Atomic Mass
It is the mass of an atom of an element or it is defined as the quantity of mass equal to the one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon 12.

Relative Atomic Mass
It is defined as the number of times an element of an atom is heavier than one twelfth of an atom of carbon 12.
Relative atomic mass \[=\frac{\text{Mass of one atom of the element}}{\frac{1}{12}\times \text{Mass of one atom of C}-\text{12}}\]

Gram Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of an element expressed in gram is called the gram atomic mass of that element.

Molecules
Molecules are the smallest particle of the substance, element or compound which can exist in Free State under the normal condition of temperature and pressure. The total number of atoms, of all types, present in one molecule of a substance is called its atomicity.
For example:
Atomicity of \[{{O}_{2}}\] is 2 and that of \[C{{O}_{2}}\] is 3. There are different types of molecules. The molecules having only one kind of atom is called monoatomic molecules, such as \[He,\,Ne,\,\,Ar\] etc.
The molecules containing two atoms are called diatomic molecules, such as \[{{O}_{2}},\,\,{{H}_{2}},\,\,C{{l}_{2}}\] etc.
The molecules containing three atoms are called triatomic molecules, such as \[C{{O}_{2}},\,\,{{O}_{3}},\,\,{{H}_{2}}O,\,\,N{{O}_{2}}\] etc.
The molecules containing four atoms are called tetratomic molecules, such as \[{{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}},\,\,N{{H}_{3}},\,{{P}_{4}}\] etc.
The molecules containing five atoms are called pentatomic molecules, such as \[NH{{O}_{3}},\,C{{H}_{4}}\] etc.
The molecules of an atom contains same kind of atoms. For example \[{{O}_{2}},\,\,{{H}_{2}},\,C{{l}_{2}}\] are all molecules of the atoms.
The molecules of the compound contains atoms of different elements. For example \[C{{O}_{2}},\,\,{{H}_{2}}O,\] etc.

Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of a substance is defined as the sum of atomic mass of all the atoms present in the substance.
For example:
The molecular mass of \[C{{O}_{2}}=1\times 12+2\times 16=44\,\,\text{amu}\].

Gram Molecular Mass
The molecular mass of the substance expressed in gram is called the gram molecular mass.

Mole Concept
A mole is a unit for expressing the smallest unit of matter, such as proton, electron, atoms, ions, etc. The number of atoms present in one gram atom of an element is equal to the \[6.023\times {{10}^{23}}\]. Thus one mole of a substance is equal to \[6.023\times {{10}^{23}}\] atoms. This constant is also called the Avogadro's constant or
Avogadro’s number. Hence we can define mole as the amount of substance which contains same number of particles as the number of carbons atoms present in 12g of C-12 isotopes of carbon.
Thus, 1 mole = gram atomic mass of atom \[=6.023\times {{10}^{23}}\] atoms
more...
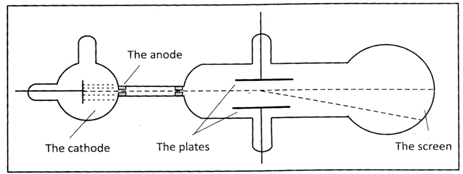 Through the gap, a small beam of cathode rays got out of the area of the cathode and anode influence. Next, the beam passed through a long vacuum tube and fell on a fluoroscopic screen leaving there a fluorescent sign. In the vacuum tube, Thomson also put two metal plates connected to a battery. That way he could create voltage between the plates, where the beam had its path. The field was directed perpendicularly to the cathode rays beam. It emerged that under the influence of voltage the beam was deflected (the spot on the screen appeared in a different place. It was the final evidence that cathode rays consisted of charged particles otherwise the beam couldn't be deflected by the electric field. The direction of the deflection also shows the charge of the particles. It emerged to of the negative charge.
It was R.A. Millikan who first measure the charge on electron in 1909, by his famous oil drop experiment. The magnitude of charge on the electron is \[\mathbf{1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-19}}}\,\mathbf{coulomb}\]. The relative charge of the electron is-1. The mass of the electron is found to be
\[\mathbf{9}\mathbf{.1\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-31}}}\,\mathbf{kg}\]. The relative mass of an electron is approximately equal to \[\frac{1}{1840}\] of the mass of the hydrogen atom.
Through the gap, a small beam of cathode rays got out of the area of the cathode and anode influence. Next, the beam passed through a long vacuum tube and fell on a fluoroscopic screen leaving there a fluorescent sign. In the vacuum tube, Thomson also put two metal plates connected to a battery. That way he could create voltage between the plates, where the beam had its path. The field was directed perpendicularly to the cathode rays beam. It emerged that under the influence of voltage the beam was deflected (the spot on the screen appeared in a different place. It was the final evidence that cathode rays consisted of charged particles otherwise the beam couldn't be deflected by the electric field. The direction of the deflection also shows the charge of the particles. It emerged to of the negative charge.
It was R.A. Millikan who first measure the charge on electron in 1909, by his famous oil drop experiment. The magnitude of charge on the electron is \[\mathbf{1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-19}}}\,\mathbf{coulomb}\]. The relative charge of the electron is-1. The mass of the electron is found to be
\[\mathbf{9}\mathbf{.1\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-31}}}\,\mathbf{kg}\]. The relative mass of an electron is approximately equal to \[\frac{1}{1840}\] of the mass of the hydrogen atom.
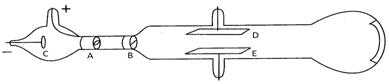 When he applied high voltage under low pressure, he observed a faint red glow on the wall behind the cathode. These rays were also called the canal rays. When these rays were allowed to pass through the charge plates placed above and below the discharge tube found that these rays were deflected towards the negative plate. He conclude that these rays must possess positive charge and hence were called protons. The charge on proton was found to be \[\mathbf{1}\mathbf{.6\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-19}}}\,\mathbf{coulomb}\] coulomb and the relative charge was + 1. The mass of proton was found to be \[\mathbf{1}\mathbf{.673\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-24}}}\,\mathbf{g}\]. The relative mass of proton was found to be 1 amu.
When he applied high voltage under low pressure, he observed a faint red glow on the wall behind the cathode. These rays were also called the canal rays. When these rays were allowed to pass through the charge plates placed above and below the discharge tube found that these rays were deflected towards the negative plate. He conclude that these rays must possess positive charge and hence were called protons. The charge on proton was found to be \[\mathbf{1}\mathbf{.6\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-19}}}\,\mathbf{coulomb}\] coulomb and the relative charge was + 1. The mass of proton was found to be \[\mathbf{1}\mathbf{.673\times 1}{{\mathbf{0}}^{\mathbf{-24}}}\,\mathbf{g}\]. The relative mass of proton was found to be 1 amu.
