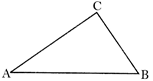
 Perimeter of the triangle \[ABC=AB+BC+CA\]
B. Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
Perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the length of its four sides.
Perimeter of the triangle \[ABC=AB+BC+CA\]
B. Perimeter of a Quadrilateral
Perimeter of a quadrilateral is the sum of the length of its four sides.
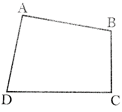 In quadrilateral ABCD, perimeter \[=AB+BC+CD+DA\]
C. Perimeter of a Rectangle
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth).
In quadrilateral ABCD, perimeter \[=AB+BC+CD+DA\]
C. Perimeter of a Rectangle
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth).
 D. Perimeter of a square \[=\mathbf{4}\times \mathbf{side}\].
D. Perimeter of a square \[=\mathbf{4}\times \mathbf{side}\].
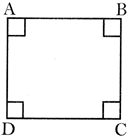 Perimeter of the square \[ABCD=4\times AB\]
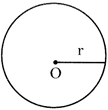
E. Perimeter of a Circle
Perimeter of a circle \[=2\pi r\]
Where \[~\pi =\frac{22}{7}~=3.14\] and r = radius of the circle
Perimeter of the square \[ABCD=4\times AB\]
E. Perimeter of a Circle
Perimeter of a circle \[=2\pi r\]
Where \[~\pi =\frac{22}{7}~=3.14\] and r = radius of the circle
 Area
All the geometrical shapes occupies some space. The occupied space by a geometrical shape is called area of that geometrical shape.
Area
All the geometrical shapes occupies some space. The occupied space by a geometrical shape is called area of that geometrical shape.
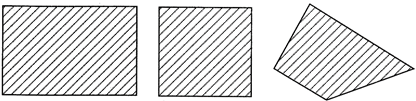 Shaded part in the above figures represent area.
Unit of area is \[c{{m}^{2}}\]or \[{{m}^{2}}\].
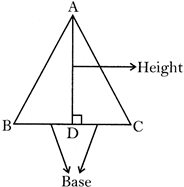
Areas of different geometrical shapes are listed belowA. Area of a Triangle
Area of a triangle \[=1/2\times ~\,base~\times \,height\].
Where base is the one side of a triangle and height is the length of the line segment drawn \[90{}^\circ \] on the base of that triangle.
Shaded part in the above figures represent area.
Unit of area is \[c{{m}^{2}}\]or \[{{m}^{2}}\].
Areas of different geometrical shapes are listed belowA. Area of a Triangle
Area of a triangle \[=1/2\times ~\,base~\times \,height\].
Where base is the one side of a triangle and height is the length of the line segment drawn \[90{}^\circ \] on the base of that triangle.
 B. Area of a Rectangle
Area of a rectangle\[\text{=length }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\,\text{breadth}\].
B. Area of a Rectangle
Area of a rectangle\[\text{=length }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\,\text{breadth}\].
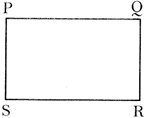
 Area of the rectangle \[PQRS=PQ\times QR\]. Where PQ is the length and QR is the breath.
C. Area of a Square
Area of a square \[\text{=sid}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=side }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\,\text{side}\]
Area of the rectangle \[PQRS=PQ\times QR\]. Where PQ is the length and QR is the breath.
C. Area of a Square
Area of a square \[\text{=sid}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=side }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }\,\text{side}\]
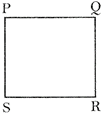 Area of the square \[PQRS=PQ~\times \,PQ=P{{Q}^{2}}\].
D. Area of a Circle
Area of the square \[PQRS=PQ~\times \,PQ=P{{Q}^{2}}\].
D. Area of a Circle
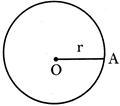 Area of the circle = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Where \[\pi =\frac{22}{7}=3.14\]
Commonly Asked Questions
Area of the circle = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\]
Where \[\pi =\frac{22}{7}=3.14\]
Commonly Asked Questions
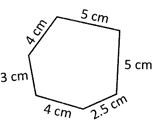 (a) 22.45 cm (b) 23.50 cm
(c) 20.15 cm (d) 15.55 cm
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Solution: Perimeter of the figure \[=4\text{ }cm+3\text{ }cm+4\text{ }cm+2.5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm=23.50\text{ }cm\].
2. Find the perimeter of the following triangle.
(a) 14.7 cm (b) 13.2 cm
(c) 13.2 c m (d) 16.5 cm
(e) None of these
(a) 22.45 cm (b) 23.50 cm
(c) 20.15 cm (d) 15.55 cm
(e) None of these
Answer: (b)
Solution: Perimeter of the figure \[=4\text{ }cm+3\text{ }cm+4\text{ }cm+2.5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm+5\text{ }cm=23.50\text{ }cm\].
2. Find the perimeter of the following triangle.
(a) 14.7 cm (b) 13.2 cm
(c) 13.2 c m (d) 16.5 cm
(e) None of these
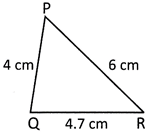 Answer: (a)
Solution: Perimeter of the triangle PQR
\[=4\text{ }cm+4.7\text{ }cm+6\text{ }cm\]
\[=14.7\text{ }cm\]
3. Find the perimeter of the following quadrilateral.
(a) 12 cm (b) 10 cm
(c) 15 cm more...
Answer: (a)
Solution: Perimeter of the triangle PQR
\[=4\text{ }cm+4.7\text{ }cm+6\text{ }cm\]
\[=14.7\text{ }cm\]
3. Find the perimeter of the following quadrilateral.
(a) 12 cm (b) 10 cm
(c) 15 cm more... 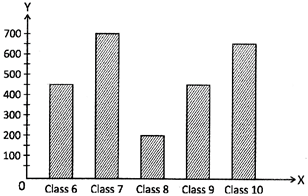 Read the graph carefully and answer the following questions:
Read the graph carefully and answer the following questions:
 FUNDAMENTAL
FUNDAMENTAL
| Types of Plants on the basis of habitat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A. | Terrestrial Plants grow on the land e.g. mango, pine, coconut | 1. Desert Plants: Leaves reduced into spine, swollen stem to store water, long roots etc. e.g. Cactus 2. Plants in hot and damp places remain evergreen and never shed leaves e.g. coconut, neem. 3. Plants of plains: They have branches and leaves shed leaves in autumn e.g. maple tree 4. Platns of hilly areas: Tall plants with lots of branches of flowers e.g. pine, cycas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | Aquatic Platns grow in water e.g. Lotus, vallisneria | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S. No. | Animals | Functions | Body Coverings | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | Snail, turtle and tortoise | Protects the body from injury and from the attack of enemies. | Shell | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | Fish and reptiles | Protects the body | Scales | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
more...
HUMAN BODY AND FOOD
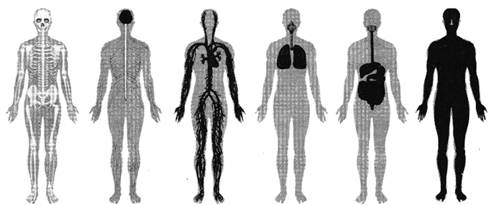 FUNDAMENTAL
Human body is a complex machine, made up of different organs and organ systems,
HUMAN BODY:
Different organ systems perform a specified function of the body in co-ordination with each other.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
It is concerned with carrying oxygen from air to the tissue level for functioning.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:
Breaks the complex food into smaller substances after digestion which can be used for producing energy.
NERVOUS SYSTEMS
It controls and co-ordinates different organ systems with input from sensory organs.
MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
Helps in movement.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS
Helps in transportation of nutrients and other substances.
EXECRATORY SYSTEMS
End products or toxic products removal from the body.
SKELETAL SYSTEMS
Frame work of bones which gives support to the human body. Skeleton has 206 bones in adult.
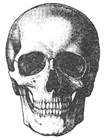
SKULL:
Skull consists of 28 bones which protects the brain. All bones of skull are immovable except the lower jaw which helps in eating and talking. In lower and upper jaw, we have teeth for cutting and chewing food.
FUNDAMENTAL
Human body is a complex machine, made up of different organs and organ systems,
HUMAN BODY:
Different organ systems perform a specified function of the body in co-ordination with each other.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
It is concerned with carrying oxygen from air to the tissue level for functioning.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:
Breaks the complex food into smaller substances after digestion which can be used for producing energy.
NERVOUS SYSTEMS
It controls and co-ordinates different organ systems with input from sensory organs.
MUSCULAR SYSTEMS
Helps in movement.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS
Helps in transportation of nutrients and other substances.
EXECRATORY SYSTEMS
End products or toxic products removal from the body.
SKELETAL SYSTEMS
Frame work of bones which gives support to the human body. Skeleton has 206 bones in adult.
SKULL:
Skull consists of 28 bones which protects the brain. All bones of skull are immovable except the lower jaw which helps in eating and talking. In lower and upper jaw, we have teeth for cutting and chewing food.
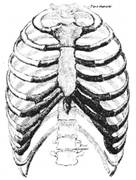
 RIB CAGE:
It is formed by the vertebral column, ribs, and sternum and encloses the heart and lungs. In humans, the rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle), forming a core portion of the human skeleton.
RIB CAGE:
It is formed by the vertebral column, ribs, and sternum and encloses the heart and lungs. In humans, the rib cage, also known as the thoracic cage, is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle), forming a core portion of the human skeleton.
 BACK BONES
It protects the spinal cord. It is not a single bone but made up of 33 small bones, called vertebral column. Higher animal e.g., Tiger, Frog, etc. have back bone and called vertebrates. Whereas lower animal e.g., snails and earthworms do not have a backbones and are called invertebrates Thigh bone (Femur) is the largest bone of the body.
STAPES
Stapes is the smallest bone of the body which is found in ear.
JOINTS
The place where two bones meet is called a joint. Joint can be movable or immovable. Except the lower jaw all other skull bones are connected through immovable joint. Movable joints provide a wide variety of movement at the joint. There are four kinds of joints in our body.
BACK BONES
It protects the spinal cord. It is not a single bone but made up of 33 small bones, called vertebral column. Higher animal e.g., Tiger, Frog, etc. have back bone and called vertebrates. Whereas lower animal e.g., snails and earthworms do not have a backbones and are called invertebrates Thigh bone (Femur) is the largest bone of the body.
STAPES
Stapes is the smallest bone of the body which is found in ear.
JOINTS
The place where two bones meet is called a joint. Joint can be movable or immovable. Except the lower jaw all other skull bones are connected through immovable joint. Movable joints provide a wide variety of movement at the joint. There are four kinds of joints in our body.
SOIL ROCK AND MINERALS
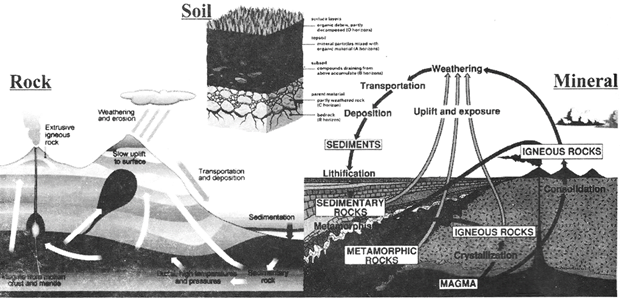 FUNDAMENTAL
Lithosphere of the earth is mainly made up of rocks and soils (natural resources).
FUNDAMENTAL
Lithosphere of the earth is mainly made up of rocks and soils (natural resources).
|