Sources of Business Finance
Facts that Matter
- No business can be started, run or expanded without finance.
- There are many sources of finance. Each source has its own merits and demerits.
- Business needs to choose right source of finance to make the best use of it.
Business Finance
It refers to the money required for carrying out business activities.
Significance of Business Finance
- Business is concerned with production and distribution of goods and services for the satisfaction of needs of society.
- No business can be carried without availability of adequate funds.
- As soon as a decision is taken to start a business, requirement of funds initiates.
- Finance is called 'life blood of a business'.
- It is very important to assess financial needs of the organization and the identification of various sources of finance.
Classification of Sources of Funds
Overall financial requirements can be classified into:
Ø Fixed Capital Requirements
Ø Working Capital Requirements.
- Fixed capital is a capital used to buy land and building, plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures etc.
- Working capital requirements refer to capital required for meeting running expenses of business.
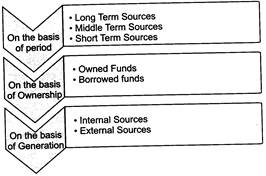
On the basis of period, funds can be categorized into
Ø Long term sources
Ø Middle term sources
Ø Short term sources
- Long term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period exceeding 5 years.
- Middle term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period of one to five years.
- Short term sources fulfil the financial requirements of an enterprise for a period not exceeding one year.
On the basis of ownership, funds can be classified into
Ø Owner's Funds
Ø Borrowed Funds
- Owner's funds are the funds that are provided by the owners of an enterprise.
- Borrowed funds refer to the funds raised through borrowings.
Equity Shares
Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in respect of payment of annual dividend and repayment of capital.
Merits of Equity Shares
- It is ideal for adventurous investors
- There is no obligation as to dividend
- It provides credit standard
- It is a source of fixed capital
- It creates no charge on assets
- It creates democratic management
- It has a small nominal value
Limitations of Equity Shares
- There is risk of fluctuating returns
- It leads to dilution of capital
- It has many legal formalities
- Equity shares capital has high cost of capital
- It suffers from the danger of over-capitalisation
Preference Shares
Preference shares are those
more...
 Equity Shares
Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in respect of payment of annual dividend and repayment of capital.
Merits of Equity Shares
Equity Shares
Equity shares are those shares which do not carry any special or preferential rights in respect of payment of annual dividend and repayment of capital.
Merits of Equity Shares
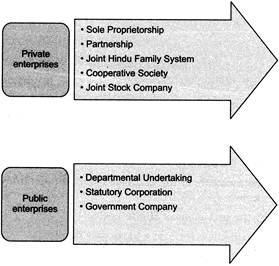 In case of corporate form of private enterprises the identity of the enterprise is a separate legal entity from that of the owner and in case of non-corporate form, the identity of the enterprise is not different from that of its owners.
Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship refers to a form of business organization which is owned, managed and controlled by an individual who is the recipient of all profits and bearer of all risks.
Features of Sole Proprietorship
In case of corporate form of private enterprises the identity of the enterprise is a separate legal entity from that of the owner and in case of non-corporate form, the identity of the enterprise is not different from that of its owners.
Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship refers to a form of business organization which is owned, managed and controlled by an individual who is the recipient of all profits and bearer of all risks.
Features of Sole Proprietorship
