Category :
MP State Exams
Chapter - 1 Madhya Pradesh: Introduction
Madhya Pradesh is a state of vivid culture, historical places, hill stations, and rich wildlife experiences. Madhya Pradesh which is also known as Hriday Pradesh lies in the middle of [India and shares its borders with five neighboring states. Spread over an area of 3,08,252 kilometer square covering 52 districts, MP has varied topographic and climatic characteristics. The state is completely landlocked. The state covers wide area of Indian plateau regions. The state is endowed with rich natural resources and fertile agro climatic conditions.
Madhya Pradesh forms part of peninsular plateau of India, lying in north central part. Most of the sate lies on the table land of Central India, which is a part of the oldest Gondwana Land. The natural boundary of Madhya Pradesh is determined by the Chambal River in the north and plains of Ganga-Yamuna, in South. In north-west Aravalli mountain range. In north-east Son River, and in South-East Amarkantak Plateau.
Geographical expansion of Madhya Parades is in between the latitude of \[21.6{}^\circ N-26.30{}^\circ N\] and longitude of \[{{74}^{o}}9'E-{{82}^{o}}{{48}^{}}E.\]
- Tropic of Cancer (\[23{}^\circ 30'\]North latitude) divides Madhya Pradesh into two equal parts, passing through 14 districts of the state- Ratlam, Ujjain, Agar-Malwa, Rajgarh, Sehore, Bhopal, Vidisha, Raisen, Sagar, Damoh, Katni, Jabalpur, Umaria and Shahdol.
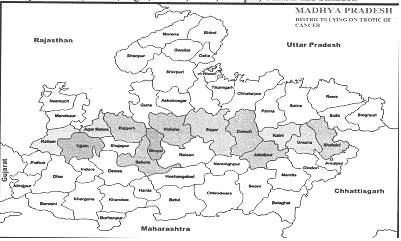
- Ratlam District is situated in the north of Tropic of Cancer. Bhopal is the only division through which the Tropic of Cancer passes through all the districts (Bhopal Sehore, Vidisha, Rajgarh, Raisen).
- Agar-Malwa was declared a district by separating it from Shajapur district on August 16, 2013, because of the separation of the district from Shajapur, now the Tropic of Cancer passes through Agar-Malwa district instead of Shajapur.
- Indian Standard Time (IST) Line or India's Meridian (\[82{}^\circ 30'\]East longitude) passes through Singrauli district under Rewa division of Madhya Pradesh.
- Singrauli district is situated between \[23{}^\circ 49\]' northern latitudes and 24°42' north latitudes and \[81{}^\circ 18'\] east longitudes and \[82{}^\circ 48'\] east longitudes. Before the formation of Singrauli district in Year 2008, the Indian standard time line passed through Sidhi district.
- The eastern and western border of Madhya Pradesh there is a difference of 34 minutes (8.4) hence sunrise half an hour earlier than the Singrauli in the most eastern district than in Alirajpur is the most western district of Madhya Pradesh. Alirajpur is located between\[22{}^\circ 18'19'\]northern latitude and \[74{}^\circ 21'9'\]east longitude and Singrauli is located \[23{}^\circ 49'\] north latitude to \[24{}^\circ 42'\]north latitude and \[81{}^\circ 18'\]east longitudes to \[82{}^\circ 48'\]east longitudes.
Political boundaries of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh is a land locked state, surrounded by five states. The northern border of Madhya Pradesh touches Uttar Pradesh, the southern boundary Maharashtra, the eastern boundary Chhattisgarh, the western boundary Gujarat, the north-west border, Rajasthan and the south-eastern boundary Chhattisgarh.
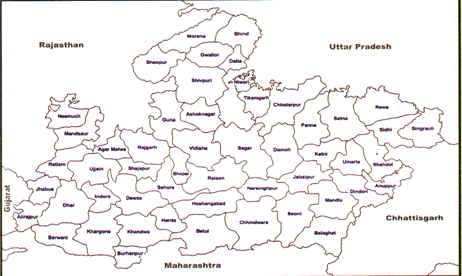
- Madhya Pradesh shares its boundaries with five states as i.e.
- U.P. in North (Maximum length)
- Chhattisgarh in East
- Rajasthan in West
- Gujarat in South-West (Minimum length)
- Maharashtra in South
- Notably, undivided Madhya Pradesh (1956-2000) was surrounded by 7 states i.e. Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
- 14 districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Morena, Bhind, Datia, Niwari, Tikamgarh, Chhatarpur, Panna, Satna, Rewa, Sidhi, Singrauli, Sagar Ashoknagar, Shivpuri shares boundary with Uttar Pradesh.
- 9 districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Khargone, Badwani, Betul, Khandwa, Chhindwara, Seoni, Balaghat, Alirajpur and Burhanpur shares boundaries with Maharashtra.
- 10 districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Morena, Shivpuri, Guna, Rajgarh, Neemuch, Mandsaur, Ratlam, Jhabua, Sheopur and Agar-Malwa shares boundaries with Rajasthan.
- 6 districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Sidhi, Shahdol, Balaghat, Dindori, Anuppur and Singrauli shares boundaries with Chhattisgarh.
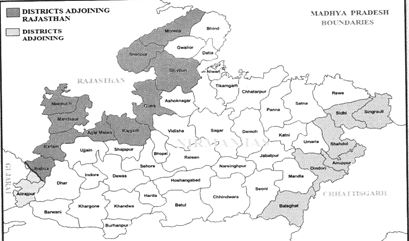
- 2 districts of Madhya Pradesh i.e. Jhabua and Alirajpur shares boundaries with Gujarat.
- Madhya Pradesh shares maximum boundary with Uttar Pradesh and least boundary with Gujarat.
- The river Chambal in the North, the ranges of Maikal and Kaimur in the East and rive Tapti in the South defines the natural boundaries of Madhya Pradesh.
Districts Sharing Boundaries with Two States
- Alirajpur district of Madhya Pradesh shares boundary with states of Gujarat an Maharashtra.
- Balaghat district of Madhya Pradesh shares boundary with Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra.
- Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh shares boundary with Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Singrauli district Madhya Pradesh shares boundary with Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisearh.
Intermediate districts
- Intermediate districts refer to districts whose boundaries do not touch other states. In Madhya Pradesh, there are eighteen intermediate districts.
Intermediate districts of Madhya Pradesh
- Hoshangabad, Harda, Damoh, Kami, Raisen, Narsinghpur, Vidisha, Ujjain, Dewas, Indore, Dhar, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Mandla, Bhopal, Sehore, Umaria and Shajapur.
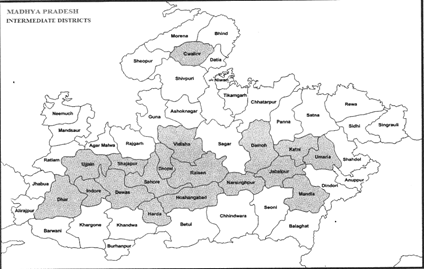
Bordering Districts
The border of Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh touches both state of Rajasthan and Gujarat. Jhabua is located in the north-western part of Madhya Pradesh, which extends from \[21{}^\circ 30'\] latitude to north latitude \[25{}^\circ 10'\]and longitude \[73{}^\circ 20'\]east longitude \[75{}^\circ 10'\]east longitudes.
|
Inter-State Borders of Madhya Pradesh
|
|
Uttar Pradesh (14)
|
Morena, Bhind, Datia, Shivpuri, Ashoknagar, Sagar, Tikamgarh, Niwari, Chhatarpur, Panna, Satna, Rewa, Sidhi, Singrauli.
|
|
Rajasthan (10)
|
Jhabua, Ratlam, Mandsaur, Neemuch, Agar-Malwa, Rajgarh, Guna, Shivpuri, Sheopur, Morena
|
|
Maharashtra (9)
|
Alirajpur, Badwani, Khargone, Khandwa, Burhanpur, Betui, Chhindwada, Seoni, Balaghat.
|
|
Gujarat (2)
|
Jhabua &Alirajpur
|
|
Chhattisgarh (6)
|
Sidhi, Singrauli, Shahdol, Anuppur, Dindori & Balaghat
|
|
States & Their Districts Adjoining Madhya Pradesh
|
|
Uttar-Pradesh (12)
|
Agra, Etawah Jhansi, Lalitpur, Hamirpur, Banda, Jalon,Prayagraj
(Allahabad), Mirzapur, Mahoba, Sonbhadra, Chitrakoot
|
|
Rajasthan (10)
|
Banswara, Pratapgarh, Chittorgarh, Bhilwara, Kota, Jhalawar, Baran, Sawai-Madhopur, Karali, Dholpur.
|
|
Maharashtra (9)
|
Dhule, Bhusawal, Amravati, Nagpur, Bhandara, Buldhana, Jalgaon, Nandurbar, Gondia
|
|
Chhattisgarh (7)
|
Surajpur, Koriya, Mungeli, Bilaspur, Kabirdham, Balrampur, Rajnandgaon
|
|
Gujarat (2)
|
Badodara, Dahod.
|
Districts of the M.P. Sharing Maximum boundary of adjoining states:-Alirajpur (Gujarat), Neemuch (Rajasthan), Niwari (Uttar Pradesh), Anuppur (Chhattisgarh), Betui (Maharashtra).
Topography
The state is traversed by the Satpura, Vindhya and Maikal ranges which run from east to west. The highest point of the state is Dhupgarh (1350m) peak of Mahadeo hills situated on the Satpura Range. Average elevation of the state is between 300 and 600 meters above mean sea level. Low lying areas are present in the narrow Narmada Valley in the central southern part of the state.
Number of significant rivers flow through this state. Thus with the presence of rivers, mighty plains and mountain ranges, Madhya Pradesh is endowed with varied physical features.
Natural Resources of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh is quite rich in term of natural resources. Minerals and power resources, forest, land and water resources are important among them-
- Mineral Resources:- Due to the wide area and the presence of rocks of many ages, Madhya Pradesh has abundant reserves of many minerals which have industrial importance. The huge deposits of cool, bauxite, copper, dolomite, lime stone, manganese and fireclay are of national importance. Apart from these Andalusite, biorites, clay, rock phosphate, sillimanite, ochre and steatite are also found in significant accumulations. There are indications of reserves of several other minerals that remain to be assessed Country's 90.18% of the country's diamond, 18.75% copper ore, about 35% of rock phosphate, 12% manganese ore and 8.78% coal reserves are in this state. There are huge deposites of dolomite and limestone.
- Forest Resources:- Forests are spread over more than 30.7% of total area of Madhya Pradesh. In this way state has very rich in vegetation compared to the country and many states. Teak and sal forest are majorly found here.
- M.P. state is rich in water resources as many major rivers namely Narmada, Chambal, Betwa, Ken, Sone, Tapti, Pench, Wainganga and Mahi originate from the state and flowing through other states.
- All the rivers of the state are rainfed under peninsular rivers component. The average surface water availability in the state at 75% dependability is estimated to be 81500 MCM. Out of this, 56,800 MCM allocated to the state and remaining 24,700 MCM of water allocated to neighboring states under various interstate agreements. The estimated quantity of ground water in the state is 34159 million cubic meter.
- Soil resources: According to the department of Land and Soil survey of India, five types of soils are found in the state. Which is as follows- Black, Red-Yellow, Alluvial, clayey and mixed soil.
Nick Names of the State
Madhya Pradesh is known by the many nicknames such as: Heart of India, Home of Rivers, Soya state, Tiger state etc.
Heart State (Hridaya Pradesh)
- As heart is located in the centre of the body. In the same way heart of country, Madhya Pradesh is located in the centre. Roads and railways form the arteries of the body and are connected through the state which makes the analogy with the heart well suited.
Soya State
- Madhya Pradesh has always been a front runner in the production of the Soybean thus it is being called the Soya State.[5.92million tones in 2018-19] (50-60% of total production in country.)
Home of Rivers (Nadiyon Ka Mayka)
- Hills and plateaus of Madhya Pradesh are the source of the many rivers such as Narmada, Tapi, Chambal etc. thus the state is called the Home of rivers.
Tiger State
- Madhya Pradesh is front runner in terms of the population of the Tigers thus it is also known as Tiger state.
- Tiger census Report- 2014: MP- No. of Tigers- 308
- Tiger census Report-2018: MP-No. of Tigers-526.
- Madhya Pradesh has bagged the coveted "Tiger Sate" status after the 2018 estimation saw it is home to 526 big cats, the highest in the country.
Probable Questions
1. Very Short Questions
- Describe the geographical location of the Madhya Pradesh
- Why Madhya Pradesh is called 'Hridaya Pradesh'?
- What is the total area of Madhya Pradesh?
- Write names of the state adjacent to Madhya Pradesh.
- Indian Standard time line passes through which district of Madhya Pradesh. ;
- Tropic of Cancer passes through how many districts of Madhya Pradesh? Write names of any three.
- Why Madhya Pradesh is called the Home of Rivers?
- Why Madhya Pradesh is called the Tiger state?
- Why Madhya Pradesh is called the Heart state (Hridaya Pradesh)?
- Name the states which surround M.P. and state its longitudinal and latitudinal extent. (MPPSC 2016)






