 Opaque objects do not allow passing of light through them. A piece of wood does not allow passing of light through it, therefore is called opaque object. The shadow of an object is formed due to the interruption of light. The light from light producing body is radiated towards different direction and a shadow of an object, which interrupt light, is formed at the opposite direction from where light is coming. For example, if the light is coming from east direction, the shadow of the object, which interrupt the light, forms in west direction. Shadow is not possible of a the transparent object. Because it allows the passing of light through
Look at the following picture of shadow formation
Opaque objects do not allow passing of light through them. A piece of wood does not allow passing of light through it, therefore is called opaque object. The shadow of an object is formed due to the interruption of light. The light from light producing body is radiated towards different direction and a shadow of an object, which interrupt light, is formed at the opposite direction from where light is coming. For example, if the light is coming from east direction, the shadow of the object, which interrupt the light, forms in west direction. Shadow is not possible of a the transparent object. Because it allows the passing of light through
Look at the following picture of shadow formation
 In the above picture, light from the candle is passing through the hole on the globe and shadow is formed on the opposite side of the light producing body.There are two parts of a shadow, umbra and penumbra. Umbra is the part of shadow, which is in complete darkness and does not receive light from the source. Penumbra is the part of shadow, which receives some part of light from the source.
Look at the following picture of path of the light
In the above picture, light from the candle is passing through the hole on the globe and shadow is formed on the opposite side of the light producing body.There are two parts of a shadow, umbra and penumbra. Umbra is the part of shadow, which is in complete darkness and does not receive light from the source. Penumbra is the part of shadow, which receives some part of light from the source.
Look at the following picture of path of the light
 In the picture above, light from candle is passing through the hole of the three cardboards. A thin streak of light is appeared at the far end of the cardboard. This proves that the light travels in straight line. This property of light is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Look at the following picture of the solar eclipse
In the picture above, light from candle is passing through the hole of the three cardboards. A thin streak of light is appeared at the far end of the cardboard. This proves that the light travels in straight line. This property of light is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Look at the following picture of the solar eclipse
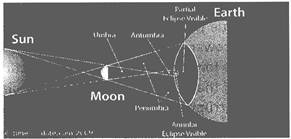 Solar eclipse is the formation of shadow of Moon on the surface of the Earth.
The solar eclipse is possible due to the passing of Moon between the Earth and the Sun. Light from the Sun is reflected by the surface of the Moon and shadow is formed on the surface of the Earth.
Look at the following picture more...
Solar eclipse is the formation of shadow of Moon on the surface of the Earth.
The solar eclipse is possible due to the passing of Moon between the Earth and the Sun. Light from the Sun is reflected by the surface of the Moon and shadow is formed on the surface of the Earth.
Look at the following picture more... 
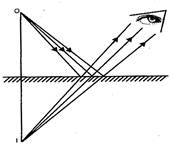 Fig. (1) Plane mirror Fig. (2) Image formation in a plane mirror
In the figure (1), a virtual image is formed by a plane mirror. In the figure (2), formation of a virtual image by a plane mirror is shown. An object (0) is placed in front of the mirror. Incident ray falls from 0 and get reflected by the mirror. The reflected rays are produced backward and they meet at the point /. The observer receives the reflected rays and image as shown at /. The image of the object is not the actual intersection of light and therefore is called virtual image. The incident ray falls on the plane mirror by 90° retraces its path or reflected through the same path. An incident ray falling on the plane mirror by 6 is reflected by the same angle (9).
Fig. (1) Plane mirror Fig. (2) Image formation in a plane mirror
In the figure (1), a virtual image is formed by a plane mirror. In the figure (2), formation of a virtual image by a plane mirror is shown. An object (0) is placed in front of the mirror. Incident ray falls from 0 and get reflected by the mirror. The reflected rays are produced backward and they meet at the point /. The observer receives the reflected rays and image as shown at /. The image of the object is not the actual intersection of light and therefore is called virtual image. The incident ray falls on the plane mirror by 90° retraces its path or reflected through the same path. An incident ray falling on the plane mirror by 6 is reflected by the same angle (9).


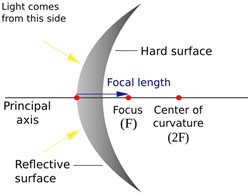 Fig.(1) Virtual image (In convex mirror) Fig.(2) Index of a convex mirror
Fig.(1) Virtual image (In convex mirror) Fig.(2) Index of a convex mirror
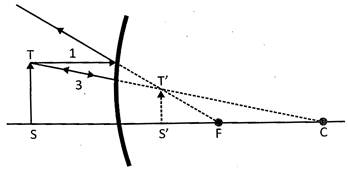 Fig. (3) Image formed by convex mirror
In the picture (1), a virtual image is shown by a convex mirror. Convex mirror is used in automobiles to get the wider view of the automobile. The curved surface of convex mirror gives the wider and clear view of the object approaching. It is used in departmental stores to get the wider view of the inside of store. Convex mirror reflects light outwards. It cannot be focused on an object, therefore cannot be used to focus light. The center of curvature and focus, both are imaginary. Therefore, they form virtual image. The center of the shiny image of the convex mirror is called vertex and denoted by V. When parallel light rays strike on the convex mirror, it gets reflected. Virtual image is formed at the imaginary intersecting point of the reflected rays, as shown in the figure (3).
Look at the following pictures of concave mirror
Fig. (3) Image formed by convex mirror
In the picture (1), a virtual image is shown by a convex mirror. Convex mirror is used in automobiles to get the wider view of the automobile. The curved surface of convex mirror gives the wider and clear view of the object approaching. It is used in departmental stores to get the wider view of the inside of store. Convex mirror reflects light outwards. It cannot be focused on an object, therefore cannot be used to focus light. The center of curvature and focus, both are imaginary. Therefore, they form virtual image. The center of the shiny image of the convex mirror is called vertex and denoted by V. When parallel light rays strike on the convex mirror, it gets reflected. Virtual image is formed at the imaginary intersecting point of the reflected rays, as shown in the figure (3).
Look at the following pictures of concave mirror

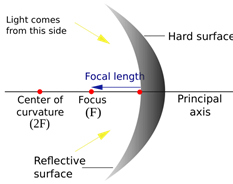 Fig. (1) Real image Fig (2) Index of a concave mirror
Fig. (1) Real image Fig (2) Index of a concave mirror
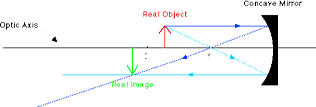 Fig (3) Image by a concave mirror
In the figure (1), an image is shown formed by a concave mirror. A real image is formed by the concave mirror when object is placed in front of the mirror. A concave mirror reflects light and reflected rays of light intersects each other outside the mirror, therefore real image (not virtual) is formed.
The center of curvature is the center of sphere and denoted by C, radius of the curvature is denoted by r. The center of the shiny surface of the mirror is called the pole of the mirror and it is denoted by P. In the figure (3), incident rays are reflected and meet at a point called focus .which is denoted by F. Focus, centerof curvature and pole of the mirror more...
Fig (3) Image by a concave mirror
In the figure (1), an image is shown formed by a concave mirror. A real image is formed by the concave mirror when object is placed in front of the mirror. A concave mirror reflects light and reflected rays of light intersects each other outside the mirror, therefore real image (not virtual) is formed.
The center of curvature is the center of sphere and denoted by C, radius of the curvature is denoted by r. The center of the shiny surface of the mirror is called the pole of the mirror and it is denoted by P. In the figure (3), incident rays are reflected and meet at a point called focus .which is denoted by F. Focus, centerof curvature and pole of the mirror more... 
 Fig. (1) Side view of convex lens Fig. (1) Front view of convex lens
Fig. (1) Side view of convex lens Fig. (1) Front view of convex lens
 Fig. (3) Side view of concave lens Fig. (3) Front view of concave lens
Lenses are made up of spherical mirrors. The same thickness of the both curvature causes zero optical power. Two surface of mirror combined and forms a lens. The surfaces of the lens are ideally perpendicular to each other. The surface of the lens can be of plane, or of spherical mirrors. The joining line between the vertexes of the both surface of the lens is called its axis.
Fig. (3) Side view of concave lens Fig. (3) Front view of concave lens
Lenses are made up of spherical mirrors. The same thickness of the both curvature causes zero optical power. Two surface of mirror combined and forms a lens. The surfaces of the lens are ideally perpendicular to each other. The surface of the lens can be of plane, or of spherical mirrors. The joining line between the vertexes of the both surface of the lens is called its axis.
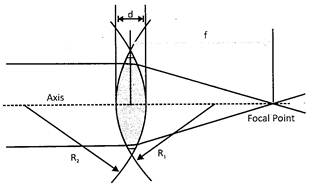
| Position of object | more...

 Sand clock is one of the instruments, which was used earlier to measure the time duration. Sand clock consists of two glass bulbs placed one above the other and are connected with the help of a narrow glass tube. Sand flows from the top to the bottom. When the top bulb gets empty, clock is inverted so that lower glass tube comes up and sand clock keeps on working. The sand takes a fixed duration of time to flow from one glass tube to other. In this way, earlier people used to measure time duration of an event.
In the modern time we use clocks to know the duration of time. Clock uses second as a unit; 60 second is equal to 1 minute and 60 minute to one hour.
Modern basis of measuring time duration
60 seconds = 1 minute
60 minutes = 1 hour
24 hours = 1 day
365 days = 1 year
10 years = 1 decade
10 decades = 1 century
10 century’s = 1 millennium
Sand clock is one of the instruments, which was used earlier to measure the time duration. Sand clock consists of two glass bulbs placed one above the other and are connected with the help of a narrow glass tube. Sand flows from the top to the bottom. When the top bulb gets empty, clock is inverted so that lower glass tube comes up and sand clock keeps on working. The sand takes a fixed duration of time to flow from one glass tube to other. In this way, earlier people used to measure time duration of an event.
In the modern time we use clocks to know the duration of time. Clock uses second as a unit; 60 second is equal to 1 minute and 60 minute to one hour.
Modern basis of measuring time duration
60 seconds = 1 minute
60 minutes = 1 hour
24 hours = 1 day
365 days = 1 year
10 years = 1 decade
10 decades = 1 century
10 century’s = 1 millennium

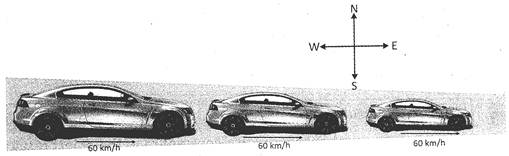 In the above figure, the car is moving in east direction with a constant speed. Therefore, it is said that the car is moving with uniform velocity.
In the above figure, the car is moving in east direction with a constant speed. Therefore, it is said that the car is moving with uniform velocity.
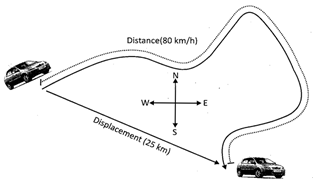
 Displacement is the distance between initial point from where object started to move and the final point where the object stopped. Displacement shows finally the object in which direction and at how far from the initial place sifted. Therefore displacement shows direction as well as distance. And it is a vector quantity.
Displacement is the distance between initial point from where object started to move and the final point where the object stopped. Displacement shows finally the object in which direction and at how far from the initial place sifted. Therefore displacement shows direction as well as distance. And it is a vector quantity.
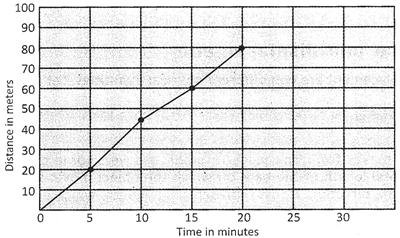
  Speed of the car does not vary in different interval of time. Therefore speed of the car is uniform.
Graphical representation of uniform speed.
Speed of the car does not vary in different interval of time. Therefore speed of the car is uniform.
Graphical representation of uniform speed.
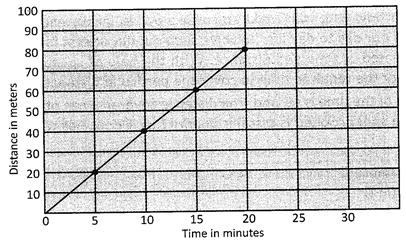 Time distance graph of a body, which has uniform, speed, is a straight line
Time distance graph of a body, which has uniform, speed, is a straight line
 In the above figure, speed of the car varies at different interval of time. Therefore, speed of the car is non-uniform.
Graphical representation of non-uniform speed.
In the above figure, speed of the car varies at different interval of time. Therefore, speed of the car is non-uniform.
Graphical representation of non-uniform speed.
 Distance-time graph of a body, which has non-uniform speed, is a curved line.
Distance-time graph of a body, which has non-uniform speed, is a curved line.

Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |