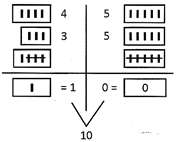 Word Problems
Word Problems
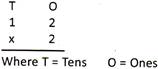 Step II:
Multiply ones as below:
\[2\,Ones\times 2=4\]
It is written as:
Step II:
Multiply ones as below:
\[2\,Ones\times 2=4\]
It is written as:
 Step III:
Multiply tens as shown below:
\[1\,ten\times 2=2\,tens\]
Write 2 under tens column.
Step III:
Multiply tens as shown below:
\[1\,ten\times 2=2\,tens\]
Write 2 under tens column.
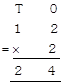 Therefore, the product of 12 and 2 = 24
Multiplication of Three Numbers
Therefore, the product of 12 and 2 = 24
Multiplication of Three Numbers
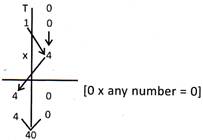
 By grouping 12 pencils into two equal groups.
By grouping 12 pencils into two equal groups.
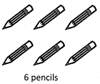
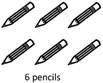 Therefore, you get 6 pencils and your friend gets 6 pencils.
Division by Repeated Subtraction
Therefore, you get 6 pencils and your friend gets 6 pencils.
Division by Repeated Subtraction
 Give 5 cakes to first child. 10 cakes are left.
Give 5 cakes to first child. 10 cakes are left.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
