Introduction
Unitary method is self-indicating that this is the method for finding the value of unit article if the values of two or more articles is given. This method is widely used for the simplification of word based problems in arithmetic and geometry. In this chapter we will learn about the concept and use of unitary method.

Unitary Method and Its Use
Unitary method is used for solving the problems if there are variation in the given quantity. In this method different quantities are converted into single unit and required unit is obtained by arithmetic operations. If a car travels 20 km in 15 minutes and it is required to find the distance travelled by car in 60 minutes then distance travelled by the car in 1 minute must be carried out, that is obtained by the division of
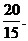
TTherefore, the distance travelled by the car in 60 minutes is obtained by multiplying the distance travelled in 1 minute by
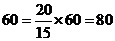
kilometres.

The weight of 4 coins is 150 grams. What is the weight of 10 such coins?
(a) 380 grams
(b) 400 grams
(c) 500 grams
(d) 1500 grams
(e) None of these
Answer (a)
Explanation The weight of 4 coins = 150 grams therefore, the weight of 1 coin
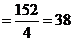
grams i.e, the weight of 10 coins
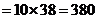
gram.

Applications of Unitary Method
The given number of articles is converted into single unit and the value of required number of articles is obtained. The cost of 7 articles is Rs 686, for finding the cost of one article Rs 686 is divided by 7. Therefore, the cost of one article,
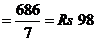
and the cost of 12 such articles
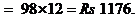

A company buys 45 computers. If the cost of total number of hard disks isB 84330, then what will be the cost of 96 such hard disks?
(a) Rs 179908
(b) Rs 179904
(c) Rs 179910
(d) Rs 170000
(e) None of these
Answer (b)
Explanation
The cost of 45 hard disks is? 84330. Therefore, the cost off one hard disk
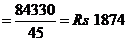
The cost of 96 such hard disks
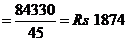
The cost of 96 such hard disk
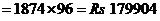

The total length of 6 equal plane figures is 54 metres. What will be the total length of 9 such plane figures?
(a) 82 metres
(b) 80 metres
(c) 81
more...
 Look at the following pictures of denominated Indian rupees:
Look at the following pictures of denominated Indian rupees: