

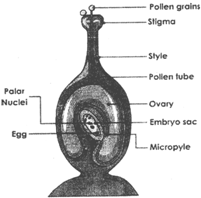




 3. Cytoplasm divides 4. Two daughter more...
3. Cytoplasm divides 4. Two daughter more... 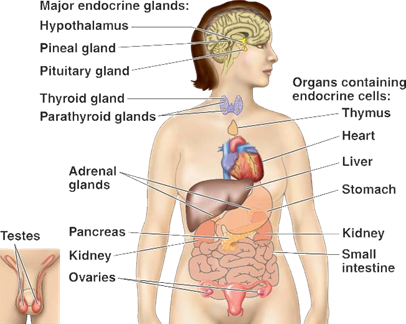




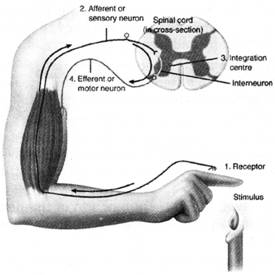 There are two types of reflex arc - autonomic reflex arc affecting inner organs and somatic reflex arc affecting muscles. When a reflex arc consists of only two neurons in an animal i.e. one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron. It is defined as monosynaptic. Monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse. In the case of peripheral muscle reflexes, brief stimulation to the muscle spindle results in contraction of the agonist or effector muscle. By contrast, in polysynaptic reflex pathways, one or more interneurons connect afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) signals.
There are two types of reflex arc - autonomic reflex arc affecting inner organs and somatic reflex arc affecting muscles. When a reflex arc consists of only two neurons in an animal i.e. one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron. It is defined as monosynaptic. Monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse. In the case of peripheral muscle reflexes, brief stimulation to the muscle spindle results in contraction of the agonist or effector muscle. By contrast, in polysynaptic reflex pathways, one or more interneurons connect afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) signals.  Neurons send signals to other cells as electrochemical waves travelling along thin fibers called axons. This causes chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions, called synapses. A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated.
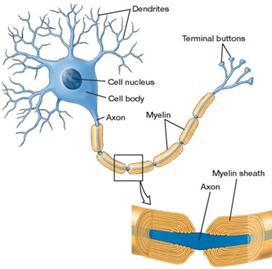
Sensory neurons are activated by physical stimuli impinging on them, and sends signals that inform the central nervous system of the state of the body and the external environment. Motor neurons, situated either in the central nervous system or in peripheral ganglia, connect the nervous system to muscles or other effector organs. Central neurons, which in vertebrates greatly outnumber the other types, make all of their input and output connections with other neurons. The interactions of all these types of neurons form neural circuits that generate an organism's perception of the world and determine its behavior. Along with neurons, the nervous system contains other specialized cells, called glial cells, which provide structural and metabolic support.
Neurons send signals to other cells as electrochemical waves travelling along thin fibers called axons. This causes chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions, called synapses. A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated.
Sensory neurons are activated by physical stimuli impinging on them, and sends signals that inform the central nervous system of the state of the body and the external environment. Motor neurons, situated either in the central nervous system or in peripheral ganglia, connect the nervous system to muscles or other effector organs. Central neurons, which in vertebrates greatly outnumber the other types, make all of their input and output connections with other neurons. The interactions of all these types of neurons form neural circuits that generate an organism's perception of the world and determine its behavior. Along with neurons, the nervous system contains other specialized cells, called glial cells, which provide structural and metabolic support.
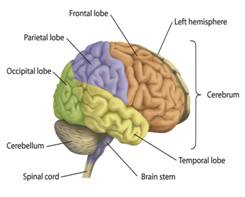
 The central nervous system (CNS) is the largest part, and includes the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cavity contains the spinal cord, while the head contains the brain. The CNS is enclosed and protected by meninges, a three- layered system of membranes, including a tough, leathery outer layer called the dura mater. The brain is also more...
The central nervous system (CNS) is the largest part, and includes the brain and spinal cord. The spinal cavity contains the spinal cord, while the head contains the brain. The CNS is enclosed and protected by meninges, a three- layered system of membranes, including a tough, leathery outer layer called the dura mater. The brain is also more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
