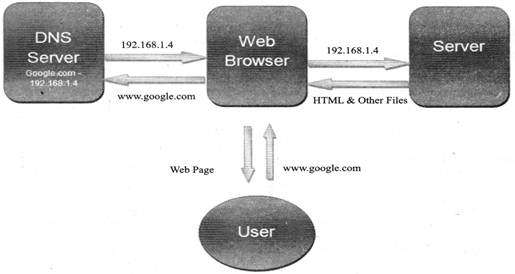
 USES AND WORKING OF INTERNET
Internet is today one of the most important part of our daily life. There are large numbers of things that can be done using the internet and so it is very important. You can say that with the progress in the internet we are progressing in every sphere of life as it not only makes our tasks easier but also saves a lot of time.
USES AND WORKING OF INTERNET
Internet is today one of the most important part of our daily life. There are large numbers of things that can be done using the internet and so it is very important. You can say that with the progress in the internet we are progressing in every sphere of life as it not only makes our tasks easier but also saves a lot of time.
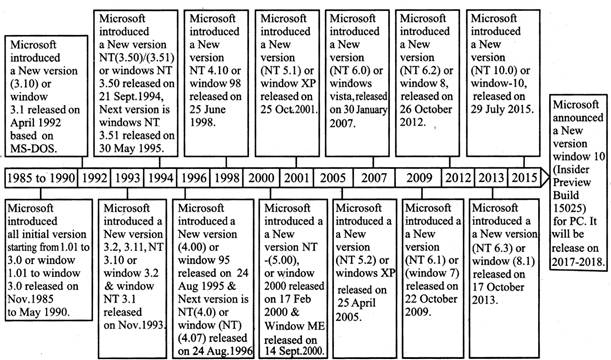 MICROSOFT WINDOWS VERSIONS
Microsoft Windows Versions for Personal Computers
The following details the history of Microsoft Windows Versions designed for personal computers (PCs).
MICROSOFT WINDOWS VERSIONS
Microsoft Windows Versions for Personal Computers
The following details the history of Microsoft Windows Versions designed for personal computers (PCs).
 SOME IMPORTANT MICROSOFT TERMINOLOGY
Microsoft Outlook
Its is a personal information manager from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft Office suite. Although often used mainly as an email application, it also includes a calendar, task manager, contact manager, note taking, journal, and web browsing.
It can be used as a stand-alone application, or can work with Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft SharePoint Server for multiple users in an organization, such as shared mailboxes and calendars, Exchange public folders, SharePoint lists, and meeting schedules.
Microsoft OneNote
Microsoft OneNote was included in all Microsoft Office offerings before eventually becoming completely free of charge. OneNote is available as a web application on Office Online, a Windows desktop app, a mobile app for Windows Phone, iOS, Android, and Symbian, and a Metro-style app for Windows 8 or later.
Microsoft OneNote is a freeware note-taking program. It gathers notes (handwritten or typed), drawings, screen clipping-sand audio commentaries. However, OneNote eventually became a core component of Microsoft Office; with the release of Microsoft Office 2013.
Microsoft Office Sway
Microsoft office Sway released by Microsoft in August 2015, Sways is stored on Microsoft's server and are tied to the user's Microsoft account. They can be viewed and edited from any web browser with a web app available in Office Online. They can also be accessed using apps for Windows 10 and iOS. Additional apps are currently in development for Android and Windows 10 Mobile.
Microsoft office, Sway allows users who have a Microsoft account to combine text and media to create a presentable website. Users can pull content locally from the device in use, or from internet sources such as. Bing, Facebook, One-Drive, and YouTube.
Microsoft Office 2010
Microsoft Office 2010 (code named Office 14) is a version of the Microsoft Office productivity suite for Microsoft Windows.
It is the successor to Microsoft Office 2007 and the predecessor to Microsoft Office 2013. Office 2010 includes extended file format support, user interface improvements, and a changed user experience.
A 64-bit version of Office 2010 is available, but not for Windows XP or Windows Server 2003. It is the first version of the productivity suite to ship in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
Office 2010 marks the debut more...
SOME IMPORTANT MICROSOFT TERMINOLOGY
Microsoft Outlook
Its is a personal information manager from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft Office suite. Although often used mainly as an email application, it also includes a calendar, task manager, contact manager, note taking, journal, and web browsing.
It can be used as a stand-alone application, or can work with Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft SharePoint Server for multiple users in an organization, such as shared mailboxes and calendars, Exchange public folders, SharePoint lists, and meeting schedules.
Microsoft OneNote
Microsoft OneNote was included in all Microsoft Office offerings before eventually becoming completely free of charge. OneNote is available as a web application on Office Online, a Windows desktop app, a mobile app for Windows Phone, iOS, Android, and Symbian, and a Metro-style app for Windows 8 or later.
Microsoft OneNote is a freeware note-taking program. It gathers notes (handwritten or typed), drawings, screen clipping-sand audio commentaries. However, OneNote eventually became a core component of Microsoft Office; with the release of Microsoft Office 2013.
Microsoft Office Sway
Microsoft office Sway released by Microsoft in August 2015, Sways is stored on Microsoft's server and are tied to the user's Microsoft account. They can be viewed and edited from any web browser with a web app available in Office Online. They can also be accessed using apps for Windows 10 and iOS. Additional apps are currently in development for Android and Windows 10 Mobile.
Microsoft office, Sway allows users who have a Microsoft account to combine text and media to create a presentable website. Users can pull content locally from the device in use, or from internet sources such as. Bing, Facebook, One-Drive, and YouTube.
Microsoft Office 2010
Microsoft Office 2010 (code named Office 14) is a version of the Microsoft Office productivity suite for Microsoft Windows.
It is the successor to Microsoft Office 2007 and the predecessor to Microsoft Office 2013. Office 2010 includes extended file format support, user interface improvements, and a changed user experience.
A 64-bit version of Office 2010 is available, but not for Windows XP or Windows Server 2003. It is the first version of the productivity suite to ship in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions.
Office 2010 marks the debut more... | 1.Rapid Skimming | \[\to \] | High Price | + | High Promotion |
| 2.Slow Skimming | more...
Introduction
According to Philip Kotler: Market segmentation is sub dividing of a market into homogeneous subset of customers. Where any subset may conceivably be selected as a market target to be reached with a distinct Marketing Mix
According to American. Marketing Association: "Market segmentation refers to dividing the heterogeneous market into smaller customer divisions having certain homogeneous characteristics that can be satisfied by the
Firm Market segment is a large identifiable group of customers within a market which shows a predictable pattern of behavior in buying situation, and which can be profitably reached by means of distribution and communication. Market segmentation is the process of dividing the total market into a number of homogenous subgroups or submarkets and designing Products to satisfy the needs of each of these subgroups. A market can be segmented by various bases and industrial markets are segmented somewhat from consumer markets like ?
(i) Geographic Segmentation: In this segmentation customers are segmented on the geographical basis. It includes District, Division, Country, City, Town /Village etc.
(ii) Demographic Segmentation: In this segmentation customers are segmented on the demographic basis. It includes Age, Sex, Marital status Occupation Profession, Education etc.
(iii) Psychographic Segmentation: In this segmentation customers are segmented on the psychographic basis. It includes Perception, culture, Attitudes, Need or Want of customers. Thought etc.
(iv) B5dsehavioral Segmentation: In this process customers are segmented on the basis of behavior it includes Loyalty, Brand Loyalty, and Consumption rate. Buying Occasion, Buying Principles. Market segmentation is a "Consumer-oriented philosophy'. We first identify customers' needs in a sub-market. Then we design a product and or a marketing programmer to reach the sub-market and satisfy those needs.
Characteristics of Market Segmentation:
(i) It should be measurable i, e. it should possible to measure the size of the segment in, terms of sales generated.
(ii) The segment should be attractive that is substantial in size.
(iii) It should be accessible by communication.
more...
Branding and Packaging
Brand Brand is a name, term, symbol, design, or a combination of these which is intended to differentiate the goods of a company from competitors' goods.
Branding: It is the practice of creating a unique name for a product and giving marketing support to that name. He has to decide whether the firm?s product will be marketed under a brand name or a generic name. Generic name refers to the name of the whole class of the product. For example a soap, a camera, etc.
When products were sold by generic names, it was very difficult for the marketers to distinguish their products from that of their competitors'. Thus most marketers give a name to their products, which helps in identifying and distinguishing their products, which helps in identifying and distinguishing their products from the competitors' products. This process of giving a name or a sign or a symbol is called Branding.
Brand Name: The pronounceable part of a Brand is called Brand Name Brand Name is the verbal component of Brand. For example?Lux, Grainier Raymond?s, TOYOTA motors etc.
Brand Mark. Brand mark or logo is the distinctive color, letter/ symbol, alphabet, which is used for the brand.
Brand Loyalty: Brand loyalty or customer loyalty is that state in which customer buys a brand not only because of habit, but also due to a preference or liking towards that brand. Habit combined with favorable attitude called loyalty. A strong loyal customer finds it very difficult to switch over to another brand and considers his chosen brand as much more superior. Although in reality there can be presence of similar an even better brands in the market.
Product Line: Product line is a group of related items which are aimed at the same target customers or which are in a common price range or which are distributed through the same network and which satisfy a common need. For example ? a range of Raymond?s cloth is a product line at it satisfies on need for different market segments. Similarly, a group of cosmetic is a product line as it satisfies different but inflated needs of one market segment say rich urban more...
Product Life Cycle
Introduction
After a new product/service has been developed and introduced in the market, the different stages through which it passes over time is known as the product/service life cycle. Generally, there are four stages in a product service life cycle namely, launch, growth, maturity, and decline. These four stages are discussed in detail below. Product life cycle (PLC) indicates the sales history of a product over time with its introduction in the market till it dies or ceases to exist as it is no longer relevant.
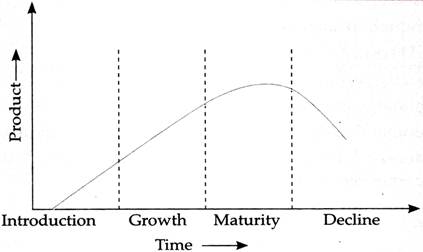 Introduction:
This is the first stage in the product life cycle wherein a product or service is introduced in the market. The main aim of marketers at this stage is to increase product/service awareness among customers. An organization can adopt any strategy in the market like skimming or penetration, depending on the size of its operations. Organizations may not earn profits at this stage as they have to cover the costs incurred.
Growth: The brand awareness created in the earlier stage helps an organization to earn revenues and reap profits at this stage. The markets continue to grow as more and more customers buy the service. Further organizations invest in promotional activities with the aid of profits. Thus, marketers strive to increase their market share and also maximize their profit margins.
Maturity: Due to high competition and limit growth in this stage, companies try to maintain their market share. Marketers try to modify their services to tap any potential for growth. They also try to increase the quality and efficiency of their services to maintain customer loyalty. They should be discreet in deciding their marketing expenses and in allocating their finances.
Decline: This is the final stage in the life cycle of a product/service and is characterized by reduction in demand and consequently a decrease in revenues and profit margins. The introduction of new services in the market or changes in customer preferences reduces demand. The best option for marketers is to discontinue the service if they cannot afford to modify o reposition it.
Factors affecting Product Life Cycle:
(i) Rate of technical change.
(ii) Rate of more...
Introduction:
This is the first stage in the product life cycle wherein a product or service is introduced in the market. The main aim of marketers at this stage is to increase product/service awareness among customers. An organization can adopt any strategy in the market like skimming or penetration, depending on the size of its operations. Organizations may not earn profits at this stage as they have to cover the costs incurred.
Growth: The brand awareness created in the earlier stage helps an organization to earn revenues and reap profits at this stage. The markets continue to grow as more and more customers buy the service. Further organizations invest in promotional activities with the aid of profits. Thus, marketers strive to increase their market share and also maximize their profit margins.
Maturity: Due to high competition and limit growth in this stage, companies try to maintain their market share. Marketers try to modify their services to tap any potential for growth. They also try to increase the quality and efficiency of their services to maintain customer loyalty. They should be discreet in deciding their marketing expenses and in allocating their finances.
Decline: This is the final stage in the life cycle of a product/service and is characterized by reduction in demand and consequently a decrease in revenues and profit margins. The introduction of new services in the market or changes in customer preferences reduces demand. The best option for marketers is to discontinue the service if they cannot afford to modify o reposition it.
Factors affecting Product Life Cycle:
(i) Rate of technical change.
(ii) Rate of more... Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |