 1. A suitable place for organisms to stay and rest.
2. It makes enough food available.
3. Provides protection to the in habitants.
4. Provides place for breeding and rearing of organisms.
5. Provides space for movement.
Terrestrial habitat refers to the land where all plants and animals survive. It includes deserts, forests and grasslands, as well as coastal and mountain regions. For example, camels and cactus plants live in deserts only.
Aquatic habitat refers to the water where plants and animals survive. Aquatic habitat includes rivers, ponds, lakes, ocean and swamps. For example, fish live in water.
Adaptation: Plants and animals develop certain features or certain habits that help them survive in their surroundings, and this is known as adaption. Different living creatures adapt to their habitats in different ways. For example, fish have gills that help them to live in water and use the oxygen dissolve in it.
6. Plants that live in water have special tissues that help to take in dissolved gas from water. For example, the ulva has ribbon-like leaves. It takes thousands of years for a livings being to adapt to its habitat.
Acclimatization: The small adjustments by the body to overcome small changes in the surrounding atmosphere for a short period of time are called acclimatization.
The components in a habitat are broadly classified into two types. They are biotic and a biotic components.
Biotic components include all the livings organisms in a habitat. These can be farther classified into following categories: more...
1. A suitable place for organisms to stay and rest.
2. It makes enough food available.
3. Provides protection to the in habitants.
4. Provides place for breeding and rearing of organisms.
5. Provides space for movement.
Terrestrial habitat refers to the land where all plants and animals survive. It includes deserts, forests and grasslands, as well as coastal and mountain regions. For example, camels and cactus plants live in deserts only.
Aquatic habitat refers to the water where plants and animals survive. Aquatic habitat includes rivers, ponds, lakes, ocean and swamps. For example, fish live in water.
Adaptation: Plants and animals develop certain features or certain habits that help them survive in their surroundings, and this is known as adaption. Different living creatures adapt to their habitats in different ways. For example, fish have gills that help them to live in water and use the oxygen dissolve in it.
6. Plants that live in water have special tissues that help to take in dissolved gas from water. For example, the ulva has ribbon-like leaves. It takes thousands of years for a livings being to adapt to its habitat.
Acclimatization: The small adjustments by the body to overcome small changes in the surrounding atmosphere for a short period of time are called acclimatization.
The components in a habitat are broadly classified into two types. They are biotic and a biotic components.
Biotic components include all the livings organisms in a habitat. These can be farther classified into following categories: more... 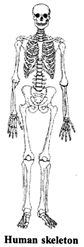 Human body movements: Humans can move their various body parts indifferent ways. We can move some parts of our body in different directions and some body parts can be moved only in one direction. Our body is made up of a frame work of bones called skeleton.
1. Bones are made of hard substance.
2. Cartilages are soft and elastic.
3. In the bone marrow, red blood cells are produced.
4. Bones are of many shapes and sizes. Some are flat, some are cylindrical and some are spherical.
5. The longest bone of our body is femur and the smallest bone is found in our internal ears.
6. Cartilages are found in our nose and external ears.
7. Skeleton system extends from the top of our head to the tip of the toes.
Functions of skeleton:
Human body movements: Humans can move their various body parts indifferent ways. We can move some parts of our body in different directions and some body parts can be moved only in one direction. Our body is made up of a frame work of bones called skeleton.
1. Bones are made of hard substance.
2. Cartilages are soft and elastic.
3. In the bone marrow, red blood cells are produced.
4. Bones are of many shapes and sizes. Some are flat, some are cylindrical and some are spherical.
5. The longest bone of our body is femur and the smallest bone is found in our internal ears.
6. Cartilages are found in our nose and external ears.
7. Skeleton system extends from the top of our head to the tip of the toes.
Functions of skeleton:
 II. Based on their life span: Depending on the duration of their life cycle, there are three types of plants:
(i) Annuals: The life cycle of these plants is completed in one yearThey grow, produce flowers and seeds during this period and thendie. E.g. wheat, pulses, gram.
II. Based on their life span: Depending on the duration of their life cycle, there are three types of plants:
(i) Annuals: The life cycle of these plants is completed in one yearThey grow, produce flowers and seeds during this period and thendie. E.g. wheat, pulses, gram.
 (ii) Biennials: These plants complete their life cycle in two years. These plants are usually herbs.
(iii) Perennials: These remain alive for many years. These are mostlyshrubs and trees. They keep producing flowers, fruits and seeds year after year. E.g. neem, mango. Hibiscus, etc.
(ii) Biennials: These plants complete their life cycle in two years. These plants are usually herbs.
(iii) Perennials: These remain alive for many years. These are mostlyshrubs and trees. They keep producing flowers, fruits and seeds year after year. E.g. neem, mango. Hibiscus, etc.
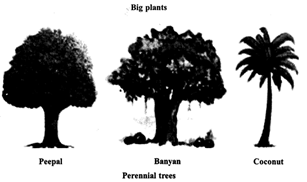 III. Classification based on the size and nature of stem. Based on nature of stem plants can be grouped into
(a) Herbs
(b) Shrubs
(c) Trees
(d) Climbers
III. Classification based on the size and nature of stem. Based on nature of stem plants can be grouped into
(a) Herbs
(b) Shrubs
(c) Trees
(d) Climbers
| Parameters | Herbs | Shrubs | Trees | Climbers | Creepers | |||||||||||
| Size | Very small, less than 1 m high | medium size 1-3 m high | tall more than 3 m high | can be very tall | can be very long | |||||||||||
| Nature of stem | green, tender stem, few brances |
Learning Objectives
1. Food provides energy and keeps the body fit and healthy.
2. We use a variety of ingredients to prepare food.
3. Food can be obtained from plants and animals.
4. Plant sources are cereals, pulses, fruits, vegetables, oil, seeds, etc.
5. Animal sources are milk, egg, meat, fish, etc.
6. There are three kinds of animals, herlivores, carnivores and omnivores.
7. Each animal is dependent on either plant or another animal for food.
8. A series of plants and animals depending on each other forms the food cycle.
9. Balance of nutrients in nature is necessary.
To keep a car engine running properly, it should be supplied with right amount of fuel and oxygen. Similarly to keep our body working properly, it must be supplied with right amount of right chemicals in food. These chemicalsubstances in food that our body needs is called nutrients.
Functions of Food
Food has 3 main functions:
It provides energy for various activities of the body.
It helps the body to grow and replace old cells.
It protects the body from various diseases and keeps it fit and healthy.
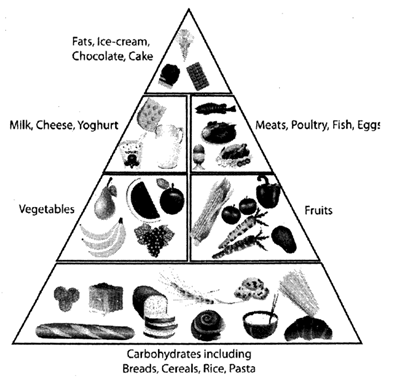 Different food items containing carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.
Different food items containing carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.
  We eat different kinds of food, we eat grains, pulses, vegetables, fruits, fish, eggs, meat and different dairy products. Different food contain different nutrients. Some nutrients help us grow, some give energy and some help income pleating diseases.
India is a vast country and people in different regions cook different dishes. A basic dish like boilde rice contain only rice and water. A vegetable pulao/biryani contain rice, vegetables, spices, water, salt and oil. It has number of ingredients. These ingredients come from two sources - plants and animals.
We eat different kinds of food, we eat grains, pulses, vegetables, fruits, fish, eggs, meat and different dairy products. Different food contain different nutrients. Some nutrients help us grow, some give energy and some help income pleating diseases.
India is a vast country and people in different regions cook different dishes. A basic dish like boilde rice contain only rice and water. A vegetable pulao/biryani contain rice, vegetables, spices, water, salt and oil. It has number of ingredients. These ingredients come from two sources - plants and animals.
 Boiled rice has 2 ingredients
Boiled rice has 2 ingredients
 Vegetable pulao has many ingredients
SOURCES OF FOOD
Food from plants: Green plants prepare their own food with the help of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight by the process of photo synthesis. Greenplants are therefore called producers. They prepare some extra food thanthey need. This extra food is stored in various parts of the plant.
Do You Know
Roots of Baobab tree are eaten during famine
PLANTS PARTS THAT ARE EATEN
Roots: We eat roots of carrot, radish, sweet potato and beetroot. In Rajasthan roots of more...
Vegetable pulao has many ingredients
SOURCES OF FOOD
Food from plants: Green plants prepare their own food with the help of carbon dioxide, water and sunlight by the process of photo synthesis. Greenplants are therefore called producers. They prepare some extra food thanthey need. This extra food is stored in various parts of the plant.
Do You Know
Roots of Baobab tree are eaten during famine
PLANTS PARTS THAT ARE EATEN
Roots: We eat roots of carrot, radish, sweet potato and beetroot. In Rajasthan roots of more...
Learning Objectives
1. To understand changes around us
2. To understand effect of causes of these changes on things around us
3. To understand classification of different changes on the basis of their effect
4. To understand characteristics of these changes.
Every day, we see different types of changes around us, like day turning into night, the season changing from winter to summer, melting of ice to water, cooking of food, rusting of iron .growth of our body and so on.
There are number of changes taking place around us -Some of these changes can be noticed immediately, some changes can be noticed after some time and there are some changes that cannot be noticed.
Every change has a cause for example day and night alternate because of the rotation of the earth around the sun. Changes in weather is due to the heat of the sun These causes can bring about changes in:
 Shape and size: There is a change in shape and size of a balloon when air is blown into it.
Making of various toys or geometrical figures (such as rectangle, square etc.) using a paper sheet bring about a change in the sheet of paper. The ball of dough takes the shape of a chapati when it is properly rolled.
State: Ice melts on heating, melting of butter and ice cream etc.
Position: Sun changes its position from east to west due to rotation of the earth around imposition of a football changes on kicking it.
Colour: On heating an iron piece it becomes red hot, colour change of silver ornament etc.
Shape and size: There is a change in shape and size of a balloon when air is blown into it.
Making of various toys or geometrical figures (such as rectangle, square etc.) using a paper sheet bring about a change in the sheet of paper. The ball of dough takes the shape of a chapati when it is properly rolled.
State: Ice melts on heating, melting of butter and ice cream etc.
Position: Sun changes its position from east to west due to rotation of the earth around imposition of a football changes on kicking it.
Colour: On heating an iron piece it becomes red hot, colour change of silver ornament etc.
 CLASSIFICATION OF CHANGES
1. Based on Speed
Slow changes: A change that occurs very slowly and takes a very long time for completion is called a slow change.
For example
CLASSIFICATION OF CHANGES
1. Based on Speed
Slow changes: A change that occurs very slowly and takes a very long time for completion is called a slow change.
For example
 Fast changes: A change that occurs spontaneously or occurs at a very fast speed is called a fast change. For example:
Fast changes: A change that occurs spontaneously or occurs at a very fast speed is called a fast change. For example:
Learning Objectives
1. To understand mixtures and types of mixture.
2. To understand requirement and Importance of separation of components of a mixture.
3. To understand different methods of separation.
4. To understand that the choice of the method of separation depends upon the nature of the component of the mixture.
5. To understand the different types of solution.
6. To understand the concept of solubility.
MIXTURES
Mixtures are absolutely everywhere you look. Mixtures are the form that are mostly found in nature e.g. rocks, air, or the ocean they are just about anything you find. They are substances held together by physical forces, not chemical.
Two or more substances (either elements or compounds) can be mixed together in any proportion and the resultant substances so obtained are called mixtures (impure substance).
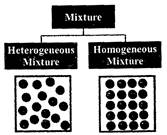
Types of Mixtures
Depending upon the nature of the components that forms the mixture we can have different types of mixtures.
(i) Homogeneous mixture: It is a mixture that has the same composition throughout, e.g. a solution of sugar in water. Such a mixture has two or more components.
(ii) Heterogeneous mixture: In such a mixture the particles of each component of the mixture remain separate and can be observed as individual grains under a microscope, e.g. mixture of grains and sand.
This type of mixtures contain physically distinct parts and have a non-uniform composition.
Do You Know
Most homogeneous mixture are also known as solutions and examples of these include air, coffees, and even metal alloys.
Learning Objectives
1. To learn about materials that are used for making objects
2. To understand grouping and sorting of materials
3. To learn about classification and its importance
4. To understand different properties of materials such as appearance .roughness .hardness, solubility, transparency, flotation, magnetic and conduction property
We have a number of objects around us like trees, toys, paper, table, chair etc.
Some of these objects are living and some are non-living. Non-living objects can be man-made or natural. Objects around us may have different size, shapes, colours and uses. All objects around us are made up of one or more type of materials such as paper, glass, plastic, cloth, wood, metal, mud, soil, cotton, etc.
An object can be made from different materials. For example, chair can be made from wood or plastic.
Different objects can be made from the same material. For example window panes and fish bowl are made from same material, glass.
Several objects are made up of combination of several materials. For example mango shake is made up of mango, milk, sugar etc.
Different materials have different properties. Many objects differing in usage can be made from the same material. There are so many ways to group objects.
Placing similar things together is called grouping-For example in supermarket grouping is done by keeping similar items on same shelf, which make it easier for us to find the item we need.
CLASSIFICATION
The process of sorting and grouping objects/things according to some basis is called Classification. It makes study of large number of objects of different type easier, simple, systematic and convenient.
PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Different types of materials have different properties. Some of the important properties of materials are given as following.
Appearance
In appearance materials usually look very different from each other. The appearance of wood is different from iron. Similarly appearance of iron is different from copper or aluminum.
Some materials when freshly cut appear shiny where as others have no shine Metals shine in their pure state. This shining property of metal is called metallicIustre.
 Some materials having lustre are iron, copper, aluminum, gold, silver, etc.
Materials can be classified on the basis of their luster as lustrous materials, for example gold, silver etc and non-lustrous materials for example wood, plastic, stone etc.
Shining property of gold, copper and silver is used for making jewelry. Some metals often loose their shine when exposed to air and moisture for some time.
Hardness
Some materials having lustre are iron, copper, aluminum, gold, silver, etc.
Materials can be classified on the basis of their luster as lustrous materials, for example gold, silver etc and non-lustrous materials for example wood, plastic, stone etc.
Shining property of gold, copper and silver is used for making jewelry. Some metals often loose their shine when exposed to air and moisture for some time.
Hardness
 Hardness: On the basis of hardness more...
Hardness: On the basis of hardness more...
Learning Objectives
1. To study different types of clothing materials
2. To understand the concept of fibers, fabric and yam
3. To know different sources to get fibers
4. To study different plants, animal and synthetic fibers
5. To understand different methods to get fabric from yam
6. To know history of clothing
We wear clothes to protect our body against heat, cold, rain, dust and insects. At the same time we wear clothes to look good. That is why many of us want towear clothes that are in fashion.People in different regions of the world weardifferent kinds of clothes the kind of clothes people wear mainly depends onthe climate of the place. The traditional clothes worn by people in our countryvary considerably from region to region..
 People living in hot countries wear light clothing. During summer we should wear loose fitting clothes to keep our body cool.People living in cold countries wear woolen clothes like -coats, jerseys, socks, caps etc. Dark coloured clothes are worn in winters because they absorb heat and warm quickly.
People living in hot countries wear light clothing. During summer we should wear loose fitting clothes to keep our body cool.People living in cold countries wear woolen clothes like -coats, jerseys, socks, caps etc. Dark coloured clothes are worn in winters because they absorb heat and warm quickly.
  FABRICS
Fabrics are materials made from weaving, knitting, spinning fibres together.
Often the fibres are spun or wound together to form a thread before beingmade into a fabric. The nature of a fabric will depend on the fibres from which it is made and the way that they are arranged, and its properties will determine the applications for which it is suitable. Cotton, wool, silk etc. are examples of fabrics.
YARN
It is made up of fibres. Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope making. Thread is a type of yarn.
FIBRES
A fibre a is thread which is strong and flexible enough to make clothes.
Fibres can be broadly classified as natural fibres and synthetic fibres e.g.
Natural fibres: Cotton, Wool, Silk, Pure jute etc.
Synthetic fibres: Nylon, Polyester, Acrylic etc.
Sources of Natural Fibres
Natural fibres are obtained from
(i) Plant sources: cotton, jute.
(i) Animal sources: wool, silk
PLANT FIBRES
Cotton, sisal, flax jute, ramie, coir and hemp are examples of plant fibres.Theyhave more extensive use than animal fibres
Cotton
Cotton is a soft fibre that is obtained from cotton plant. Cotton is generally grown in such places that have black soil and warm climate. The fruits ofcotton plant are called cotton bolls. They more...
FABRICS
Fabrics are materials made from weaving, knitting, spinning fibres together.
Often the fibres are spun or wound together to form a thread before beingmade into a fabric. The nature of a fabric will depend on the fibres from which it is made and the way that they are arranged, and its properties will determine the applications for which it is suitable. Cotton, wool, silk etc. are examples of fabrics.
YARN
It is made up of fibres. Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, suitable for use in the production of textiles, sewing, knitting, weaving, embroidery, and rope making. Thread is a type of yarn.
FIBRES
A fibre a is thread which is strong and flexible enough to make clothes.
Fibres can be broadly classified as natural fibres and synthetic fibres e.g.
Natural fibres: Cotton, Wool, Silk, Pure jute etc.
Synthetic fibres: Nylon, Polyester, Acrylic etc.
Sources of Natural Fibres
Natural fibres are obtained from
(i) Plant sources: cotton, jute.
(i) Animal sources: wool, silk
PLANT FIBRES
Cotton, sisal, flax jute, ramie, coir and hemp are examples of plant fibres.Theyhave more extensive use than animal fibres
Cotton
Cotton is a soft fibre that is obtained from cotton plant. Cotton is generally grown in such places that have black soil and warm climate. The fruits ofcotton plant are called cotton bolls. They more...
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
Current Affairs CategoriesArchive
Trending Current Affairs
You need to login to perform this action. | ||||||||||||||