Category :
MP State Exams
CHAPTER - 4 CLIMATE
Madhya Pradesh is located in center of India, with wide latitudinal and longitudinal spread which affects the climate of the state to a great extent.
Madhya Pradesh has a latitudinal spread of 870 km from east to west for this reason varied climatic conditions prevail over the state.
Presence of Tropic of Cancer responsible for making climate of Madhya Pradesh tropical, which passes through 14 districts located in the central part of Madhya Pradesh. districts are Ratlam, Ujjain, Agar-Malwa, Rajgarh, Sehore, Bhopal, Vidisha, Raisen, Sagar, Damoh, Katni, Jabalpur, Umaria and Shahdol.
Madhya Pradesh is located in a sub-tropical climate region and has a tropical mansoon climate. The climate of Madhya Pradesh is governed by a monsoon weather pattern. The distinct seasons are summer (March through May), winter (November through February), and the intervening rainy months of the south-west monsoon (June through September).
Climatic features of Madhya Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh has Monsoonal climate.

- Regional variation:- Madhya Pradesh weather is markedly different in the following climate zones the Northern Plains, the Hilly Region of the Vindhyan, the Narmada Valley, and the Malwa Plateau.
- Temperature variation:- The seasons found here also vary in temperature. The maximum temperature in the state is in May and the lowest in January.
- Unequal distribution of the Rainfall:- There is a wide regional variation in the rainfall e.g. Pachmarhi has average rainfall of 212.3 cm while Bhind gets only 62.4cm.
Factors affecting the climate of Madhya Pradesh
- Geographical location
- Land locked (No coastal connection)
- High Temp Range.
- Distance from Sea: No moderating effect of the sea
- Tropic of Cancer passing through centre: Result in high Temp.
- Presence of mountain ranges.
- Activities of South-Western Monsoon.
Classification of Climate of Madhya Pradesh

- According to A.R. Subramanian and T. Shreemannarayana:- A R Subranmaniam and T Srimannarayana (1991) have classified the climate of Madhya Pradesh into 3 parts based on Madhya Pradesh's climatological study.
- Semi dry and Steppe Type-It extends to the north-west in Neemuch, Mandaur districts and to the north Chambal valley districts- Shivpuri, morena, Sheopur, Bhind, Datia and Gwalior districts
-
- Hot Tropical-It had wide terrain from west to east in the central part of the State.
- Tropical Humid and Dry Type-Occupies limited southern part of the State.
- According to Koppen:-The Koppen's climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification system. It was first published by the German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Koppen in 1884. According to Koppen, the climate of Madhya Pradesh has been classified into 3 parts:
- Tropical savanna climate (Aw) is found in the districts of Barwani, Khargone, Khandwa, Burhanpur, Alirajpur, Dhar and Jhabua etc. in the southwest and west of Madhya Pradesh.
- Hot-summer Mediterranean climate in Gwalior, Jabalpur, Sagar, Singrauli, Rewa.
- Hot semi-arid climates in other parts of the state.
|
Classification
|
Count
|
Koppen- Geiger
|
Examples
|
|
Hot-summer Mediterranean climate
|
311
|
Csa
|
Gwalior, Jabalpur, Sagar, Singrauli, Rewa
|
|
Tropical savanna climate
|
196
|
Aw
|
Indore, Bhopal, Dewas, Khandwa, Ujjain
|
|
Hot semi-arid climates
|
41
|
BSh
|
Burhanpur, Bhind, Khargone, Sabalgarh, Baroda
|
Seasons in Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh has a subtropical climate with a hot dry summer (April-June), followed monsoon rains (July-September) and a cool and relatively dry winter. Climate of Madhya Pradesh has been divided into 3 seasons based on temperature, rainfall and air pressure in summer, rainy season and winter season respectively.
Classification of Seasons in Madhya Pradesh
|
Season
|
Period
|
|
Summer
|
Mid-March to Mid-June (15 March to 15 June)
|
|
Rainy Season
|
Mid June to Mid-October (15 June to 15 October)
|
|
Winter
|
Mid-October to Mid-March (15 October to 15 March)
|
Summer Season
- Summer starts in Madhya Pradesh from mid-March and lasts till mid-June, In this period, after March 21, due to the northward movement of sun, the temperature increase and the air pressure starts to decrease, as a result of which there is a severe heat in the month of May. The average May temperature in Madhya Pradesh is around 40° Celsius.
-
- In Madhya Pradesh summer, season is locally known as Unala. During this time, the temperature in Gwalior, Morena, Datia and Southern Balaghat is around 47°C.
- GanjBasoda (Vidisha district) is the hottest place in the state which records temperature of about 48.70C in summer.
- In this season, the isotherm of 40°C divides the state in two equal halves. The regions of Madhya Pradesh are divided into two temperature zones according to the extreme temperature.
- This season is normally dry with very low humidity. The sky is generally clear across the state and sometimes also facts sand blowing winds locally known as Loo.
- During the summer season in Madhya Pradesh; in May and June, high temperature in north-west India builds steep pressure gradient, Hot, dusty laden and strong wind known as Loo blows. Loo normally starts blowing by 9.00 A.M. increases gradually and reaches maximum intensity in the afternoon. It blows with an average speed of 30-40 km per hour and persists for days. In terms of temperature, most of the state of Madhya Pradesh falls in the Mega Thermal category. Like others states of India, in Madhya Pradesh, after 21 March, the sun starts to move northwards, due to which the temperature rises and on 21 June, the sun is perpendicular near the Tropic of Cancer.
Rainy Season
The south-west Monsoon usually breaks out in mid-June and the entire state receive a major share of its rainfall between June and September. It comes from both the southwest monsoon branches of Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal branch respectively with the arrival of monsoon in Madhya Pradesh, rainfall first starts from the southeastern regions, then in the north- eastern, intermediate and western parts.
- The onset of this season depends on the onset of South-West monsoon winds on the West coast of India. This season prevails from June to September.
- Madhya Pradesh receives about 85 percent of the rainfall i.e. 100 to 125 cm from the southwest monsoon but as per Economic Survey 2018-19 of Madhya Pradesh the average rainfall in the state is 102.6 cm and the actual rainfall in the year 2018 is 82.3 cm, recorded in Madhya Pradesh, which is about 19.82 percent less than the normal average.
- The south and south-east regions tend to experience a higher rainfall whereas the parts of north-west receive less. Mandla, Balaghat, Sidhi, Jabalpur and other extreme eastern parts receive more than 150 cm rainfall. The south-eastern part of Madhya Pradesh receives the highest rainfall due to its proximity to the sea level and the Kerala branch of the Arabian Sea, the Mumbai branch and the Bay of Bengal branch hitting the Satpura Maikal Range, the highest mountain range of the state.
- Due to increased distance from the coast of north and northwestern part of Madhya Pradesh, Bay of Bengal, i.e., the coastline, and as a result of increasing temperature and humnidity due to friction while descending in the mountainous region of Mumbai branch of Arabian Sea monsoon. The western part receives the least rainfall during the rainy season.
- The amount of rainfall in Madhya Pradesh decreases from east to west and south to north respectively.
- In the eastern and southeastern regions of Madhya Pradesh, most of the rainfall is received from Bay of Bengal branch, while in the northwest and intermediate regions, both branches Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal receive rainfall. Major contribution of rainfall is from Arabian Sea branch.
- The highest rainfall occurs in the state during June to September. In Madhya Pradesh, the rainy season is locally known as Chaumasa.
- This season leads to a sudden fail in the day temperature due to the clouds, humidity and rains.
- Till July, the complete Eastern Madhya Pradesh comes under the impact of these monsoon winds.
- The monsoon winds originate from Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
- The hilly and plateau regions receive more rain as compared to the plains. For example the Mahadeo hills of Satpura range receive an average monthly rainfall of 23 cm while, the average rainfall m plain areas of Jhabua, Dhar and Khargone is 4-5 cm.
Rainfall Distribution in the State
On the basis of intensity of rainfall, the areas of the state are divided into four categories:
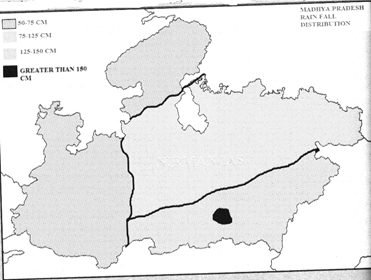
Areas with Excess Rainfall
The South-Eastern areas of the state receive an excess rainfall i.e. more than 150 cm. Such places in Madhya Pradesh are Pachmarhi, Mahadeo hills, Mandla, Sidhi and Balaghat. The major source of such excess rainfall is the South-Western monsoon originating from the Arabian Sea. Pachmarhi (Hoshangabad), located under the Satpura mountain range in the
southeastern part of Madhya Pradesh, is called Cherrapunji of Madhya Pradesh due to being the most rainy place. Pachmarhi in Madhya Pradesh receive the highest rainfall of 215 cm.
Areas with more than Average Rainfall
Betul, Chhindwara, Seoni, Narsinghpur districts come under this category. Because of being on the Eastern side of the state, these places receive more rainfall due to more humidity. The average rainfall in these areas is 125 cm to 150 cm.
Areas with Average Rainfall
The North-Eastern places of the state come under this section. Central highlands, plateau of Bundelkhand, Rewa-Panna plateau are the areas which receive lesser rainfall due to the lack of humidity and their physical features. These areas include places with 75 cm to 100 cm of rainfall.
- Areas with Minimum Rainfall
The areas that come under this category are Neemuch, Mandsaur, Ratlam, Dhar, Jhabua, etc. The Western areas of the state receive the minimum rainfall i.e. of 50 cm to 75 cm. The main reason behind the minimum rainfall is the absence of humidity. Till the South-Western monsoon reaches here, it either becomes void of moisture or has a very low humidity. Bhind (Gohad) is the least rainy place in the northern part of Madhya rain fall may vary from 50 to 75 centimeter.
Winter Season
- Madhya Pradesh, the winter season prevails from November to February. This season is locally known as Siyala in the state.
- The winter season in Madhya Pradesh starts from mid-October and lasts till mid-March (15 October to 15 March). Humidity prevails in the air after the return of the monsoon in mid- October, there is a sharp decline in the mercury level, especially during the months of December and January.
Western disturbances
Western Disturbances are the cause of the most winter and pre-monsoon season rainfall across West and North-West India. This low pressure system, originate over the Mediterranean Sea and western Asia and move into India, along -with the Westerly flow.
This phenomenon is usually associated with cloudy sky, higher night temperature and unusual rainfall. It is estimated that India gets close to 5-10% of its total annual rainfall from western disturbances. In M.P. northern districts- Sheopur, Morena, Gwalior, Datia, and Shivpuri,, and receives rainfall due to western disturbances.
- The average temperature in the winter season in Madhya Pradesh is 22° Celsius, but it is the coldest in January and the state average temperature is 10° Celsius. Rainfall also occurs during the winters due to western disturbances.
- During December-January, there could be some rain because of the Western disturbances which are locally known as Mawath.
- From 23rd September, as soon as the Sun starts moving towards South, the average temperature starts falling.
- The temperature in the North Western region during this season remains 15°-21°C. and the temperature in South-Western region remains 18°-21°C.
- Shivpuri is the coldest place of the state.
- During this season, the sky is generally clear. Colder nights sometimes cause a fog and mist on high plateaus or hilly regions.
- As soon as March comes, the temperature again starts rising and marks the onset of Summer.
Climatic Zones of Madhya Pradesh
The climate of the state is tropical monsoon type. Different climatic conditions are found in the different zones of the state due to the large geographical area and physical variations. Based on the variations of the climate, Madhya Pradesh is divided into the following categories:
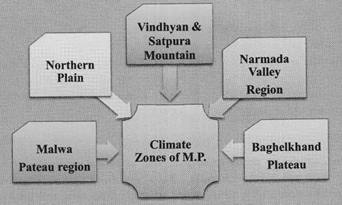
State is assumed to have 5 climatic zones:
- Malwa plateau (Moderate hot and Moderate cold)
- Northern Plain (very hot and very cold).
- Vindhyan mountain region (Average hot and average cold).
- Nannada valley region (very hot and less cold)
- Baghelkhand plateau (very hot and moderate cold).
Malwa Plateau Region
- The climate of this region of Madhya Pradesh is slightly dry continental as compared to tropical monsoon of the state. Therefore, this zone remains slightly hot and moderately cold in summers and winters respectively.
- The daily average temperature here during summer is 40°C to 42.5°C and in winters, it is 10°C to 12.5°C.
- The hottest month of the year is May. Major rains take place in this region due to the South-West monsoon of the Arabian Sea.
- The rainfall distribution decreases from South-Eastern to North-Eastern parts of the zone.
Northern Plains
- This region has a continental climate. As this region is very far from sea, the summers are too hot and winters are too cold.
- The average temperature for summer is 40°C to 45°C and for winters, it is 15°C to 18°C.
- Average rainfall for this zone is even lesser than 75 cm because of which this zone lies in sub-tropical humid climatic zone.
- This region includes Bundelkhand, Rewa-Panna and Madhya Bharat.
Vindhyan/Satpura Mountain Region
- This region has a moderate type of climate. As this is hilly region, it is not too hot during summers and even the winters are moderate.
- Rainfall takes place in this region due to monsoon of Bay of Bengal and Arabian sea.
- Famous hill stations like Panchmari and Amarkantak are in this climatic zone.
Narmada Valley Region
- This region is situated very close to the Tropic of Cancer. Due to this, the summers in this region are extremely hot and the winters are moderately cold.
- The average maximum temperature in this zone is in the month of May and the minimum is in December.
- The average rainfall varies from 142.5 cm in the East to 57.5 cm in the West.
Baghelkhand Plateau Region
- This region has a monsoon climate because the Tropic of Cancer passes almost from the middle of the region.
- Here the summers are hot and humid whereas the winters are moderate and dry.
- The average temperature of summer is 35.5°C whereas in winters, it is 12.5°C. Average rainfall in this region is 125 cm.
Summary
Climatic Features of MP
- Madhya Pradesh has Monsoonal climate
- Regional variation
- Temperature variation
- Unequal distribution of the Rainfall
Factors affecting the climate of MP
- Geographical location and Longitudinal Extent
- Land locked (No coastal connection): High Temp Range.
- Distance from Sea: No moderating effect of the sea
- Tropic of Cancer passing through centre: Result in high Temp.
- Presence of mountain ranges.
- Activities of South-Westem Monsoon
Classification of Climate of MP
- According to A.R. Subramanian and T. Shreemannarayana.
- A R Subramanian and T Srimannarayana (1991) have classified the climate of Madhya Pradesh into 3 parts based on Madhya Pradesh's climatologically study.
1. Semi dry and Steppe Type
2. Hot Tropical
3. Tropical Humid and Dry Type.
Koppen's Classification
- Under the Koppen's climate classification Climate of Madhya Pradesh is divided into:
- "Hot dry-summer' climates (classified as Csa) and
- "Cool dry-summer" climates (classified as Csb) are often referred to as "Mediterranean"
- Hot semi-arid climates as Bsh.
Climate Zones of M.P.
- State is assumed to have 5 climatic zones;
- Malwa plateau
- Northern Plain (very hot and very cold).
3. Satpura mountain region (Average hot and average cold). Amarkantak and Panchmari are located in Satpura region.
4. Narmada valley region (very ho less cold)
5. Baghelkhand plateau (very hot moderate cold).
Seasons in Madhya Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh has a subtropical climate with three seasons:
- Hot dry summer (April-June),
- Monsoon rains (July-September)
- Cool and relatively dry winter.
Rainfall regions
- Madhya Pradesh is divided into four parts based on rainfall
- Areas with Excess Rainfall(more than 150cm)
- Areas with more than Average Rainfall(125-150cm)
- Areas with Average Rainfall(75-125cm) 125cm)
- Areas with low Rainfall(less than 75 cm)
Probable Questions
1. Very Short Questions
- What type of Climate Madhya Pradesh has?
- Name the place with minimum temperature in Madhya Pradesh?
- Name 1he place with maximum temperature in Madhya Pradesh?
- Unala
- Chaumasa
- Mawath
- Siyala
- Name the place with highest rainfall in Madhya Pradesh?
- Write the names of the climatic zones in Madhya Pradesh.
2. Short Questions
- Write the features of the climate of Madhya Pradesh.
- What are the factors affecting the climate of Madhya Pradesh?
- Explain the distribution of rainfall in Madhya Pradesh.
- Explain the reasons behind me variation in rainfall in Madhya Pradesh.
- Discuss me factors affecting the climate of Madhya Pradesh in detail.
3. Long questions
- Write the characteristics of me climate of Madhya Pradesh explaining the factors affecting them.
- Explain the pattern of rainfall distribution in Madhya Pradesh.




