-
Why are solids rigid?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Why do solids have a definite volume?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Classify the following as amorphous or crystalline solids: Polyurethane, naphthalene, benzoic acid, teflon, potassium nitrate, cellophane, polyvinyl chloride, fibre glass, copper.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Why is glass considered a super-cooled liquid?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Refractive index of a solid is observed to have to same value along all directions. Comment on the nature of this solid. Would it show cleavage property?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Classify the following solids in different categories based on the nature of intermolecular forces operating in them:
Potassium sulphate, tin, benzene, urea, ammonia, water, zinc sulphide, graphite, rubidium, argon, silicon carbide.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Solid A is very hard electrical insulator in solid as well as in molten state and melts at extremely high temperature. What type of solid is it?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Ionic solids conduct electricity in molten state but not in solid state. Explain.
View Answer play_arrow
-
What type of solids are electrical conductors, malleable and ductile?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Give the significance of a lattice point?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Name the parameters that characterise a unit cell.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Distinguish between
(i) Hexagonal and monoclinic crystal system.
(ii) Face-centred and end-centred unit cell.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Explain how much portion of an atom located at (i) corner and (ii) body-centre of a cubic unit cell is part of its neighbouring unit cell.
View Answer play_arrow
-
What is the two dimensional coordination number of a molecule in square close packed layer?
View Answer play_arrow
-
A compound forms hexagonal close-packed structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mol of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
View Answer play_arrow
-
A compound is formed by two elements M and N. The element N forms ccp and atoms of M occupy 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Which of the following lattices has the highest packing efficiency (i) simple cubic (ii) body centred cubic and (iii) hexagonal close packed lattice?
View Answer play_arrow
-
An element with molar mass 2.7 x 10-2 kg mol-1 forms a cubic unit cell with edge length 405pm. If its density is 2.7 x 103 kg m-3, what is the nature of the cubic unit cell?
View Answer play_arrow
-
What type of defect can arise when a solid is heated? Which physical property is affected by it and in what way?
View Answer play_arrow
-
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by :
(i) ZnS (ii) AgBr
View Answer play_arrow
-
Explain how vacancies are introduced in an ionic solid when a cation of higher valence in added as an impurity in it.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Ionic solids, which have anionic vacancies due to metal- excess defect, develop colour. Explain with the help of a suitable example.
View Answer play_arrow
-
A group 14 element is to be converted into n-type semiconductor by doping it with a suitable impurity. To which group should this impurity belong?
View Answer play_arrow
-
What type of substances would make better permanent magnets, ferromagnetic or ferromagnetic. Justify your answer.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Define the term 'amorphous'. Give a few examples of amorphous solids.
View Answer play_arrow
-
What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be converted into glass?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Classify each of the following solids as ionic, metallic, molecular, network (covalent) or amorphous.
View Answer play_arrow
-
(a) What is meant by the term 'coordination number'?
(b) What is the coordination number of atoms:
(i) in a cubic close packed structure?
(ii) in a body centred cubic structure ?
View Answer play_arrow
-
How can you determine the atomic mass of an unknown metal if you know its density and the dimension of its unit cell? Explain.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting points. Comment. Collect melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane from the data book. What can you say about the inter-molecular forces between these molecules?
View Answer play_arrow
-
How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms :
(a) Hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing?
(b) Crystal lattice and unit cell?
(c) Tetrahedral void and octahedral void?
View Answer play_arrow
-
How many lattice points are there in one unit cell of each of the following lattices?
(a) Face centred cubic
(b) Face centred tetragonal
(c) Body centred cubic
View Answer play_arrow
-
Explain :
(a) The basis of similarities and differences between metallic and ionic crystals.
(b) Ionic solids are hard and brittle.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Calculate the efficiency of packing (or packing fraction) in case of a metal crystal for
(a) Simple cubic
(b) Body centered cubic
(c) Face centered cubic (with the assumptions that atoms are touching each other).
View Answer play_arrow
-
Silver crystallizes in fcc lattice. If edge length of the cell is 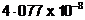 cm and density is
cm and density is 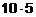 g cm-3, calculate the atomic mass of silver.
g cm-3, calculate the atomic mass of silver.
View Answer play_arrow
-
A cubic solid is made of two elements P and Q. Atoms of Q are at the corners of the cube and P at the body-center. What is the formula of the compound? What are the coordination numbers of P and Q?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Niobium
crystallizes in body centered cubic structure. If density is 8.55 g cm-3,
calculate atomic radius of niobium using its atomic mass 93 u.
View Answer play_arrow
-
If the radius of the octahedral void is r and radius of the atoms in close packing is R, derive relation between r and R.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Copper crystallizes into a fcc lattice with edge length 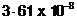 cm. Show that the calculated density is in agreement with its measured value of
cm. Show that the calculated density is in agreement with its measured value of 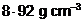 .
.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Analysis shows that nickel oxide has formula 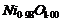 . What fractions of nickel exist as Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions?
. What fractions of nickel exist as Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions?
View Answer play_arrow
-
What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Non-stoichiometric cuprous oxide, Cu2O can be prepared in laboratory. In this oxide, copper to oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2 : 1. Can you account for the fact that this substance is a p-type semiconductor?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Ferric oxide crystallises in a hexagonal close packed array of oxide ions with two out of every three octahedral holes occupied by ferric ions. Derive the formula of the ferric oxide.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Classify each of the following as being either a p-type or an n-type semiconductor :
(i) Ge doped with In
(ii) B doped with Si
View Answer play_arrow
-
Gold (atomic radius = 0.144 nm) crystallises in a face centred unit cell. What is the length of a side of the cell?
View Answer play_arrow
-
In terms of a hand theory, what is the difference
(i) between a conductor and an insulator
(ii) between a conductor and a semiconductor
View Answer play_arrow
-
Explain the following terms with suitable examples :
(i) Schottky defect (ii) Frenkel defect
(iii) Interstitials (iv) F-centres.
View Answer play_arrow
-
Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close-packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm.
(a) What is the length of the side of the unit cell?
(b) How many unit cells are there in 1.00 cm3 of aluminium?
View Answer play_arrow
-
If NaCl is doped with 10–3 mol % of SrCl2, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
View Answer play_arrow
-
Explain the following with suitable examples :
(i) Ferromagnetism (ii) Paramagnetism
(iii) Ferrimagnetism (iv) Antiferromagnetism
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer51)
Which of the following conditions favours the
existence of a substance in the solid state?
(a) High temperature
(b) Low temperature
(c) High thermal
energy
(d) Weak cohesive forces
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer52)
Which of the following is not a characteristic
of a crystalline solid?
(a) Definite and characteristic heat of
fusion
(b) Isotropic nature
(c) A regular periodically
repeated pattern of arrangement of constituent particles in the entire crystal
(d) A true solid
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer53)
Which of the following is, an amorphous solid?
(a) Graphite (C) (b)
Quartz glass (SiO2)
(c) Chrome alum (d)
Silicon carbide
(SiC)
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer54)
Which of the following arrangements shows
schematic alignment of magnetic moments of antiferromagnetic substances?
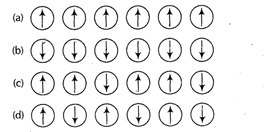
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer55)
Which of the following is true about the value
of refractive index of quartz glass?
(a) Same in all directions
(b) Different in different
directions
(c) Cannot be
measured
(d) Always zero
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer56)
Which of the following statement is not true
about amorphous solids?
(a) On heating they may become
crystalline at certain temperature
(b) They may become crystalline
on keeping for long time
(c) Amorphous solids can be
moulded by heating
(d) They are anisotropic in
nature
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer57)
The sharp melting point of crystalline solids is
due to..........
(a) a regular arrangement of constituent
particles observed over a short distance in the crystal lattice
(b) a regular arrangement of
constituent particles observed over a long distance in the crystal lattice
(c) same arrangement of
constituent particles in different directions
(d) different arrangement of
constituent particles in different directions
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer58)
Iodine molecules are held in the crystals
lattice by..........
(a) London forces
(b) dipole-dipole interactions
(c) covalent
bonds
(d) coulombic forces
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer59)
Which of the following is a network
solid?
(a) SO2 (solid) (b)
I2
(c) Diamond (d)
H2O (ice)
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer60)
Which of the following solids is not an
electrical conductor?
1. Mg(s) 2.
TiO (s)
(a) Only 1 (b)
Only 2
3. I2 (s) 4.H2O
(s)
(c) 3 and 4 (d)
2, 3 and 4
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer61)
Which of the following is not the characteristic
of ionic solids?
(a) Very low value of electrical
conductivity in the molten state
(b) Brittle nature
(c) Very strong forces of
interactions
(d) Anisotropic nature
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer62)
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due
to the presence of..........
(a) Lone pair of electrons
(b) free valence electrons
(c)
cations
(d) anions
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer63)
Which of the following oxides behaves as
conductor or insulator depending upon temperature?
(a) TiO (b)
SiO2
(c) Ti03 (d)
MgO
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer64)
Which of the following oxides shows electrical
properties like metals?
(a) SiO2 (b)
MgO
(c) SO2 (S) (d)
CrO2
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer65)
The lattice site in a pure crystal cannot be
occupied by..........
(a) molecule (b)
ion
(c) electron (d)
atom
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer66)
Graphite cannot be classified as..........
(a) conducting solid (b) network
solid
(c) covalent solid (d)
ionic solid
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer67)
Cations are present in the interstitial sites in.........
.
(a)
Frenkel defect (b) Schottky defect
(c) vacancy defect (d) metal
deficiency
Defect
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer68)
Schottky defect is observed in crystals when..........
(a) some cations move from their lattice
site to interstitial sites
(b) equal number of cations and
anions are missing from the lattice
(c) some lattice sites are
occupied by electrons
(d) some impurity is present in
the lattice
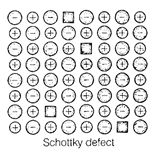
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer69)
Which of the following is true about the charge
acquired by p ? type semiconductors?
(a) Positive
(b) Neutral
(c) Negative
(d) Depends on concentration of
p impurity
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer70)
To get a n-type semiconductor from silicon, it
should be doped with a substance with valency..........
(a) 2 (b)
1 (c) 3 (d) 5
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer71)
The total number of tetrahedral voids in the
face centred unit cell is
(a),6 (b)8
(c)10 (d)12
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer72)
Which of the following point defects are shown
by AgBr(s) crystals?
1. Schottky
defect
2. Frenkel
defect
3. Metal excess
defect
4. Metal deficiency
defect
(a) 1 and 2 (b)
3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3 (d)
2 and 4
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer73)
In which pair most efficient packing is
present?
(a) hcp and bcc (b) hcp
and ccp
(c) bcc and ccp (d)
bcc and simple
cubic cell
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer74)
The percentage of empty space in a body centred
cubic arrangement is
(a) 74 (b) 68 (c) 32
(d) 26
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer75)
Which of the following statement is not true
about the hexagonal close packing?
(a) The coordination number is 12
(b) It has 74% packing
efficiency
(c) Tetrahedral voids of the
second layer are covered by the spheres of the third layer
(d) In this arrangement spheres
of the fourth layer are exactly aligned with those of the first layer
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer76)
In which of the following structures coordination
number for cations and anions in the packed structure will be same?
(a) Cl- ions form fee lattice
and Na'1' ions occupy all octahedral voids of the unit cell
(b) Ca2+ ions form
fee lattice and F~ ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell
(c) O2- ions form fee
lattice and Na4' ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell
(d) S2- ions form fee
lattice and Zn21' ions go into alternate tetrahedral voids of the unit cell
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer77)
What is the coordination number in a square
close packed structure in two
dimensions?
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c)
4 (d) 6
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer78)
Which kind of defects are introduced by doping?
(a) Dislocation defect (b) Schottky
defect
(c) Frenkel defect (d)
Electronic defect
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer79)
Silicon doped with electron rich impurity
forms..........
(a) p -type semiconductor
(b) n - type semiconductor
(c) intrinsic
semiconductor
(d) insulator
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer80)
Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) Paramagnetic substances are weakly
attracted by magnetic field
(b) Ferromagnetic substances
cannot be magnetised permanently
(c) The domains in
antiferromagnetic substances are oppositely oriented with respect to each other
(d) Pairing of electrons cancels
their magnetic moment in the diamagnetic substances
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer81)
Which of the following is not true about the
ionic solids?
(a) Bigger ions form the close packed
structure
(b) Smaller ions occupy either
the tetrahedral or the octahedral voids depending upon their size
(c) Occupation of all the voids
is not necessary
(d) The fraction of octahedral
or tetrahedral voids occupied depends upon the radii of the ions occupying the voids
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer82)
A ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent
magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field because..........
(a) all the domains get oriented in the
direction of magnetic field
(b) all the domains get oriented
in the direction opposite to the direction of magnetic field
(c) domains get oriented
randomly
(d) domains are not affected by
magnetic field
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer83)
The correct order of the packing efficiency in
different types of unit cells is..........
(a) fee < bcc < simple
cubic
(b) fee > bee > simple
cubic
(c) fee < bcc > simple
cubic
(d) bcc < fee > simple
cubic
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer84)
Which of the following defects is also known as
dislocatiqn defect?
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Non-stoichiometric
defect
(d) Simple interstitial defect
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer85)
In the cubic close packing, the unit cell has..........
(a) 4 tetrahedral voids each of which is
shared by four adjacent unit cells
(b) 4 tetrahedral voids within
the unit cell
(c) 8 tetrahedral voids each of
which is shared by four adjacent unit cells
(d) 8 tetrahedral voids within
the unit cells
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer86)
The edge lengths of the unit cells in terms of
the radius of spheres constituting fee, bcc and simple cubic unit cells are respectively..........
(a) 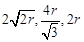 (b)
(b)
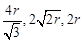 (c)
(c) 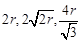 (d)
(d)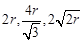
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer87)
Which of the following represents correct order
of conductivity in solids?
(a) 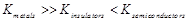 (b)
(b) 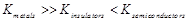 (c)
(c) 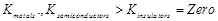 (d)
(d) 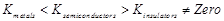
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer88)
Which of the following is not true about the
voids formed -in 3 dimensional hexagonal close packed structure?
(a) A tetrahedral void is formed when a
sphere of the second layer is present above triangular void in the first layer
(b) All the triangular voids are
riot covered by the spheres of the second layer
(c) Tetrahedral voids are formed
when the triangular voids in the second layer lie above the triangular voids in
the first layer and the triangular shapes of these voids do not overlap
(d) Octahedral voids are formed
when the triangular voids in the second layer exactly overlap with similar
voids in the first layer
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer89)
The value of magnetic moment is zero in the case
of antiferromagnetic substances because the domains..............
(a) get oriented in the direction of the
applied magnetic field
(b) get oriented opposite to the
direction of the applied magnetic field
(c) are oppositely oriented with
respect to each other without the application of magnetic field
(d) cancel out each other's magnetic
moment
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer90)
Which of the following statements are not true?
(a) Vacancy defect results in a decrease
in the density of the substance
(b) Interstitial defects results
in an increase in the density of the substance
(c) Impurity defect has no
effect on the density of the substance
(d) Frenkel defect results in an
increase in the density of the substance
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer91)
Which of the following statements are true about
metals?
(a) Valence band overlaps with
conduction band
(b) The gap between valence band
and conduction band is negligible
(c) The gap between valence band
and conduction band cannot be determined
(d) Valence band may remain
partially filled
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer92)
Under the influence of electric field, which of
the following statement is true about the movement of electrons and holes in a
^D-type semiconductor?
(a) Electron will move towards the
positively charged plate through electron holes
(b) Holes will appear to be
moving towards the negatively charged plate
(c) Both electrons and holes
appear to move towards the positively charged plate
(d) Movement of electrons is not
related to the movement of holes
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer93)
Which of the following statements are true about
semiconductors?
(a) Silicon doped with electron rich
impurity is a p -type semiconductor
(b) Silicon doped with an
electron rich impurity is an n-type semiconductor
(c) Delocalised electrons
increase the conductivity of doped silicon
(d) An electron vacancy
increases the conductivity of n-type semiconductor
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer94)
An excess of potassium ions makes KCl crystals
appear violet or lilac in colour since...........
(a) some of the anionic sites are
occupied by an unpaired electron
(b) some of the anionic sites
are occupied by a pair of electrons
(c) there are, vacancies at some
anionic sites
(d) F - centres are created
which impart colour to the crystals
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer95)
The number of tetrahedral voids per unit cell in
NaCI. crystal is...........
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) twice the number of
octahedral voids
(d) four times the number of
octahedral voids
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer96)
Amorphous solids can also be called..........
(a) pseudo solids (b)
true solids
(c) super cooled liquids (d)
super
cooled solids
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer97)
A perfect crystal of silicon (fig) is doped with
some elements as given in the options. Which of these options shows n -type
semiconductors?
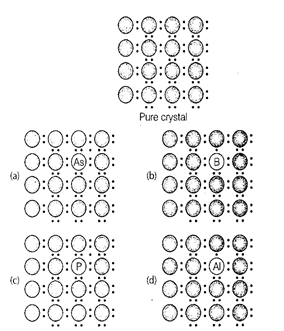
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer98)
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Ferrimagnetic substances lose
ferrimagnetism on heating and become paramagnetic
(b) Ferrimagnetic substances do
not lose ferrimagnetism on heating and remain ferrimagnetic
(c) Antiferromagnetic substances
have domain structures similar to ferromagnetic substances and their magnetic
moments are not cancelled by each other
(d) In ferromagnetic substances,
all the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field and remain as
such even after removing magnetic field
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer99)
Which of the following features are not shown by
quartz glass?
(a) This is a crystalline solid
(b) Refractive index is same in
all the directions
(c) This has definite heat of
fusion
(d) This is also called super
cooled liquid
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer100)
Which of the following cannot be regarded as
molecular solid?
(a) SiC (silicon carbide) (b)
AIN
(c) Diamond
(d) I2
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer101)
In which of the following arrangements
octahedral voids are formed?
(a) hcp (b)
bcc
(c) simple cubic (d)
fee
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer102)
Frenkel defect is also known as...........
(a) stoichiometric defect
(b) dislocation defect
(c) impurity
defect
(d) non-stoichiometric defect
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer103)
Which of the following defects decrease the
density?
(a) Interstitial defect (b) Vacancy
defect
(c) Frenkel defect (d)
Schottky defect
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer104)
Why are liquids and gases categorised as fluids?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer105)
Why are solids incompressible?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer106)
Inspite of long range order in the arrangement
of particles why are the crystals usually not perfect?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer107)
Why does table salt, Nacl sometimes appear
yellow in colour?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer108)
Why is Fe0(s) not formed in stoichiometric
composition?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer109)
Why does white Zn0 (s} becomes yellow upon heating?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer110)
Why does the electrical conductivity of
semiconductors increase with rise in temperature?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer111)
Explain why does conductivity of germanium
crystals increase on doping with galium?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer112)
In a compound, nitrogen atoms (N) make cubic
close packed lattic and metal atoms (M) occupy one-third of the tetrahedral
voids present.
Determine the formula of the compound
formed by M and N?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer113)
Under which situations can an amorphous substance
change to crystalline form?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer114)
Match the defects given in Column I with the
statements in given Column II.
|
|
Column 1
|
Column 11
|
|
A.
B.
C.
D.
|
Simple vacancy
defect Simple
interstitial defect
Frenkel defect Schottky defect
|
1. Shown by non-ionic solids and increases
density of the solid
2. Shown by ionic solids and decreases density of
the solid
3. Shown by non-ionic solids and density of the
solid decreases
4. Shown by ionic solids and density of the solid
remains the same
|
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer115)
Match the type of unit cell
given in Column I with the features given in
|
Column 1
|
Column 11
|
|
A. Primitive cubic unit cell
B. Body centred cubic unit cell
C. Face centred cubic unit cell
D. End centred orthorhombic unit cell
|
1. Each of the three perpendicular edges
compulsorily have the different edge length i.e., 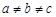 2. Number of atoms per unit cell is one
3. Each of the three perpendicular edges
compulsorily have the same edge length i.e., a = b = c
4.In addition to the contribution from the corner
atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is one
5. In addition to the contribution from the
corner atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is three
2. Number of atoms per unit cell is one
3. Each of the three perpendicular edges
compulsorily have the same edge length i.e., a = b = c
4.In addition to the contribution from the corner
atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is one
5. In addition to the contribution from the
corner atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is three
|
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer116)
Match the types of defect given in Column I with
the statement given in
|
|
Column I
|
Column II
|
|
A.
B.
C.
|
Impurity defect Metal excess defect
Metal deficiency defect
|
1. NaCl with anionic sites called F-centres
2. Fed with Fe3+
3. NaCI with Sr2+ and some cationic
sites vacant
|
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer117)
Match the items given in Column I with the items
given in Column II.
|
|
Column 1
|
Column 11
|
|
A.
B.
C.
D.
|
Mg in solid state
MgCI2 in molten state
Silicon with phosphorus Germanium with boron
|
1. p - type semiconductor
2. n -type semiconductor
3. Electrolytic conductors
4. Electronic conductors
|
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer118)
Match the type of packing given
in Column I with the items given in Column II.
|
|
Column 1
|
Column 11
|
|
A.
|
Square close packing in two dimensions
|
1. Triangular voids
|
|
B.
|
Hexagonal close packing in two dimensions
|
2. Pattern of spheres is repeated in every fourth
layer
|
|
C.
|
Hexagonal close packing in three dimensions
|
3. Coordination number = 4
|
|
D.
|
Cubic close packing in three dimensions
|
4. Pattern of sphere is repeated in alternate
layers
|
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer119)
Assertion (A) The total number of atoms
present in a simple cubic unit cell is one.
Reason (R) Simple cubic unit cell
has atoms at its corners, each of which is shared between eight adjacent unit
cells.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer120)
Assertion (A) Graphite is a good conductor
of electricity however diamond belongs to the category of insulators.
Reason (R) Graphite is soft in
nature on the other hand diamond is very hard and brittle.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer121)
Assertion (A) Total number of octahedral
voids present in unit cell of cubic close packing including the one that is
present at the body centre, is four.
Reason (R) Besides the body
centre there is one octahedral void present at the centre of each of the six
faces of the unit cell and each of which is shared between two adjacent unit
cells.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer122)
Assertion (A) The packing efficiency is
maximum for the fee structure.
Reason (R) The coordination
number is 12 in fee structures.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer123)
Assertion (A) Semiconductors are solids with
conductivities in the intermediate range from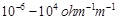 .
Reason (R) Intermediate
conductivity in semiconductor is due to partially filled valence band.
.
Reason (R) Intermediate
conductivity in semiconductor is due to partially filled valence band.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer124)
With the help of a labelled diagram show that
there are four octahedral voids per unit cell in a cubic close packed
structure.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer125)
Show that in a cubic close packed structure,
eight tetrahedral voids are present per unit cell.
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer126)
How does the doping increase the conductivity of
semiconductors?
View Answer play_arrow
-
question_answer127)
A sample of ferrous oxide has actual formula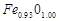 . In this sample, what
fraction of metal ions are Fe2+ions? What type of non-stoichiometric
defect is present in this sample?
. In this sample, what
fraction of metal ions are Fe2+ions? What type of non-stoichiometric
defect is present in this sample?
View Answer play_arrow
