Co-ordinate Geometry
In this chapter we will discuss about the two as well as three dimensional geometry. We will discuss about the position of the points and locate the point in the plane or on the surface. The three mutually perpendicular lines in the plane are called coordinate axes of the plane. The numbers in a plane which represent the position of a point is called coordinates of the point with reference to the coordinate planes. The eight equal regions into which space is divided by three dimensional axes are called octants.
Distance Formula
Let us consider the two points \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and B(\[{{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}}\]), in a two dimensional plane, then the distance between the two points is given by \[AB=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}.}\] If it is a three dimensional plane containing the points \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}},\text{ }{{z}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}},\text{ }{{z}_{2}} \right),\]then the distance between the points is given by:
\[AB=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{l}})}^{2}}}\]
Section Formula
Let us consider the point P(x, y) which divides the line segment joining \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and in the ratio k : 1 internally, then the coordinates of the point P(x, y) is given by:
\[x=\frac{{{x}_{1}}+k{{x}_{2}}}{k+1}\,\,\,and\,\,y\frac{{{y}_{1}}+k{{y}_{2}}}{k+1}\]
Coordinates of Midpoint
The coordinates of the mid-point of a line segment AB with coordinates \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is given by \[\left( \frac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\frac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right)\]
Note:
(i) If the mid-point of \[\Delta \] ABC are \[P({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}}),\]\[Q\,({{x}_{2}},\,\,{{y}_{2}})\] and \[R\,({{x}_{3}},\,\,{{y}_{3}})\] then its vertices will be \[A\,(-{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}},-{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}),\] \[B\,({{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}},\,\,{{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}})\] and \[C\,({{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{3}},\,\,{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{3}})\]
(ii) The fourth vertex of a parallegogram whose three vertices in order are \[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right),\text{ }\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( {{x}_{3}},\text{ }{{y}_{3}} \right)\] is \[\left( {{x}_{1}}\text{ }{{x}_{2}}+\text{ }{{x}_{3}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}}-\text{ }{{y}_{2}}+\text{ }{{\text{y}}_{3}} \right)\]
Centroid of a Triangle
It is defined as the point of intersection of the medians of the triangle. The coordinates of centroid of a triangle with vertices \[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right),\text{ }\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( {{x}_{3}},\text{ }{{y}_{3}} \right)\] is: \[\left( \frac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}}{3},\frac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}}{3} \right)\]
Note: in an equilateral triangle orthocentre, centroid, circumcentre, incentre coincide.
Area of a Triangle
Let A\[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right),\text{ }B\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\text{ }and\text{ }C\left( {{x}_{3}},\text{ }{{y}_{3}} \right)\]be the vertices of a triangle, then the area of the triangle is given by:
\[=\frac{1}{2}\left| {{x}_{1}}({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{3}})+{{x}_{2}}({{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}})+{{x}_{3}}({{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}}) \right|\]
Conditions for Collinearity
Let the given points be A\[\left( {{x}_{1}},\text{ }{{y}_{1}} \right),\text{ }B\left( {{x}_{2}},\text{ }{{y}_{2}} \right)\text{ }and\text{ }C\left( {{x}_{3}},\text{ }{{y}_{3}} \right)\]. If A, B and C are collinear then. Area of \[\Delta \]ABC = 0.
\[\Rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\left| {{x}_{1}}({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{3}})+{{x}_{2}}({{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}})+{{x}_{3}}({{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}}) \right|=0.\]
Also if ABC are collinear, then slope of AB = slope of BC = slope of CA
Locus
The curve described by a point which moves under given condition(s) is called its locus. The equation of the locus of a point is satisfied by the coordinates of every point.
Slope of a Line
The trigonometrical tangent of the angle that a line makes with the positive direction of the x-axis in anticlockwise direction is called the slope of the line.
more...
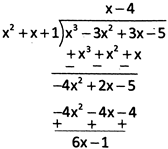 Here we have quotient \[q\left( x \right)=x-4,\] and remainder \[r\left( x \right)=6x-1\].
Graph of Polynomials
In this section we will learn about the construction of linear, quadratic and cubic polynomial graphs. In order to draw a graph of the polynomial f(x), we first find some values of x which satisfy the equation of f(x) and plot these points on a rectangular co-ordinate system and then join these points with free hand curve.
Graph of more...
Here we have quotient \[q\left( x \right)=x-4,\] and remainder \[r\left( x \right)=6x-1\].
Graph of Polynomials
In this section we will learn about the construction of linear, quadratic and cubic polynomial graphs. In order to draw a graph of the polynomial f(x), we first find some values of x which satisfy the equation of f(x) and plot these points on a rectangular co-ordinate system and then join these points with free hand curve.
Graph of more...