 Land preparation and cultivation methodology is among the basic factors which affect the yield of crops. For getting better yield, it is important to prepare land thoroughly, so that the weeds are destroyed and water absorption capacity of the soil is increased.
Crops
When the same kind of plants are grown in the fields on a large scale to obtain foods like cereals, pulses, vegetables and fruits, etc., it is called a crop.
Agriculture
The growing of plants (or crops) in the fields for obtaining food is called agriculture. Crop production involves various agricultural practices such as:
Land preparation and cultivation methodology is among the basic factors which affect the yield of crops. For getting better yield, it is important to prepare land thoroughly, so that the weeds are destroyed and water absorption capacity of the soil is increased.
Crops
When the same kind of plants are grown in the fields on a large scale to obtain foods like cereals, pulses, vegetables and fruits, etc., it is called a crop.
Agriculture
The growing of plants (or crops) in the fields for obtaining food is called agriculture. Crop production involves various agricultural practices such as:
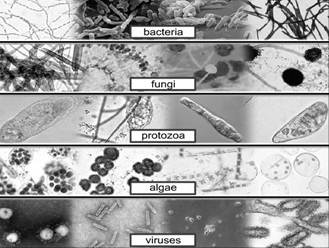 A microorganism or microbe is an organism that is microscopic (usually too small to be seen by the naked human eye). The study of microorganisms is called microbiology. Microorganisms live in all parts of the biosphere where there is liquid water, including soil, hot springs, on the ocean floor, high in the atmosphere and deep inside rocks within the earth's crust.
Major Groups of Micro-organisms
A microorganism or microbe is an organism that is microscopic (usually too small to be seen by the naked human eye). The study of microorganisms is called microbiology. Microorganisms live in all parts of the biosphere where there is liquid water, including soil, hot springs, on the ocean floor, high in the atmosphere and deep inside rocks within the earth's crust.
Major Groups of Micro-organisms
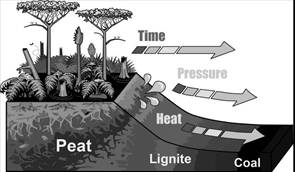 Coal is a sedimentary rock formed from plants that flourished millions of years ago when tropical swamps covered large areas of the world. Lush vegetation, such as early club mosses, horsetails, and enormous ferns, thrived in these swamps. Generations of this vegetation died and settled to the swamp bottom and over time the organic material with a high percentage of carbon. Layers of mud and sand accumulated over the decomposed plant matter, compressing and hardening the organic material as the sediments deepened. Over millions of years, depending sediments layers, known as overburden, exerted tremendous heat and pressure on the underlying plant matter, which eventually became coal.
Types of coal
Coal is a sedimentary rock formed from plants that flourished millions of years ago when tropical swamps covered large areas of the world. Lush vegetation, such as early club mosses, horsetails, and enormous ferns, thrived in these swamps. Generations of this vegetation died and settled to the swamp bottom and over time the organic material with a high percentage of carbon. Layers of mud and sand accumulated over the decomposed plant matter, compressing and hardening the organic material as the sediments deepened. Over millions of years, depending sediments layers, known as overburden, exerted tremendous heat and pressure on the underlying plant matter, which eventually became coal.
Types of coal
 As geological process apply pressure to dead dead biotic matter over time, under suitable conditions it is transformed successively into:
Peat: It is considered to be a precursor of coal, has industrial importance as a fuel in some regions, for example, Ireland and Finland.
Lignite: It is also referred as brown coal, is the lowest rank of coal and used almost exclusively as fuel for electric power generation.
Bituminous: It is dense rock which is usually black but sometimes dark brown, used primarily as fuel in steam-electric power generation, with substantial quantities also used for heat and power applications in manufacturing and to make coke.
Anthracite: It is the highest rank of coal; a harder, glossy, black coal used primarily for give some other use.
Petroleum
It is, also known as crude oil, a fossil fuel, formed over a period of millions of years, from organisms that lived in the sea at that time. Their dead bodies sank to the bottom of sea and were covered with mud and sand. Due to high pressure, heat, in the absence of air, the dead remains of tiny plants and animals were slowly converted into petroleum. Process of separating crude petroleum oil into more useful fractions is called refining. The various useful fractions obtained by the refining of petroleum are: Petroleum gas, Petrol, Kerosene, Diesel, Lubricating oil, Paraffin wax and bitumen.
Combustion
It is a process of rapid oxidation or burning of a substance in the presence of oxygen to produce heat and light.
Requirements for the occurrence of combustion are:
As geological process apply pressure to dead dead biotic matter over time, under suitable conditions it is transformed successively into:
Peat: It is considered to be a precursor of coal, has industrial importance as a fuel in some regions, for example, Ireland and Finland.
Lignite: It is also referred as brown coal, is the lowest rank of coal and used almost exclusively as fuel for electric power generation.
Bituminous: It is dense rock which is usually black but sometimes dark brown, used primarily as fuel in steam-electric power generation, with substantial quantities also used for heat and power applications in manufacturing and to make coke.
Anthracite: It is the highest rank of coal; a harder, glossy, black coal used primarily for give some other use.
Petroleum
It is, also known as crude oil, a fossil fuel, formed over a period of millions of years, from organisms that lived in the sea at that time. Their dead bodies sank to the bottom of sea and were covered with mud and sand. Due to high pressure, heat, in the absence of air, the dead remains of tiny plants and animals were slowly converted into petroleum. Process of separating crude petroleum oil into more useful fractions is called refining. The various useful fractions obtained by the refining of petroleum are: Petroleum gas, Petrol, Kerosene, Diesel, Lubricating oil, Paraffin wax and bitumen.
Combustion
It is a process of rapid oxidation or burning of a substance in the presence of oxygen to produce heat and light.
Requirements for the occurrence of combustion are:
 Conservation is the sustainable use and protection of natural resources including plants, animals, mineral deposits, soil, clean water, clean air and fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. Natural resources are grouped into two categories: renewable resource is the one that may be replaced over the time by natural processes such as fish populations, natural vegetation or is inexhaustible such as the solar energy. Nonrenewable resources are those which are limited in supply and cannot be replaced even over extremely long period of time. The nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels and mineral deposits, such as iron ore and gold ore. Conservational activities for the nonrenewable resources focus on maintaining an adequate supply of these resources well in the future.
Natural resources are conserved for their biological, economical and recreational values, as well as their natural beauty and importance to the local cultures. For example, tropical rain forests are protected for their important role in both the global ecology and the economic livelihood of the local culture. A coral reef may be protected for its recreational value for scuba divers and a scenic river may be protected for its natural beauty.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological variety denotes the number and variety of different organisms and ecosystems in a certain area. We should conserve forests and wildlife to preserve biodiversity to prevent endangered species from becoming extinct and to maintain ecological balance in nature.
Deforestation
Conservation is the sustainable use and protection of natural resources including plants, animals, mineral deposits, soil, clean water, clean air and fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum and natural gas. Natural resources are grouped into two categories: renewable resource is the one that may be replaced over the time by natural processes such as fish populations, natural vegetation or is inexhaustible such as the solar energy. Nonrenewable resources are those which are limited in supply and cannot be replaced even over extremely long period of time. The nonrenewable resources include fossil fuels and mineral deposits, such as iron ore and gold ore. Conservational activities for the nonrenewable resources focus on maintaining an adequate supply of these resources well in the future.
Natural resources are conserved for their biological, economical and recreational values, as well as their natural beauty and importance to the local cultures. For example, tropical rain forests are protected for their important role in both the global ecology and the economic livelihood of the local culture. A coral reef may be protected for its recreational value for scuba divers and a scenic river may be protected for its natural beauty.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological variety denotes the number and variety of different organisms and ecosystems in a certain area. We should conserve forests and wildlife to preserve biodiversity to prevent endangered species from becoming extinct and to maintain ecological balance in nature.
Deforestation
 Deforestation means large scale removal of forest prior to its replacement by other land uses. Forests are removed for a variety of reasons, including agriculture, timber harvesting, mining and to make way for roads, dams and human settlements.
Protected Areas
Protected areas are the areas of land or sea especially dedicated to the protection and maintenance of biodiversity. These are managed through legal means and have set up within the legal frame work of Indian wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. Examples of protected areas are national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
National Parks
A national park is a large area dedicated to conserve the environment, natural resources and the wildlife therein. In a national park,
Deforestation means large scale removal of forest prior to its replacement by other land uses. Forests are removed for a variety of reasons, including agriculture, timber harvesting, mining and to make way for roads, dams and human settlements.
Protected Areas
Protected areas are the areas of land or sea especially dedicated to the protection and maintenance of biodiversity. These are managed through legal means and have set up within the legal frame work of Indian wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. Examples of protected areas are national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
National Parks
A national park is a large area dedicated to conserve the environment, natural resources and the wildlife therein. In a national park,
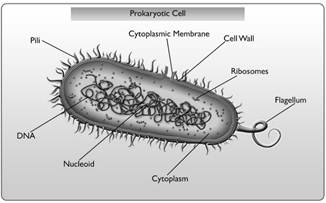 Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are typically about ten times larger than the prokaryotic cells. In animal cells, the plasma membrane rather than a cell wall, forms the cell's outer boundary. With a design similar to the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells, it separates the cell from its surroundings and regulates the traffic across the membrane.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are typically about ten times larger than the prokaryotic cells. In animal cells, the plasma membrane rather than a cell wall, forms the cell's outer boundary. With a design similar to the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells, it separates the cell from its surroundings and regulates the traffic across the membrane.
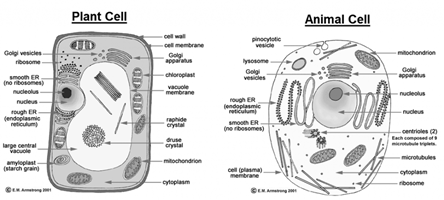 The eukaryotic cell cytoplasm is similar to that of the prokaryotic cell except for one major difference. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and numerous other membrane-enclosed organelles. Like separate rooms of a house, these organelles enable specialized functions to be carried out efficiently. For example, the building of proteins and lipids takes in separate organelles where specialized enzymes geared for each job are located.
The nucleus is the largest organelle in an animal cell. It contains numerous strands of DNA, the length of each strand being many times the diameter of the cell. Unlike the circular prokaryotic DNA, long sections of eukaryotic DNA pack into the nucleus by wrapping around proteins. As a cell begins to divide, each DNA strand folds over on to itself several times, forming a rod-shaped chromosome.
Cell Functions
To stay alive, cells must be able to carry out a variety of functions. Some cells must beable to move and most cells must be able to divide. All cells must maintain the right concentration of chemicals in their cytoplasm, ingest food and use it for energy, recycle molecules, expel wastes and construct proteins. Cells must also be able to respond to changes in their environment.
Movement
Many unicellular organisms swim, glide, thrash or crawl to search for food and escapes enemies. Swimming organisms often move by means of a flagellum, a long tail-like structure made of protein. For example, many bacteria have one, two or many flagella that rotate like propellers to drive the organism along. Some more...
The eukaryotic cell cytoplasm is similar to that of the prokaryotic cell except for one major difference. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and numerous other membrane-enclosed organelles. Like separate rooms of a house, these organelles enable specialized functions to be carried out efficiently. For example, the building of proteins and lipids takes in separate organelles where specialized enzymes geared for each job are located.
The nucleus is the largest organelle in an animal cell. It contains numerous strands of DNA, the length of each strand being many times the diameter of the cell. Unlike the circular prokaryotic DNA, long sections of eukaryotic DNA pack into the nucleus by wrapping around proteins. As a cell begins to divide, each DNA strand folds over on to itself several times, forming a rod-shaped chromosome.
Cell Functions
To stay alive, cells must be able to carry out a variety of functions. Some cells must beable to move and most cells must be able to divide. All cells must maintain the right concentration of chemicals in their cytoplasm, ingest food and use it for energy, recycle molecules, expel wastes and construct proteins. Cells must also be able to respond to changes in their environment.
Movement
Many unicellular organisms swim, glide, thrash or crawl to search for food and escapes enemies. Swimming organisms often move by means of a flagellum, a long tail-like structure made of protein. For example, many bacteria have one, two or many flagella that rotate like propellers to drive the organism along. Some more... 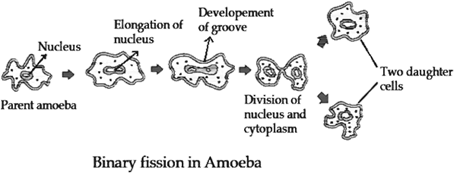
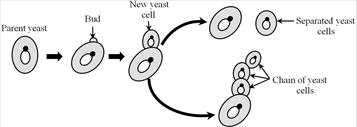 Budding in yeast
Budding in yeast
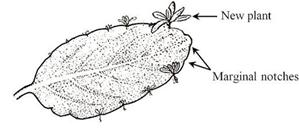 Vegetative propagation by leaves in Bryophyllum
Vegetative propagation by leaves in Bryophyllum
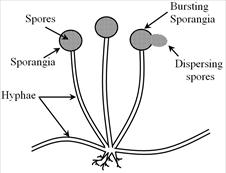 Spore formation in Rhizopus
Spore formation in Rhizopus
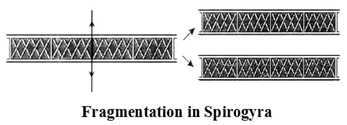 Sexual Reproduction
It is a method of reproduction of producing a new individual from two parents by combining their genetic information. For example, human beings, dog, cat, etc.
Fertilisation
The process of formation of zygote by the fusion of male gamete and female gamete is known as fertilisation. There are two types of fertilization: internal and external Fertilisation.
Sexual Reproduction
It is a method of reproduction of producing a new individual from two parents by combining their genetic information. For example, human beings, dog, cat, etc.
Fertilisation
The process of formation of zygote by the fusion of male gamete and female gamete is known as fertilisation. There are two types of fertilization: internal and external Fertilisation.
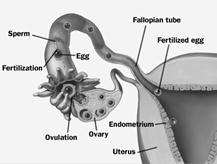 Fertilisation in humans from a zygote (fertilised egg)
Fertilisation in humans from a zygote (fertilised egg)
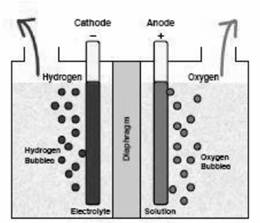 Process of Electrolysis
Electroplating
The process of covering a more reactive metal with a less reactive metal with the help of electricity is known as electroplating. Material to be plated should be connected cathode while anode usually loses material.
Light
The sense of sight is one of the most important senses. Through this we see things around us. Light is an electromagnetic radiation, specifically radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye.
Luminous and Non-luminous Objects
Process of Electrolysis
Electroplating
The process of covering a more reactive metal with a less reactive metal with the help of electricity is known as electroplating. Material to be plated should be connected cathode while anode usually loses material.
Light
The sense of sight is one of the most important senses. Through this we see things around us. Light is an electromagnetic radiation, specifically radiation of a wavelength that is visible to the human eye.
Luminous and Non-luminous Objects
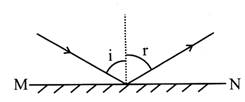 Laws of Reflection
According to first law of reflection: the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal ray, all lie in the same plane.
According to second law of reflection: the angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
Periscope
is a long, tubular device used to observe over, around or through an object that is out of direct line of sight. A periscope works on the reflection of light from two plane mirrors arranged parallel to one another.
Human Eye
The eye enables us to see the various objects around us. The main parts of human eye are:
Laws of Reflection
According to first law of reflection: the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal ray, all lie in the same plane.
According to second law of reflection: the angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
Periscope
is a long, tubular device used to observe over, around or through an object that is out of direct line of sight. A periscope works on the reflection of light from two plane mirrors arranged parallel to one another.
Human Eye
The eye enables us to see the various objects around us. The main parts of human eye are:
 more...
more... 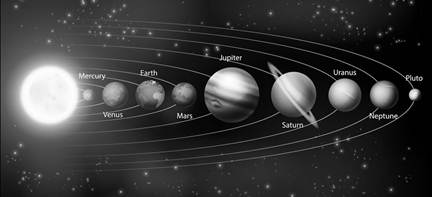 Solar System
Sun
Sun is the closest star to the earth. Its average distance from the earth is about 150 million kilometres. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. Diameter of sun is about
1.4 million km. The temperature at its surface is about\[{{6000}^{o}}C\].
Planets
Based on the distances of planets from the sun they are as follows: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All the planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path called orbit. Planets which are close to the sun like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called inner planets or terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are known as the outer planets or jovian planets as they are far from the sun.
Mercury - is nearest to the sun. This planet has a rocky surface which is covered with craters. It is the smallest planet of the solar system.
Venus - is the second planet from the sun. Venus is a rocky planet. It is the hottest planets as its atmosphere is mainly made up of carbon dioxide. It rotates on its axis from east to west.
Earth - is the third planet from the sun. Earth's atmosphere has sufficient oxygen, the gas we need to live and water.
Mars - is also known as a red planet. The thin atmosphere of mars contains mainly carbon dioxide with small amounts of nitrogen, oxygen, noble gases and water vapour. It appears red due to the high amount of iron oxide present on its surface.
Jupiter - is the biggest planet and is made mainly of hydrogen and helium.
Saturn - is the second biggest planet of the solar system and is made up of mainly hydrogen and helium. It has well developed system of rings surrounding it. It is the least dense planet and can float in water.
Uranus - is the third biggest planet of the solar system and is mainly made up of hydrogen and helium.
Neptune - is the outermost planet of the solar system and is made mainly of liquid and frozen hydrogen and helium gases.
The Moon
A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as natural satellite or moon of the planet. The earth has only one moon. It reflects the light of the sun. Its surface is covered with craters and mountains.
Phases of moon
Shapes of the bright part of the moon, as seen from the earth, are known as the phases of moon.
Solar System
Sun
Sun is the closest star to the earth. Its average distance from the earth is about 150 million kilometres. It consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. Diameter of sun is about
1.4 million km. The temperature at its surface is about\[{{6000}^{o}}C\].
Planets
Based on the distances of planets from the sun they are as follows: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. All the planets revolve around the sun in a fixed path called orbit. Planets which are close to the sun like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are called inner planets or terrestrial planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are known as the outer planets or jovian planets as they are far from the sun.
Mercury - is nearest to the sun. This planet has a rocky surface which is covered with craters. It is the smallest planet of the solar system.
Venus - is the second planet from the sun. Venus is a rocky planet. It is the hottest planets as its atmosphere is mainly made up of carbon dioxide. It rotates on its axis from east to west.
Earth - is the third planet from the sun. Earth's atmosphere has sufficient oxygen, the gas we need to live and water.
Mars - is also known as a red planet. The thin atmosphere of mars contains mainly carbon dioxide with small amounts of nitrogen, oxygen, noble gases and water vapour. It appears red due to the high amount of iron oxide present on its surface.
Jupiter - is the biggest planet and is made mainly of hydrogen and helium.
Saturn - is the second biggest planet of the solar system and is made up of mainly hydrogen and helium. It has well developed system of rings surrounding it. It is the least dense planet and can float in water.
Uranus - is the third biggest planet of the solar system and is mainly made up of hydrogen and helium.
Neptune - is the outermost planet of the solar system and is made mainly of liquid and frozen hydrogen and helium gases.
The Moon
A celestial body that revolves around a planet is known as natural satellite or moon of the planet. The earth has only one moon. It reflects the light of the sun. Its surface is covered with craters and mountains.
Phases of moon
Shapes of the bright part of the moon, as seen from the earth, are known as the phases of moon.
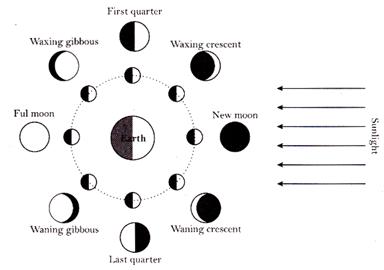 more...
more... You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
