

 ABCD is a rectangle in which
(i) \[\angle \text{A}=\angle \text{B}=\angle \text{C}=\angle \text{D}=\text{9}0{}^\circ \]
(ii) AB = CD = 6 cm, and BC = AD = 4 cm.
ABCD is a rectangle in which
(i) \[\angle \text{A}=\angle \text{B}=\angle \text{C}=\angle \text{D}=\text{9}0{}^\circ \]
(ii) AB = CD = 6 cm, and BC = AD = 4 cm.
 ABCD is a rectangle in which (i) \[\angle \text{A}=\angle \text{B}=\angle \text{C}=\]\[\angle \text{D}=\text{9}0{}^\circ \](ii)\[\text{AB}=\text{BC}=\text{CD}\]\[=\text{DA}=\text{5 cm}\]
ABCD is a rectangle in which (i) \[\angle \text{A}=\angle \text{B}=\angle \text{C}=\]\[\angle \text{D}=\text{9}0{}^\circ \](ii)\[\text{AB}=\text{BC}=\text{CD}\]\[=\text{DA}=\text{5 cm}\]  In the above picture, OP and OR are two rays which have a common end point 0. The inclination between the rays OP and OR is called angle POR and it is denoted as
In the above picture, OP and OR are two rays which have a common end point 0. The inclination between the rays OP and OR is called angle POR and it is denoted as 




 \[\Delta \text{ABC}\] is an equilateral triangle as AB = BC = AC = 4 cm In triangle ABC,\[\angle \text{ABC}=\angle \text{BCA}=\angle \text{CAB}=\text{6}0{}^\circ \].
\[\Delta \text{ABC}\] is an equilateral triangle as AB = BC = AC = 4 cm In triangle ABC,\[\angle \text{ABC}=\angle \text{BCA}=\angle \text{CAB}=\text{6}0{}^\circ \].
 \[\Delta \text{ABC}\] is a isosceles triangle as AB = AC= 4 cm. In \[\Delta \text{ABC}\],\[\angle \text{ABC}=\angle \text{BCA}=\text{7}0{}^\circ \]
\[\Delta \text{ABC}\] is a isosceles triangle as AB = AC= 4 cm. In \[\Delta \text{ABC}\],\[\angle \text{ABC}=\angle \text{BCA}=\text{7}0{}^\circ \]
 \[\Delta \text{PQR}\] is a scalene triangle as\[PQ\ne QR\ne PR\] In\[\Delta \text{PQR}\], \[\angle PQR\ne \angle QRP\ne \angle RPQ\]
\[\Delta \text{PQR}\] is a scalene triangle as\[PQ\ne QR\ne PR\] In\[\Delta \text{PQR}\], \[\angle PQR\ne \angle QRP\ne \angle RPQ\]
 ABC is an acute - angled triangles as its every angles\[(\angle A,\angle B,\angle C)\]measures between\[0{}^\circ \] and\[\text{9}0{}^\circ \].
ABC is an acute - angled triangles as its every angles\[(\angle A,\angle B,\angle C)\]measures between\[0{}^\circ \] and\[\text{9}0{}^\circ \].
 \[\Delta ABC\] is a right - angled triangle more...
\[\Delta ABC\] is a right - angled triangle more...  The unitary method is a technique in elementary algebra for solving a class of problems in variation.
Unitary method consists of altering one of the variables to a single unit, i.e. 1, and then performing the operation necessary to alter it to the desired value.
The unitary method is a technique in elementary algebra for solving a class of problems in variation.
Unitary method consists of altering one of the variables to a single unit, i.e. 1, and then performing the operation necessary to alter it to the desired value.

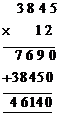 Thus Rs.
Thus Rs. 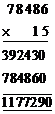 Thus Rs. \[784.86\times 15\] = Rs. 11772.9
Thus Rs. \[784.86\times 15\] = Rs. 11772.9
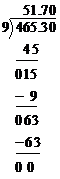 Rs. 51.70
Rs. 51.70
| Rs. \[1=1\times 100p=100p\] | Rs. \[3.50=3\times 100p+50p=350p\] |
| Rs. \[2=2\times 100p=200p\] | Rs. \[4.50=4\times 100p+50p=450p\] |
| Rs. \[3=3\times 100p=300p\] | Rs. \[5.50=5\times 100p+50p=550p\] |
| Rs. \[4=4\times 100p=400p\] | Rs. \[80.50=80\times 100p+50p=8050p\] |
| Rs. \[80=80\times 100p=8000p\] | Rs. \[90.50=90\times 100p+50p=9050p\] |


 more...
more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
