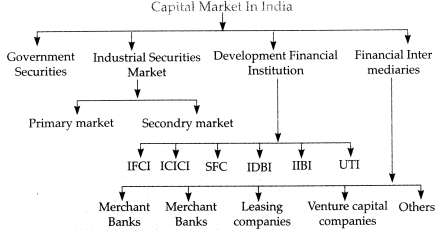
 · Thus the capital market embraces the system through which the public more...
· Thus the capital market embraces the system through which the public more...  A computer is a manmade electronic machine which stores, reads and processes data to produce meaningful information as output. It works very fast and does not make mistakes but its capacity is limited. It is made of English word 'compute?. It operates under the control of a set of instructions that is stored in its memory unit. A computer accepts data from an input device and processes it into useful information which it displays on its output device. Actually, a computer is a collection of hardware and software components that helps us to accomplish many different tasks. Hardware consists of the computer itself and includes a CPU, a monitor, a keyboard, a mouse and any equipment connected to it. Software is the set of instructions that the computer follows in performing a task.'
Calculators and Calculation
A calculator is a small electronic device used for doing mathematical calculations. A calculator cannot be used for writing letters or awing images, while a computer can be used to calculate, draw images 'write letters, and do many other things as well.
Human Being and Computers
Computers cannot work on their own. They do what we want them to do, only we give them the right command. Its memory is better than human memory. It can't forget anything, it has saved, so it is also called an artificial intelligence
Comparison between human beings and computers
A computer is a manmade electronic machine which stores, reads and processes data to produce meaningful information as output. It works very fast and does not make mistakes but its capacity is limited. It is made of English word 'compute?. It operates under the control of a set of instructions that is stored in its memory unit. A computer accepts data from an input device and processes it into useful information which it displays on its output device. Actually, a computer is a collection of hardware and software components that helps us to accomplish many different tasks. Hardware consists of the computer itself and includes a CPU, a monitor, a keyboard, a mouse and any equipment connected to it. Software is the set of instructions that the computer follows in performing a task.'
Calculators and Calculation
A calculator is a small electronic device used for doing mathematical calculations. A calculator cannot be used for writing letters or awing images, while a computer can be used to calculate, draw images 'write letters, and do many other things as well.
Human Being and Computers
Computers cannot work on their own. They do what we want them to do, only we give them the right command. Its memory is better than human memory. It can't forget anything, it has saved, so it is also called an artificial intelligence
Comparison between human beings and computers
| Human being | computer | |||||||||||||||
| Human being are slow in doing calculation | Computers to can do complex calculations in second | |||||||||||||||
| Human beings cannot remember lots of thing at one time. | Computer can store and remember a large amount Of information at on time. | |||||||||||||||
| Human being can make mistakes. | more...
Development of Computer
Introduction
Computer is a man ?mad electronic machine that change the way we work live and play .A machine that has done all this and more ,now exits in invention is the computer the computer is a one of the most powerful innovation in human history .the electronic computer has been around for over a half century butt its ancestor abacus has been around for 2000 years however only in the last 40 year it has changed the of lifestyle from the first wooden abacus to the latest high speed microprocessor the computer has changed the nearly every aspect of people lives for the better .with the use of computer people are suddenly able to perfumed a large amount of computation at dazzling speed information can be crunched ,organized and display in the blink of an eye .thing that were only dreams a few years ago are now possible due to computer.
Evolution of computers
1. Abacus: The abacus one of the earliest known computation device. It is a tool that help in calculating answer of arithmetic problems. It is simple a wooden rack holding parallel wires on which beads are strung calculation are done by manipulating the beads the abacus was enveloped China about 5000 years ago so successful that its use spread from china to many other countries
 2. Pascal Calculator: the first real mechanical calculating was invented by French scientist and mathematical Blaise Pascal, around 1645. the device was constructed by interlocking gears representing the number 0 to 9 it was only able to do addition and subtraction so it is called adding machine
2. Pascal Calculator: the first real mechanical calculating was invented by French scientist and mathematical Blaise Pascal, around 1645. the device was constructed by interlocking gears representing the number 0 to 9 it was only able to do addition and subtraction so it is called adding machine
 3. Analytical Engine: In 1801, Joseph Marie Jacquard perfected the loom. Using holes punched into a series of connected cards, Jacquard was able to control the weaving of fabrics the lacquered loom not only cut back on the around of human labor, but also Allowed for patterns to be stored now on cards and to be utilized over and we again to achieve the same product. In 1820Babbage failed to build a fully operational model of Difference or Analytical Engine. In 1842Lady Lovelace wrote Demonstration program and her contribution to binary arithmetic was later used by John Von Neumann in developing the modern computer. So she is often regarded as the "first computer programmer
3. Analytical Engine: In 1801, Joseph Marie Jacquard perfected the loom. Using holes punched into a series of connected cards, Jacquard was able to control the weaving of fabrics the lacquered loom not only cut back on the around of human labor, but also Allowed for patterns to be stored now on cards and to be utilized over and we again to achieve the same product. In 1820Babbage failed to build a fully operational model of Difference or Analytical Engine. In 1842Lady Lovelace wrote Demonstration program and her contribution to binary arithmetic was later used by John Von Neumann in developing the modern computer. So she is often regarded as the "first computer programmer
 4. Herman Hollerith and Punch Card: In 1890 the united more...
4. Herman Hollerith and Punch Card: In 1890 the united more...
Input and Output Device
Introduction
There are a lot of devices that are attached to the computer. Some of them are input devices while others are output devices. These devices are collectively referred to as peripheral devices Input Devices: Information or data that is entered into a computer is called input. It can come from an external source and be fed into computer software. It is done by an input device. In other words, devices that are used to give instruction to the computer are known as input devices. They send information into the CPU. Without any input device that computer would simply be a display device like a TV. Some most commonly used input devices are given below
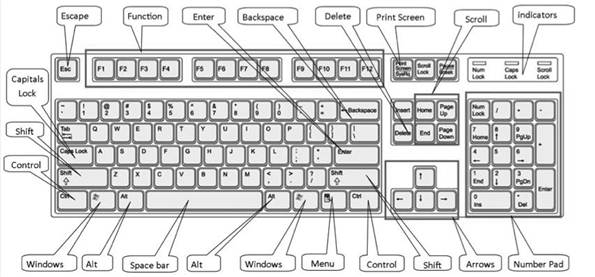 1. more...
1. more...
Memory
Computer memory refers to the devices that are used to store data or programs on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer. Any data or instruction entered into the memory of a computer is considered as storage. It is one of the fundamental components of all modern computers coupled with a central processing unit. For central processing unit to process the input data, there must be a place for storing the data and instruction this is provided in the memory unit.
Data Representation
The memory unit of the CPU consists of a large number of cells called location. Each location is identified with a unique label called an address which is used to store data or instruction. The CPU keeps track of all data and program instructions through the use of memory address. Computer represents information in binary code, written as sequences of so and Is. '1' represents an on state and '0' represents an off state in a circuit. To store the data in location is called 'Write' and fetch the data in location is called 'Read' Each location can contain fixed number of bits called word length. Word length can be 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits. Bit is smallest unit of binary digit. A word i an arrangement of binary digits. abet is the unit of memory which is a group of 8 bits in EBCDIC ( Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) and 7 bits in ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange).
Types of Memory
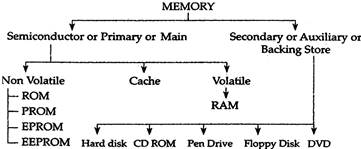 Memory usually refers to a form of semi-conductor storage known a Random-Access Memory (RAM) and sometimes other forms of fast but temporary storage. It is a place in the computer system where data and are tenderly storage it is a place in the computer system where data and program Are temporarily stored in internal storage area in the computer the terms memory identify data storage that comes in the forms of chips Similarly, storage today more commonly refers to mass storage such as optical disks, forms of magnetic storage such as hard disk drives, and other types slower than RAM, but of a more permanent nature. The primary device that a computer uses to store information is hard drive. Memory and storage were respectively called main memory and secondary storage. The terms internal memory and external memory are also used. Storage an memory differ with respect to price reliability and speed
Primary or Main Memory or Semiconductor Memory or Internal Memory
Computer memory usually refers to the semiconductor technology that is used to store information in electronic devices. Current primary computer memory makes use of 1C consisting of silicon-based transistors
There are two main types of memory
Volatile and Non-volatile. Volatile memory is computer memory more...
Memory usually refers to a form of semi-conductor storage known a Random-Access Memory (RAM) and sometimes other forms of fast but temporary storage. It is a place in the computer system where data and are tenderly storage it is a place in the computer system where data and program Are temporarily stored in internal storage area in the computer the terms memory identify data storage that comes in the forms of chips Similarly, storage today more commonly refers to mass storage such as optical disks, forms of magnetic storage such as hard disk drives, and other types slower than RAM, but of a more permanent nature. The primary device that a computer uses to store information is hard drive. Memory and storage were respectively called main memory and secondary storage. The terms internal memory and external memory are also used. Storage an memory differ with respect to price reliability and speed
Primary or Main Memory or Semiconductor Memory or Internal Memory
Computer memory usually refers to the semiconductor technology that is used to store information in electronic devices. Current primary computer memory makes use of 1C consisting of silicon-based transistors
There are two main types of memory
Volatile and Non-volatile. Volatile memory is computer memory more... Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |