Conservation of Plants & Animals
Conservation, sustainable use and protection of natural resources including plants, animals, mineral deposits, soils, clean water, clean air, and fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Natural resources are grouped into two categories, renewable and nonrenewable. A renewable resource is one that may be replaced over time by natural processes, such as fish populations or natural vegetation, or is inexhaustible, such as solar energy. Nonrenewable resources are those in limited supply that cannot be replaced or can be replaced only over extremely long periods of time. Nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels and mineral deposits, such as iron ore and gold ore. Conservation activities for nonrenewable resources focus on maintaining an adequate supply of these resources well into the future.

Natural resources are conserved fortheir biological, economic, and recreational values, as well as their natural beauty and importance to local cultures. For example, tropical rain forests are protected for their important role in both global ecology and the economic livelihood of the local culture; a coral reef may be protected for its recreational value for scuba divers; and a scenic river may be protected for its natural beauty.

Biodiversity Conservation
Biodiversity, or biological diversity, denotes the number and variety of different organisms and ecosystems in a certain area. Preserving biodiversity is essential for ecosystems to respond flexibly to damage or change. For example, a single - species corn crop may be quickly destroyed by a certain insect or disease, but if several different species of corn are planted in the field, some of them may resist the insect or disease and survive.
Humans benefit greatly from the many medicines, crops, and other products that biodiversity provides. As many as 40 percent of our modern pharmaceutical medicines are derived from plants or animals. For instance, a small plant from Madagascar, the rosy periwinkle, produces substances that are effective in fighting two deadly cancers, Hodgkin's disease and leukemia.
Unfortunately, human activities have greatly reduced biodiversity around the world. The 20th century encompasses one of the greatest waves of extinction, or elimination of species, to occur on the planet. The greatest threat to biodiversity is loss of habitat as humans develop land for agriculture, grazing livestock, industry, and habitation. The most drastic damage has occurred in the tropical rain forests, which cover less than seven percent of the Earth's surface but contain well over half of the planet's biodiversity. Only 8 percent of the rain forests in Madagascar, home of the rosy periwinkle, remain intact.

Deforestation
Deforestation means large-scale removal of forest prior to its replacement by other land uses. Forests are removed for a variety of reasons, including agriculture, timber harvesting, and mining, and to make way for roads, dams, and human settlements.
At the end of
more...

 Natural resources are conserved fortheir biological, economic, and recreational values, as well as their natural beauty and importance to local cultures. For example, tropical rain forests are protected for their important role in both global ecology and the economic livelihood of the local culture; a coral reef may be protected for its recreational value for scuba divers; and a scenic river may be protected for its natural beauty.
Natural resources are conserved fortheir biological, economic, and recreational values, as well as their natural beauty and importance to local cultures. For example, tropical rain forests are protected for their important role in both global ecology and the economic livelihood of the local culture; a coral reef may be protected for its recreational value for scuba divers; and a scenic river may be protected for its natural beauty.
 Food Preservation
Food Preservation





 Algae
Algae


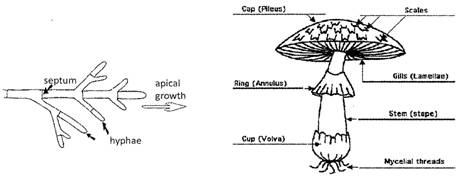 Fungi
Fungi

 Localized Irrigation
Localized Irrigation

 Drip Irrigation
Drip Irrigation
 Crop Production Systems
Crop Production Systems

