Nutrition in Plants
Synopsis
- Green plants, synthesise their food themselves by the process of photosynthesis. They are autotrophs. Non-green plants and animals are heterotrophs.
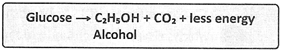
- Photosynthesis can be summarised as follows.
\[\text{carbon}\,\text{dioxide+}\,\text{water}\xrightarrow[\text{Chlorophyll}]{\text{Sunlight}}\text{Glucose+Oxygen}\]
- Photosynthesis provide food and oxygen to all the living organisms.
- The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
- Gaseous exchange in the leaves takes place through tiny pores, which are generally located on the lower surface of a leaf called stomata.
- In some plants like crotons, the green colour of the chlorophyll is hidden by other pigments and appear dark red.
- Some plants like pitcher plant and venus fly trap, feed on trapped insects and fulfill their nitrogen requirement. They are called insectivorous plants.
- The organisms which feed on dead and decaying organisms are called saprophytes. e.g., moulds, mushrooms and some bacteria.
- Plants which depend completely on other plant for food and habitat are called parasites. e.g., cuscuta.
- Some plants, like mistle toe, depend on other plant as well as prepare their own food. They are called partial parasites.
- Symbiosis is a beneficial relationship between two organisms.