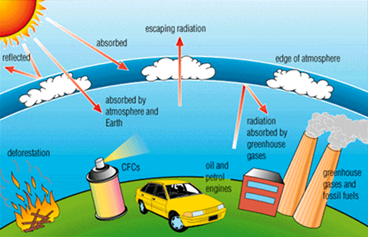
 Thus, the layer of \[{{\mathbf{O}}_{3}}\] molecule formed in the upper atmosphere. This protect us from the harmful ultraviolet radiation, and is called ozone layer. These harmful ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer and can also damage our eyes by causing an eye diseases, called cataract. It also destroy our immune system. Hence we can say that ozone layer is very useful to us and is also very essential for the earth's life forms. In recent past it has been found that the ozone layer is depleting and hole has appeared in the polar region of the ozone layer, which is a matter of great concern. The main reason for the depletion of ozone layer is the release of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC). This CFC is widely used in refrigerator and other coolants and this CFC reacts with ozone layer and gradually destroy it and thus leading to its depletion.
Thus, the layer of \[{{\mathbf{O}}_{3}}\] molecule formed in the upper atmosphere. This protect us from the harmful ultraviolet radiation, and is called ozone layer. These harmful ultraviolet radiation can cause skin cancer and can also damage our eyes by causing an eye diseases, called cataract. It also destroy our immune system. Hence we can say that ozone layer is very useful to us and is also very essential for the earth's life forms. In recent past it has been found that the ozone layer is depleting and hole has appeared in the polar region of the ozone layer, which is a matter of great concern. The main reason for the depletion of ozone layer is the release of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC). This CFC is widely used in refrigerator and other coolants and this CFC reacts with ozone layer and gradually destroy it and thus leading to its depletion.


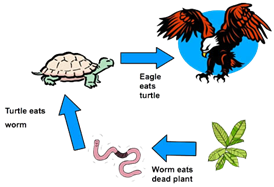
 Dead tissue and waste products are produced at all levels. Scavengers, detritivores, and decomposers collectively account for the use of all such "waste" — consumers of carcasses and fallen leaves may be other animals, such as crows and beetles, but ultimately it is the microbes that finish the job of decomposition. Usually when we think of food chains we visualize green plants, herbivores, and so on. These are referred to as grazer food chains, because living plants are directly consumed. In many circumstances the principal energy input is not green plants but dead organic matter. These are called detritus food chains. Examples include the forest floor or a woodland stream in a forested area, a salt marsh, and most obviously, the ocean floor in very deep areas where all sunlight is extinguished 1000's of meters above.
Dead tissue and waste products are produced at all levels. Scavengers, detritivores, and decomposers collectively account for the use of all such "waste" — consumers of carcasses and fallen leaves may be other animals, such as crows and beetles, but ultimately it is the microbes that finish the job of decomposition. Usually when we think of food chains we visualize green plants, herbivores, and so on. These are referred to as grazer food chains, because living plants are directly consumed. In many circumstances the principal energy input is not green plants but dead organic matter. These are called detritus food chains. Examples include the forest floor or a woodland stream in a forested area, a salt marsh, and most obviously, the ocean floor in very deep areas where all sunlight is extinguished 1000's of meters above.




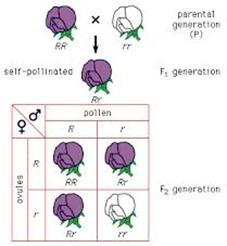
 Mendel gave the following conclusion from his experiment:
Mendel gave the following conclusion from his experiment:
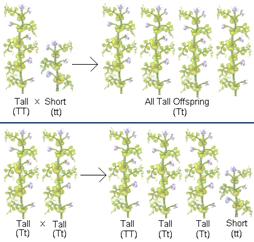
 When the traits of \[{{F}_{1}}\] were crossed among themselves, the 75% of plants in \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation were tall and 25% of them were dwarf. Thus, the phenotype ratio was 3:1.
When the traits of \[{{F}_{1}}\] were crossed among themselves, the 75% of plants in \[{{F}_{2}}\] generation were tall and 25% of them were dwarf. Thus, the phenotype ratio was 3:1.
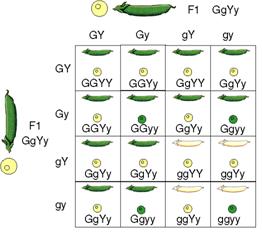 After performing the experiments on the inheritance of traits of one character he performed an experiment with the two character or dihybrid cross. He crossed the plants of round and yellow seeds with the plants of wrinkled and green seeds: and found that all the plants \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation are round and yellow. When the plants of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation were crossed among themselves he found that it gave rise to four types of seeds. Of these 301 were round and yellow, 102 were round and green, 96 were wrinkled and yellow and 30 were wrinkled and green. Hence their phenotype ratio was about 9:3:3:1.
After performing the experiments on the inheritance of traits of one character he performed an experiment with the two character or dihybrid cross. He crossed the plants of round and yellow seeds with the plants of wrinkled and green seeds: and found that all the plants \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation are round and yellow. When the plants of \[{{F}_{1}}\] generation were crossed among themselves he found that it gave rise to four types of seeds. Of these 301 were round and yellow, 102 were round and green, 96 were wrinkled and yellow and 30 were wrinkled and green. Hence their phenotype ratio was about 9:3:3:1.
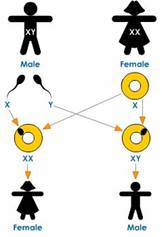
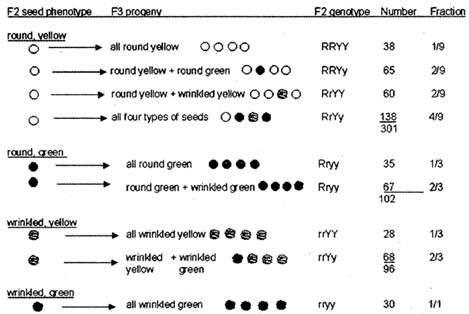 The genotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross is found to be 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1. He found that it was actually the gene which were responsible for the traits of an organisms. These traits are presents on the chromosomes of the genes of an organisms. It is the dominant gene which shows it character in the physical appearance of an organisms.
The genotypic ratio of the dihybrid cross is found to be 1:2:2:4:1:2:1:2:1. He found that it was actually the gene which were responsible for the traits of an organisms. These traits are presents on the chromosomes of the genes of an organisms. It is the dominant gene which shows it character in the physical appearance of an organisms. 

You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
