 To Create a presentation, follow the steps listed below:
v Click on File menu.
v Select New option.
v The new presentation dialog box will appear.
v Click on blank presentation option or any of the template design. Shortcut key to create a new blank presentation is Ctrl + N.
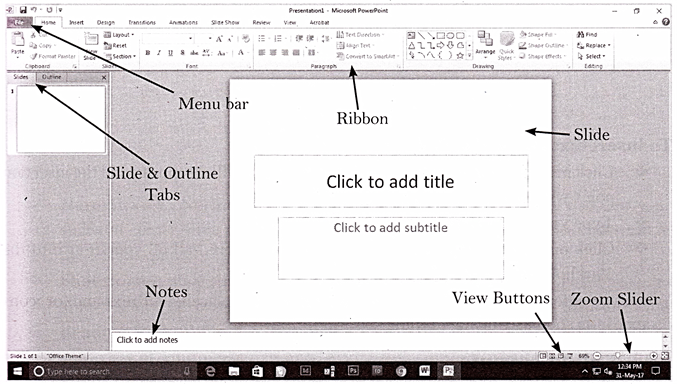
Slide Basics
A slide is an individual page of a presentation. Slides keeps attention of audience during a presentation and provide additional supporting information in textual or graphic format. Slides contain placeholders or areas on a slide that are enclosed by dotted borders. Placeholders can contain many different items, including text, pictures, and charts. Some placeholders have placeholder text, or text that you can replace, and thumbnail-sized icons that represent specific commands such as Insert Picture, Insert Chart, and Insert Clip Art. Hover over each icon to see the type of information you can insert.
To Create a presentation, follow the steps listed below:
v Click on File menu.
v Select New option.
v The new presentation dialog box will appear.
v Click on blank presentation option or any of the template design. Shortcut key to create a new blank presentation is Ctrl + N.
Slide Basics
A slide is an individual page of a presentation. Slides keeps attention of audience during a presentation and provide additional supporting information in textual or graphic format. Slides contain placeholders or areas on a slide that are enclosed by dotted borders. Placeholders can contain many different items, including text, pictures, and charts. Some placeholders have placeholder text, or text that you can replace, and thumbnail-sized icons that represent specific commands such as Insert Picture, Insert Chart, and Insert Clip Art. Hover over each icon to see the type of information you can insert.
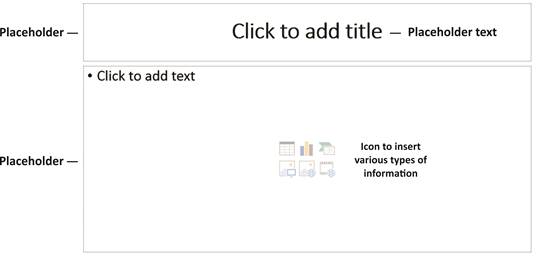 To insert text into a placeholder:
v Click inside the placeholder. The placeholder text will disappear, and the insertion point will appear.
v Type your text once the insertion point is visible.
v Click outside the placeholder when you have entered all of your text into the placeholder.
When you enter text or use the icons to insert items, the placeholder text and/or icons disappear as soon as you start typing.
About Slide Layouts
The placeholders are arranged in different layouts that you can select when you insert a new slide or that can be applied to existing slides.
A slide layout arranges your slide content. Layouts contain different types of placeholders you can use, depending on what information you want to include in your presentation. Each layout has a descriptive name, but the image of the layout shows you how the placeholders are arranged on the slide. You can use layout by clicking Layout button in the Slides group.
Creating Graphics in a Slide
PowerPoint allows the user to edit text and more...
To insert text into a placeholder:
v Click inside the placeholder. The placeholder text will disappear, and the insertion point will appear.
v Type your text once the insertion point is visible.
v Click outside the placeholder when you have entered all of your text into the placeholder.
When you enter text or use the icons to insert items, the placeholder text and/or icons disappear as soon as you start typing.
About Slide Layouts
The placeholders are arranged in different layouts that you can select when you insert a new slide or that can be applied to existing slides.
A slide layout arranges your slide content. Layouts contain different types of placeholders you can use, depending on what information you want to include in your presentation. Each layout has a descriptive name, but the image of the layout shows you how the placeholders are arranged on the slide. You can use layout by clicking Layout button in the Slides group.
Creating Graphics in a Slide
PowerPoint allows the user to edit text and more... 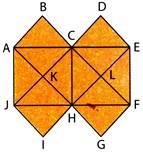 (a) 7 (b) 6 (c) 9 (d) 10
Explanation (a):
The squares composed of two components each are ABCK, CDEL, JKHI, HLFG and KCLH, i.e. 5 in number.
The squares composed of four components each are ACHJ and CEFH, i.e. 2 in number.
(a) 7 (b) 6 (c) 9 (d) 10
Explanation (a):
The squares composed of two components each are ABCK, CDEL, JKHI, HLFG and KCLH, i.e. 5 in number.
The squares composed of four components each are ACHJ and CEFH, i.e. 2 in number.
 (a)
(a) 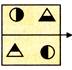 (b)
(b) 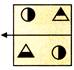 (c)
(c) 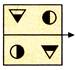 (d)
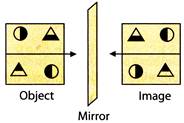
(d) 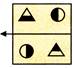 Explanation (d):
The right side of an object becomes left side of its image in the mirror.
Explanation (d):
The right side of an object becomes left side of its image in the mirror.
 WATER IMAGE
The water image of an object is the vertically inverted (upside down) image of the object.
The position of the water layer is horizontally just below the object.
2. Select the water image of the given word.
E M A N A T E
(a)
WATER IMAGE
The water image of an object is the vertically inverted (upside down) image of the object.
The position of the water layer is horizontally just below the object.
2. Select the water image of the given word.
E M A N A T E
(a) 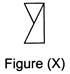 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (c):
Figure (c) embeds the figure (X).
Look at below:
Explanation (c):
Figure (c) embeds the figure (X).
Look at below:
 So, the correct option is (c).
Figure Formation
This section deals with the following types of problems:
I. Formation of a Figure from its Segments: In such type of problems, all the parts to form a figure are given. A student is required to identify the figure so formed out of the four options.
II. Choosing a Pattern which has the same components as a given pattern: In such type of problems, a pattern of several components is given. A pattern out of four options contains the same components. A student is required to choose such pattern.
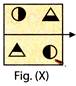
2. Which of the figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) can be formed from the pieces given in Fig. (X)?
So, the correct option is (c).
Figure Formation
This section deals with the following types of problems:
I. Formation of a Figure from its Segments: In such type of problems, all the parts to form a figure are given. A student is required to identify the figure so formed out of the four options.
II. Choosing a Pattern which has the same components as a given pattern: In such type of problems, a pattern of several components is given. A pattern out of four options contains the same components. A student is required to choose such pattern.
2. Which of the figures (a), (b), (c) and (d) can be formed from the pieces given in Fig. (X)?
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c) 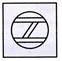 (d)
(d) 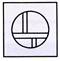 Explanation (d):
Only figure (d) can be formed from the pieces given in Fig. (X).
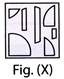
3. Select from the options in which the specified components of the given Fig. (X) are found.
Explanation (d):
Only figure (d) can be formed from the pieces given in Fig. (X).
3. Select from the options in which the specified components of the given Fig. (X) are found.
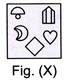 (a)
(a) 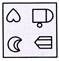 (b)
(b) 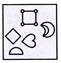 (c)
(c) 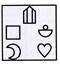 (d)
(d) 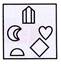 Explanation (a):
Figure (a) consists of all the components of figure (X).
Construction of Squares
Such type of problems are on the basis of the geometrical figures.
A group of some geometrical figures is provided.
A student is required to identify that members of the group which can more...
Explanation (a):
Figure (a) consists of all the components of figure (X).
Construction of Squares
Such type of problems are on the basis of the geometrical figures.
A group of some geometrical figures is provided.
A student is required to identify that members of the group which can more... 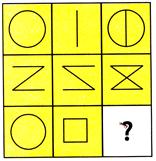 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b)  (c)
(c)  (d)
(d)  Explanation (a):
In each row, the third figure is the combination of the first and second figure.
Explanation (a):
In each row, the third figure is the combination of the first and second figure. 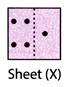 (a)
(a) 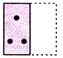 (b)
(b) 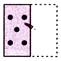 (c)
(c) 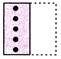 (d)
(d)  Explanation (b):
Clearly, the right half of the sheet (X) is put on the left half.
The combination of the design in left half and mirror image of the design in the right half will appear on the folded sheet.
This combination is shown in figure (b).
So, the correct option is (b).
Cutting a Folded Paper
In such type of problems, a paper is folded twice or thrice. Then one or more pieces of it are cut. After this the paper is absolutely unfolded. In this situation the paper has many cuts or holes on it. So, it contains a pattern.
A student is required to identify a figure from given four options that shows the similar paper sheet as the pattern made.
Usually, the paper sheet is folded along the dotted lines marked on it. And arrows show the directions of the folds.
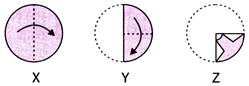
2. There are three figures marked X, Y and Z on a circular paper. Figures X and Y show the two consecutive folds of the paper. And figure Z shows the cuts on the folded paper.
Choose one figure from the four options that resembles the unfolded form of the sheet Z.
Explanation (b):
Clearly, the right half of the sheet (X) is put on the left half.
The combination of the design in left half and mirror image of the design in the right half will appear on the folded sheet.
This combination is shown in figure (b).
So, the correct option is (b).
Cutting a Folded Paper
In such type of problems, a paper is folded twice or thrice. Then one or more pieces of it are cut. After this the paper is absolutely unfolded. In this situation the paper has many cuts or holes on it. So, it contains a pattern.
A student is required to identify a figure from given four options that shows the similar paper sheet as the pattern made.
Usually, the paper sheet is folded along the dotted lines marked on it. And arrows show the directions of the folds.
2. There are three figures marked X, Y and Z on a circular paper. Figures X and Y show the two consecutive folds of the paper. And figure Z shows the cuts on the folded paper.
Choose one figure from the four options that resembles the unfolded form of the sheet Z.
 (a)
(a)  (b)
(b) 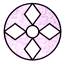 (c)
(c)  (d)
(d) 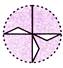 Explanation (b):
In figure (X), the circular sheet of paper has been folded along the vertical line of symmetry so that the left half of the sheet overlaps the right half.
In figure (Y), the sheet is folded further to a quarter.
In figure (Z), the paper is cut along the design.
Clearly, the design will be created in each quarter of the paper.
Thus, when the paper is unfolded, a design will appear symmetrically over it and the paper will then appear as shown in figure (b).
So, the correct option is more...
Explanation (b):
In figure (X), the circular sheet of paper has been folded along the vertical line of symmetry so that the left half of the sheet overlaps the right half.
In figure (Y), the sheet is folded further to a quarter.
In figure (Z), the paper is cut along the design.
Clearly, the design will be created in each quarter of the paper.
Thus, when the paper is unfolded, a design will appear symmetrically over it and the paper will then appear as shown in figure (b).
So, the correct option is more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
