| Length | Weight | Volume |
| 1 km = 1000m | 1 kg = 1000 g | 1 Kl = 1000 | |
| 1 km = 100m | 1 hg = 100 g | 1 hl = 100 | |
| 1 dam = 10 m | 1 dag = 10 g | more...
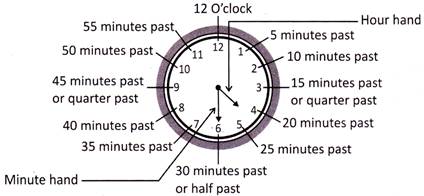
Geometrical Shapes
Introduction
Lines, angles and rays are the basic concept of geometrical figures. Basic geometrical figure was first introduced in text by great mathematician Euclid.
Lines and Its Characteristics
Point
A precise location or place on a plane. Point is usually represented by dot.
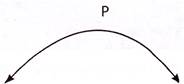 Straight line Curved line
Line Segment
A straight line which links two points without extending beyond them.
Straight line Curved line
Line Segment
A straight line which links two points without extending beyond them.
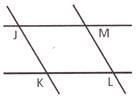 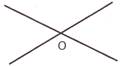 In the pictures above points J, K, L, M and O are intersecting points.
To Draw a Line Segment of a given Length
more...
In the pictures above points J, K, L, M and O are intersecting points.
To Draw a Line Segment of a given Length
more...
Data Handling
Introduction
Pictograph is referred as the representation of data in picture form. In ancient time pictograph was the method for writing the information. Numbers were also represented in picture form.
Pictograph and Its Use
Information about anything in the form of picture is called pictograph. There are different types of graphs which are used for the representation of data. These are bar graph, line graph, venn diagram.
A picture of a house
History of Computing Hardware
Introduction
The development of modern computer is based on the invention of ancient counting devices. Ancient people used pieces of stone, drawing lines and pieces of ropes to record the information. Among the various method of calculation, Abacus is known as the first calculating device. But the computer, first time is better known as the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) developed by John Mauchly and Eckert in 1946. It was used to do mathematical operations and store data.
First Calculating Device- The Abacus
It was the first calculating device which was discovered by the Mesopotamians and improved by the Chinese. It is also called a counting frame and is a calculating tool used primarily in parts of Asia for performing arithmetic processes. An Abacus is made of frames, beads and rods. Calculation is done by the position of beads in the abacus. It allows performing basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It can also carry out operations like counting up to decimal places, calculates sums having negative numbers, etc.
 Napier's bones
Napier's bone was created by John Napier in 1617 for multiplication and division of numbers. Sir John Napier was a great mathematician of Scotland. It was a manual device made of rods. There are ten bones corresponding to the digits 0-9, and a special eleventh bone that is used to represent the multiplier. The multiplier bone is simply a list of the digits 1-9 arranged vertically downward.
Napier's bones
Napier's bone was created by John Napier in 1617 for multiplication and division of numbers. Sir John Napier was a great mathematician of Scotland. It was a manual device made of rods. There are ten bones corresponding to the digits 0-9, and a special eleventh bone that is used to represent the multiplier. The multiplier bone is simply a list of the digits 1-9 arranged vertically downward.
 Mechanical Device - The Pascaline
The calculating machine Pascaline was a mechanical device which was designed and built by the French mathematician- philosopher Blaise Pascal between 1642 and 1644. It was made of chain and toothed wheels. It could add and subtract numbers and capable of carry transfer automatically.
Mechanical Device - The Pascaline
The calculating machine Pascaline was a mechanical device which was designed and built by the French mathematician- philosopher Blaise Pascal between 1642 and 1644. It was made of chain and toothed wheels. It could add and subtract numbers and capable of carry transfer automatically.
 Leibniz Calculator
It was a mechanical calculator invented by German mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz around 1672 and completed in 1694. It also performed multiplication and division. It was made of copper and steel.
Leibniz Calculator
It was a mechanical calculator invented by German mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz around 1672 and completed in 1694. It also performed multiplication and division. It was made of copper and steel.
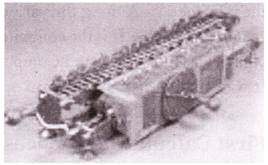 Punch Card in- Jacquard's Loom
The Jacquard loom is a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801 that simplified the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns. It was the first machine that used punch cards to control a sequence of operations.
Punch Card in- Jacquard's Loom
The Jacquard loom is a mechanical loom, invented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1801 that simplified the process of manufacturing textiles with complex patterns. It was the first machine that used punch cards to control a sequence of operations.
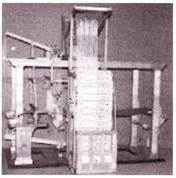 Difference Engine
This was an early calculator designed by Charles Babbage. The difference engine was made to calculate various mathematical functions and mathematical tables. This project was started in 1821 and it employed wheels and rods but failed its test in 1833 because the technology at that time was not so developed.
Difference Engine
This was an early calculator designed by Charles Babbage. The difference engine was made to calculate various mathematical functions and mathematical tables. This project was started in 1821 and it employed wheels and rods but failed its test in 1833 because the technology at that time was not so developed.
 Analytical Engine
The analytical engine was an important more...
Analytical Engine
The analytical engine was an important more...
Growth of Modern Computer
Introduction
The growth of modern computer is the development of hardware and software development of ancient calculating devices. Enhanced capability of different generation of computer are based on the invention of new techniques and components. Ancient world did not imagine that a non-living matter can store data in its memory as a living being can store it. It was possible with the help of punch card. The enhanced version of storage was introduced with the help of magnetic drum. The magnetic drum storage technique is still in use as a platter of a hard drive is coated with magnetic material for storage.
Generation of Computers
The first generation of computer had introduce with the development of storage media. Machine, that was invented before the first generation was only capable of performing arithmetic operation therefore, they were known as calculating machine.
A generation refers to the state of improvement in the development of a product. This term is also used in the different advancements of computer technology. Each phase of computer development is known as a separate generation of computers.
The First Generation Computers (1949-55)
The first generation computers were huge, slow, expensive and often undependable. In 1946, two Americans, Presper Eckert and John Mauchly built the ENIAC electronic computer which used very large and heavy electronic vacuum tubes, which took up a lot of space and gave off a great deal of heat like the light bulbs.
 Limitations:
First generation computer was a first step towards the invention of present form of computer, therefore, it had many limitations.
Some of them are the following:
v These computers were very big in size. The ENIAC machine was 30 x 50 feet in size and 30 tons in weight. Therefore, these machines required a very large space to work.
v Their power consumption was very high.
The Second Generation Computers (1956-65)
The second generation computer started with the invention of transistors.. In 1947, three scientists, John Bardeen, William Shockley and Walter Brattain working at AT&T's Bell Labs invented the transistor which functioned like a vacuum tube. The transistor was faster, more reliable, smaller and much cheaper to build than a vacuum tube. The IBM 1401 was a computer developed during the second generation computer hired on rent by Nepal for Census.
Limitations:
First generation computer was a first step towards the invention of present form of computer, therefore, it had many limitations.
Some of them are the following:
v These computers were very big in size. The ENIAC machine was 30 x 50 feet in size and 30 tons in weight. Therefore, these machines required a very large space to work.
v Their power consumption was very high.
The Second Generation Computers (1956-65)
The second generation computer started with the invention of transistors.. In 1947, three scientists, John Bardeen, William Shockley and Walter Brattain working at AT&T's Bell Labs invented the transistor which functioned like a vacuum tube. The transistor was faster, more reliable, smaller and much cheaper to build than a vacuum tube. The IBM 1401 was a computer developed during the second generation computer hired on rent by Nepal for Census.
 Limitations:
After removing the limitations of 1st generation computers, 2nd generation computers were developed. Despite of that, it had many limitations.
Some of them are as follows:
v The use of transistors instead of vacuum tubes in the second generation computer required heat absorber because, transistors produced excess heat. Therefore, air conditioning was required for cooling the machine.
v more...
Limitations:
After removing the limitations of 1st generation computers, 2nd generation computers were developed. Despite of that, it had many limitations.
Some of them are as follows:
v The use of transistors instead of vacuum tubes in the second generation computer required heat absorber because, transistors produced excess heat. Therefore, air conditioning was required for cooling the machine.
v more...
Introduction to Hardware and Software
Introduction
Let us understand the difference between hardware and software with the help of our body. Our body is hard and we can touch it, move it but what about our feelings? We cannot touch our feelings. Computers are also made in the same way. It consists of two parts, one is hardware and another is software. One without the other is of no use. To run a computer both hardware and software are necessary. Hardware is the part that you can see and touch, parts which cannot be touched are called Software.
Physical parts of Computer (Hardware)
Hardware refers to the physical components of the computer that run the software such as the hard drive, motherboard, video and sound cards, monitor, printer, keyboard and mouse.
 Logical parts of Computer (Software)
Software is a collection of code and instructions that tell a computer and/or hardware how to operate. Software is a set of programs that you install on your computer to help us to do different kinds of work including Games, Word Processing programs, WordPad, Notepad etc.
Relationship Between Hardware and Software
There is a close relationship between computer hardware and software. If hardware is the body, then software is just like the soul in a body. Just as the body cannot live without the soul, the computer cannot perform without software.
Software is code and instructions that tell a computer and/or hardware how to operate. This code can be viewed and executed using a computer or other hardware device.
Software requirement for Hardware of Computer
There are many hardware connected with the computer such as, hard drive, CD drive, RAM, etc. Every connected hardware of a computer requires software to run that is called driver software.
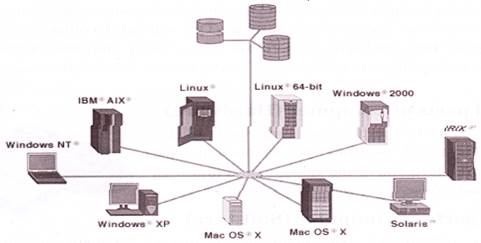
For example: When we connect Printer with the computer, it requires driver software for proper function of the Printer. The user uses computer resource with the help of operating system. Operating system contains system software and some application software also.
Look at the following picture of different types of Operating system:
Logical parts of Computer (Software)
Software is a collection of code and instructions that tell a computer and/or hardware how to operate. Software is a set of programs that you install on your computer to help us to do different kinds of work including Games, Word Processing programs, WordPad, Notepad etc.
Relationship Between Hardware and Software
There is a close relationship between computer hardware and software. If hardware is the body, then software is just like the soul in a body. Just as the body cannot live without the soul, the computer cannot perform without software.
Software is code and instructions that tell a computer and/or hardware how to operate. This code can be viewed and executed using a computer or other hardware device.
Software requirement for Hardware of Computer
There are many hardware connected with the computer such as, hard drive, CD drive, RAM, etc. Every connected hardware of a computer requires software to run that is called driver software.
For example: When we connect Printer with the computer, it requires driver software for proper function of the Printer. The user uses computer resource with the help of operating system. Operating system contains system software and some application software also.
Look at the following picture of different types of Operating system:
What is Booting Up?
Introduction
The booting of a computer is a process in which it checks all the connected hardware in the computer. The POST (Power on Self-Test) report appears during the booting of a computer. Booting process is done very fast, therefore, one of the key on the keyboard is used to view the process during the POST.
Computer requires user attention to minimize the error occurred. Computer room should also be moisture free for the proper functioning and long life of the computer.
Booting Up
The term Booting is used to describe the process of powering on a computer.
It is a process or set of operations that loads and starts the operating system, starting from the point when user switches the powder button.
In your computer lab session in the school, your teacher has handed you an assignment. Once you enter the computer room, you must make your computer ready for doing work. When the computer is first turned on, the system performs a POST (Power On Self-Test.00;.). The computer Power-On Self-Test the computer to make sure it meets the necessary system requirements and that all the hardware is working properly before starting the remainder of the boot process.
The process of loading or copying the operating system is called Booting Process.
These are the following steps:
1. Switch on the Power Supply Button.
2. Switch on the UPS.
3. Switch on the CPU.
4. Switch on the Monitor.
5. Wait for the message on the Monitor.
6. Then wait for the cursor on the Monitor Screen.
7. Computer is ready to work.
You need to turn on the following switches to start a computer.
1. Power Supply Switch: Turn on the switch at the source of the power supply. The stabilizer will start receiving the current.
2. On/Off Switch of UPS: Turn on switch of UPS. The UPS is used to regulate the flow of current.
3. On/Off Switch of CPU: Turn on switch of CPU. The current will start passing through the system.
4. On/Off Switch of the Monitor: Turn on switch of monitor. Look at the monitor and you will see some messages. After these messages you will see the cursor on the monitor screen. Now you can begin working on the computer.
Thus we saw the entire Booting Up process to make the computer ready to work.
There are two types of Booting:
1. Cold booting
2. Warm booting
v Cold booting: If we shut down the computer completely and properly, after a while it starts again on the computer is known as a cold booting.
v Warm booting: If we take the computer to restart button or a key by simply pressing it so Ctrl+Alt+Del is called a warm booting.
Input and Output Devices
Introduction
The computer will be of no use unless it is able to communicate with the outside world. Input/output devices are required for users to communicate with the computer. An input device send information to a computer system for processing. An input device tor a computer allows you to enter information. An output device can receive data from another device, but it cannot send data to another device. There are different devices of he computer that help it to do work.
Input Devices
The devices which are used to input the data and the program in the computer are known as "Input Devices". For the text input, keyboard are used, microphone is used for audio or sound input.
 Keyboard
The keyboard is the most common input device. A 'keyboard' is a human interface device which is "-presented as a layout of buttons. It is a text based input device that allows the user to interact with the computer through a set of keys mounted on a board.
Keyboard
The keyboard is the most common input device. A 'keyboard' is a human interface device which is "-presented as a layout of buttons. It is a text based input device that allows the user to interact with the computer through a set of keys mounted on a board.
 Mouse
After the keyboard, the mouse is the most common type of input device. A mouse makes the process of navigating the screen much easier than trying to use just a keyboard. A mouse usually uses a ball, light or a laser to track movement.
Mouse
After the keyboard, the mouse is the most common type of input device. A mouse makes the process of navigating the screen much easier than trying to use just a keyboard. A mouse usually uses a ball, light or a laser to track movement.
 Joystick
A joystick is an input device consisting of a large pointed stick and input buttons on it. We can use this for playing games on the computer. The joystick is a vertical stick which moves the graphic cursor in a direction the stick is moved. It typically has a button on top that is used to select the option pointed by the cursor.
Joystick
A joystick is an input device consisting of a large pointed stick and input buttons on it. We can use this for playing games on the computer. The joystick is a vertical stick which moves the graphic cursor in a direction the stick is moved. It typically has a button on top that is used to select the option pointed by the cursor.
 Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
An OMR is a device which detects alpha numeric characters printed or written on a paper.
Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
The MICR is an input device or a technology used to verify the original paper documents, especially cheques.
Bar Code Reader
A bar code Reader also called a price scanner of point-of-scale (POS) Scanner, is a hand held or stationary input device, used to read information contained in a bar code.
Output Devices
An output device is used to send data from a computer to another device used. They are pieces of hardware that process data sent from a computer and translate it into a form readable by human. This information can be inany form that includes text, sound, images, etc. Output devices such as a printer, video display or speaker present data from a computer to a user. Thus we see that output devices are things we use to get information of a computer that has been held o generated within a computer. more...
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
An OMR is a device which detects alpha numeric characters printed or written on a paper.
Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
The MICR is an input device or a technology used to verify the original paper documents, especially cheques.
Bar Code Reader
A bar code Reader also called a price scanner of point-of-scale (POS) Scanner, is a hand held or stationary input device, used to read information contained in a bar code.
Output Devices
An output device is used to send data from a computer to another device used. They are pieces of hardware that process data sent from a computer and translate it into a form readable by human. This information can be inany form that includes text, sound, images, etc. Output devices such as a printer, video display or speaker present data from a computer to a user. Thus we see that output devices are things we use to get information of a computer that has been held o generated within a computer. more... Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. |