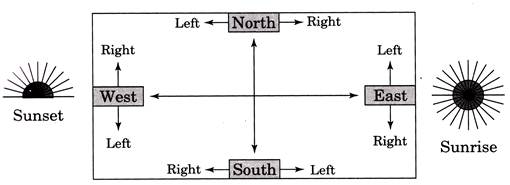
 Cardinal Directions
A direction between two main directions is called cardinal direction. Clearly, there are four cardinal directions.
(i) N-E (North-East)
(h) N-W (North-West)
(iii) S-E (South-East) and
(iv) S-W (South-West)
Cardinal Directions
A direction between two main directions is called cardinal direction. Clearly, there are four cardinal directions.
(i) N-E (North-East)
(h) N-W (North-West)
(iii) S-E (South-East) and
(iv) S-W (South-West)
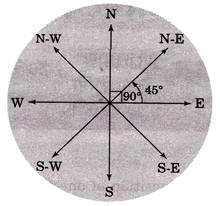 Note: Angle formed between two main directions is \[90{}^\circ \] and angle formed between a cardinal direction and main direction is \[45{}^\circ \] as shown in the above diagram.
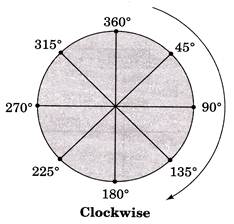
Rotation of Angles
To solve angle movement questions, it is necessary to know about the rotations of angles which are given below.
(i) For right direction movement (Clockwise)
Note: Angle formed between two main directions is \[90{}^\circ \] and angle formed between a cardinal direction and main direction is \[45{}^\circ \] as shown in the above diagram.
Rotation of Angles
To solve angle movement questions, it is necessary to know about the rotations of angles which are given below.
(i) For right direction movement (Clockwise)
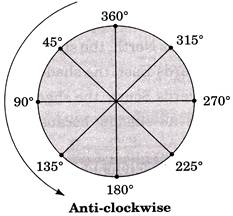
 (ii) For left direction movement (Anti-clockwise)
(ii) For left direction movement (Anti-clockwise)
 Left turn Anti-clockwise direction
Right turn Clockwise direction
The change in direction when a person or vehicle takes a right more...
Left turn Anti-clockwise direction
Right turn Clockwise direction
The change in direction when a person or vehicle takes a right more... 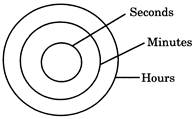 Clearly, seconds are a part of minutes and minutes are a part of hours.
CASE 2:
If the items evidently belong to three different groups, i.e., they are not correlated with each other in any way. They are represented as shown.
Example 2:
Whale, Crocodile, Bird
Explanation:
Clearly, seconds are a part of minutes and minutes are a part of hours.
CASE 2:
If the items evidently belong to three different groups, i.e., they are not correlated with each other in any way. They are represented as shown.
Example 2:
Whale, Crocodile, Bird
Explanation:
 They all belong to different categories.
more...
They all belong to different categories.
more...  Example 1:
Four families P, Q, R and S are living in houses in a row. Q has P and S as neighbours. S has Q and R as heighbours. Who lives next to P?
(a) P (b) Q
(c) R (d) S
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The information can be represented as:
Example 1:
Four families P, Q, R and S are living in houses in a row. Q has P and S as neighbours. S has Q and R as heighbours. Who lives next to P?
(a) P (b) Q
(c) R (d) S
Ans. (b)
Explanation: The information can be represented as:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday | ||||
| 4.5 km | 3.5 km | 1.5 km | 2 km | 4 km | more...
Geometrical Shapes
Objectives
· To identify different objects which represent some kind of geometrical shapes which we are coming across in our day to day life. (Both 2D and 3D)
· To recognise different parts of various geometrical shapes such as vertex and sides of a particular geometrical pattern.
· Use of different geometrical shapes for creating Tangrams.
· Knowledge of line of symmetry. (Horizontal and vertical)
Geometric Shape
Geometric Shape is defined as a set of points or vertices and sides connecting to the point to form a closed entry. There are various kinds of geometrical shapes. They are identified based upon the number of vertices and sides..
2D Geometrical Shapes
|